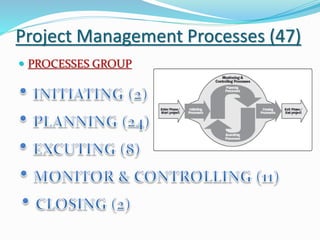
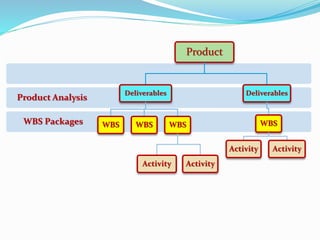
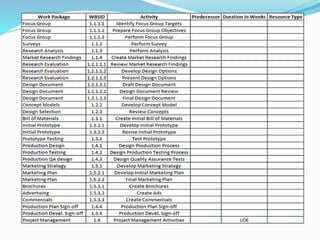
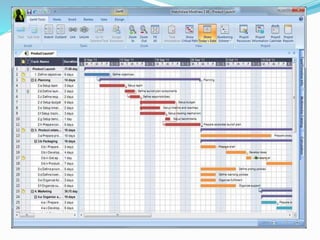
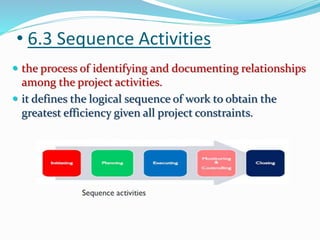
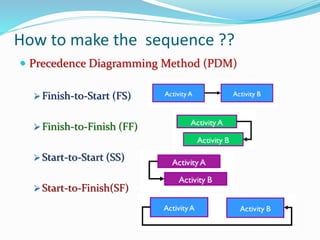
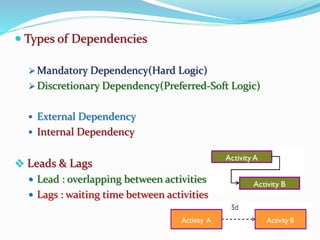
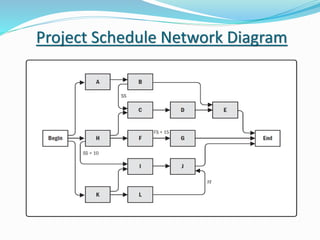
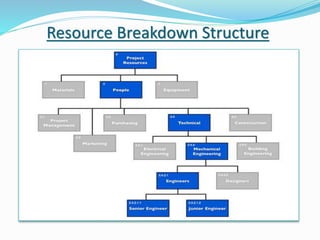
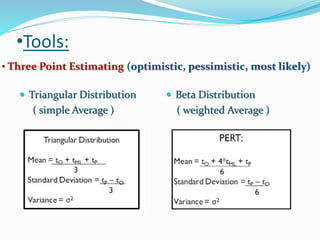
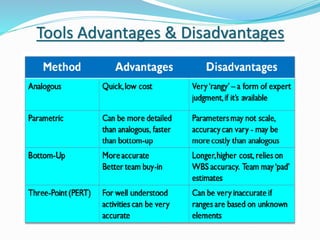
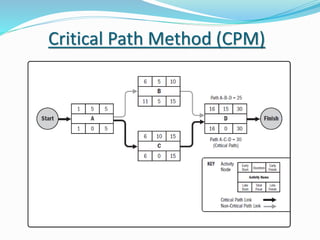
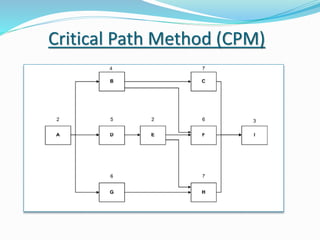
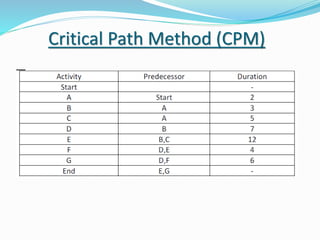
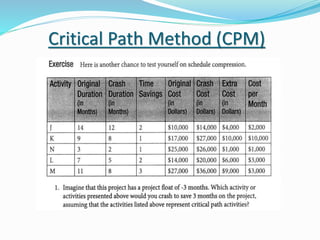
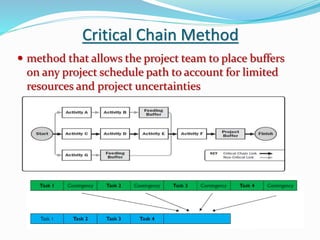
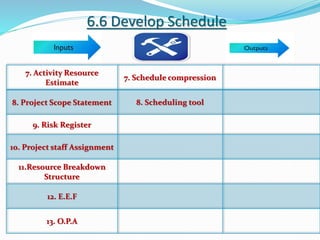
This document discusses the key processes involved in project schedule management. It describes the seven processes as follows: 1) Plan Schedule Management which establishes policies and documentation for managing the project schedule. 2) Define Activities which identifies specific work to produce deliverables. 3) Sequence Activities which determines the logical order of work. 4) Estimate Activity Resources which estimates resource needs. 5) Estimate Activity Durations which estimates activity timelines. 6) Develop Schedule which analyzes activity details to create a schedule model. 7) Control Schedule which monitors schedule status and manages changes. For each process, it outlines important inputs, tools, and outputs involved in effective schedule management.