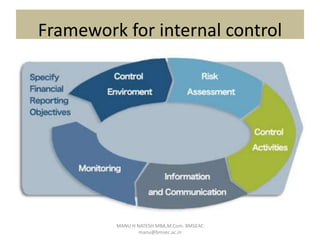
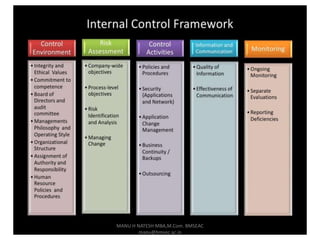
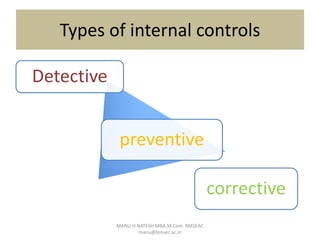
Internal control is defined as a process for assuring achievement of an organization's objectives relating to operational efficiency, reliable financial reporting, and compliance with laws. It involves directing, monitoring, and measuring how an organization's resources are used. Internal control plays an important role in preventing and detecting fraud and protecting both physical and intangible assets. An effective internal control system includes preventive, detective, and corrective controls to mitigate risks and ensure objectives are met. However, limitations exist as controls rely on human judgment and can be overridden or circumvented.