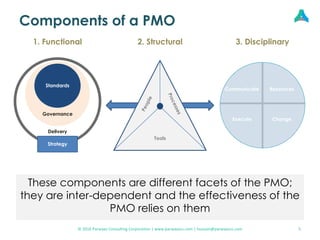
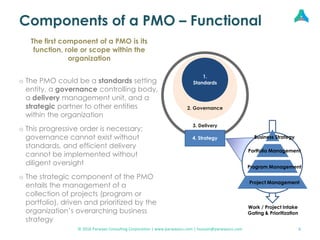
This document provides an overview of setting up a Project Management Office (PMO). It discusses what a PMO is, why organizations need them, and the key components and structures of an effective PMO. A PMO sets standards, provides governance, and establishes processes to manage projects consistently. It aims to deliver projects efficiently and successfully while improving reporting, resource management, and alignment with organizational strategy. The document outlines the functional, structural, and disciplinary facets of a PMO and how they work interdependently. It also promotes accessing the full guide online for more details on PMO components, maturity levels, setup, and considerations.