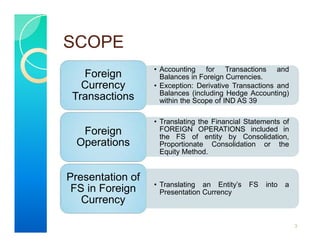
1. IND AS 21 outlines the accounting treatment for foreign currency transactions and foreign operations. It addresses how to include such items in financial statements and how to translate financial statements into a presentation currency.
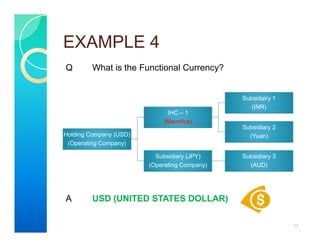
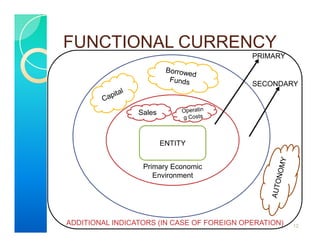
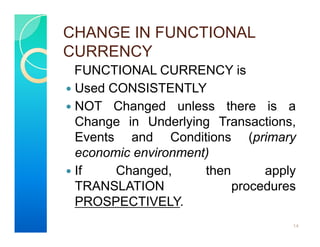
2. The standard establishes guidelines for determining an entity's functional currency. The functional currency is primarily the currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity operates, which is normally the currency that mainly influences sales prices and operating costs.
3. IND AS 21 provides rules for re-measuring foreign currency items into the functional currency, including the use of spot or average exchange rates. It also addresses the translation of financial statements from the functional currency into the presentation currency.