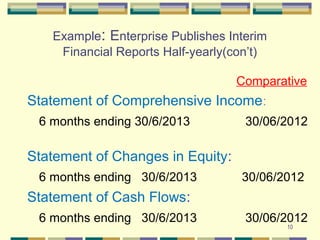
This document discusses interim financial reporting requirements under MFRS 134. It defines interim financial reports and explains their importance in providing timely information to investors. The document outlines the content requirements for interim financial statements, including comparative figures. It also discusses the recognition and measurement principles, noting that the same accounting policies must be applied as in annual reports. Significant events affecting financial position or performance since the last annual report must be disclosed.