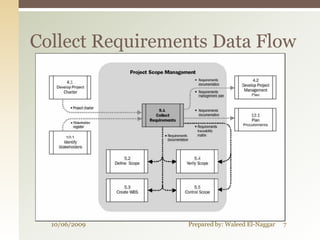
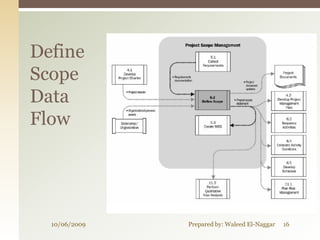
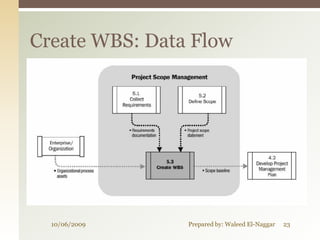
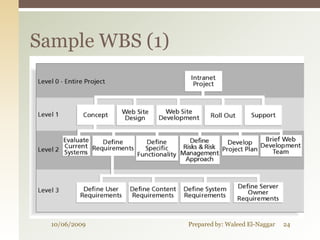
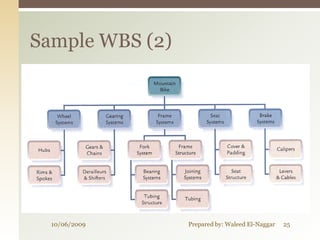
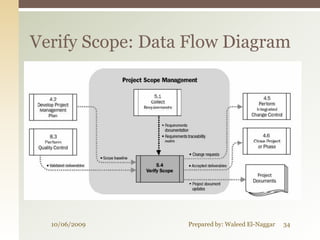
The document discusses project scope management. It covers collecting requirements, defining scope, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS), controlling scope, and verifying scope. The presenter outlines the key inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs for each scope management process. He provides examples of a project charter, WBS, and quizzes to reinforce the material. The overall presentation provides a comprehensive overview of how to plan, monitor, and control the scope of a project.