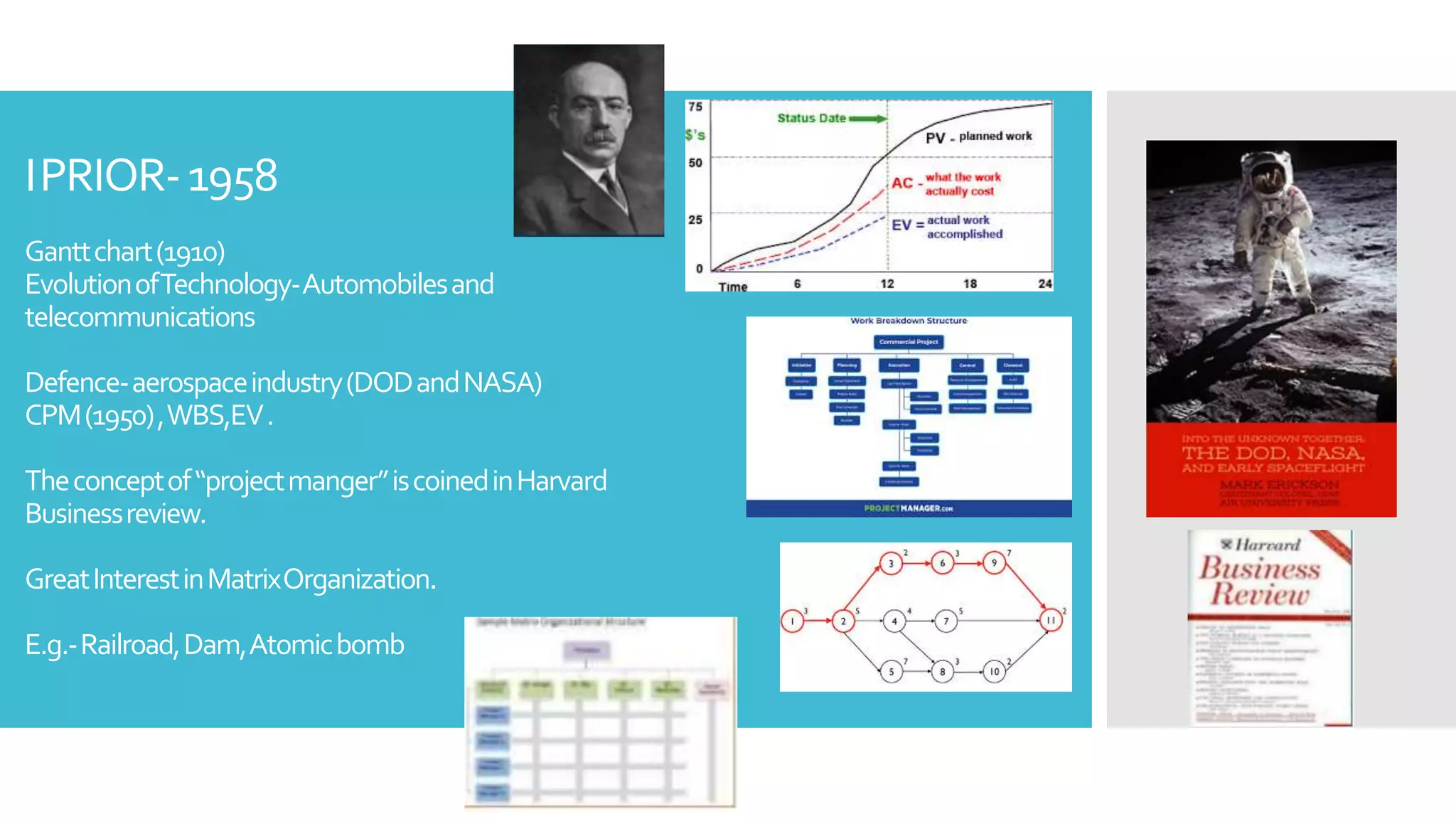
The document is a presentation by Dr. Richa Singhal on project management, discussing its definition, functions, and evolution over time. It contrasts traditional management with project management, highlighting key differences and the role of project and product managers. The presentation covers the historical development of project management methodologies and the essential skills required in the field.