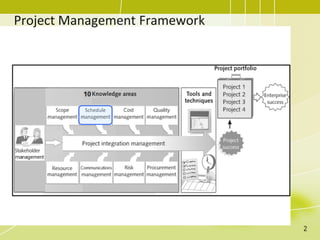
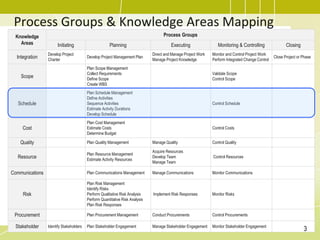
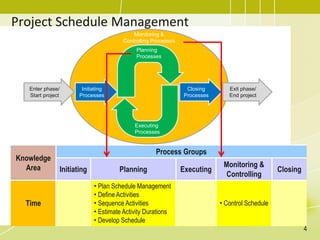
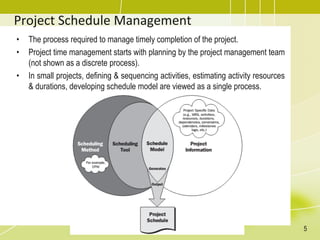
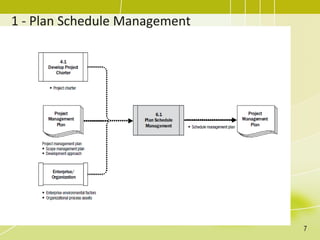
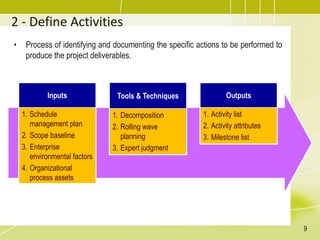
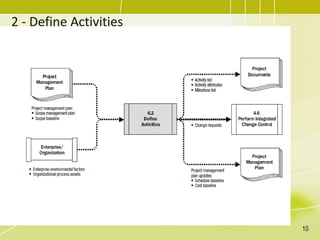
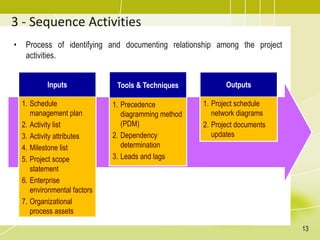
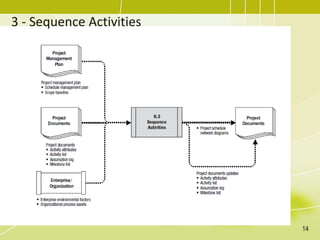
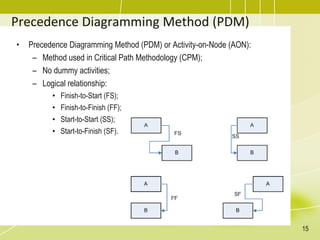
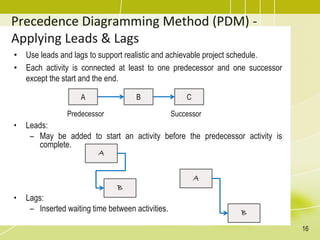
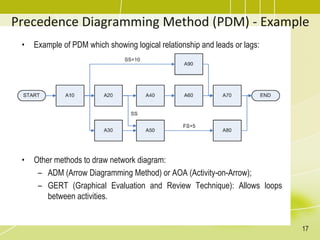
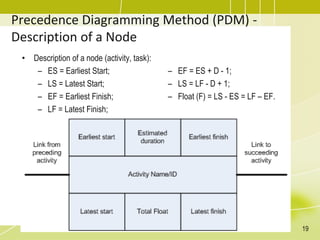
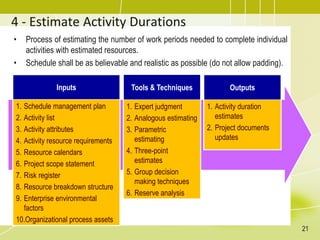
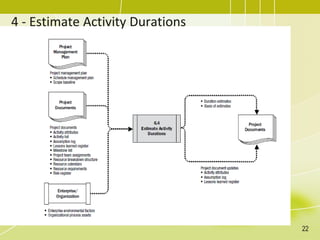
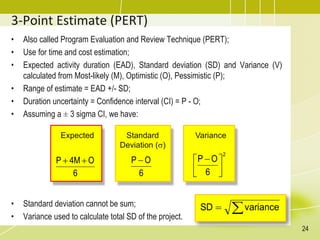
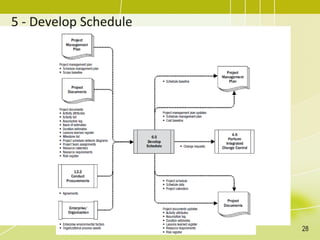
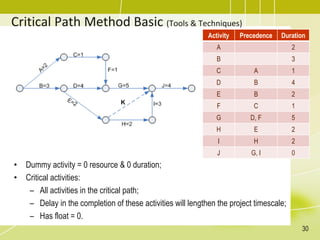
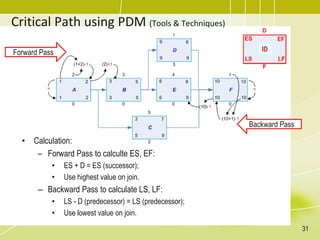
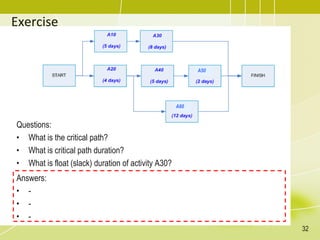
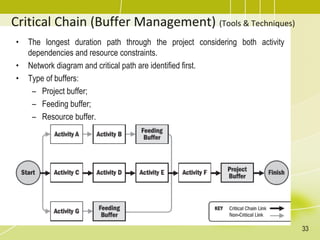
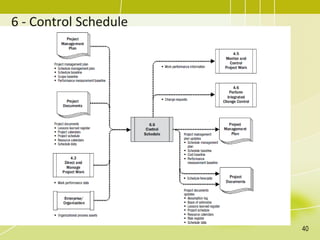
The document discusses project schedule management. It outlines the key knowledge areas, process groups, and processes involved in project schedule management based on the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK). Specifically, it describes the six processes for schedule management: (1) plan schedule management, (2) define activities, (3) sequence activities, (4) estimate activity durations, (5) develop schedule, and (6) control schedule. For each process, it provides the inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs as defined in PMBOK.