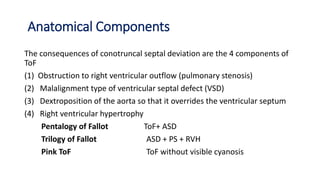
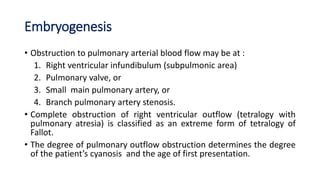
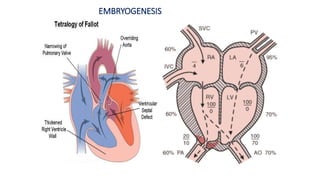
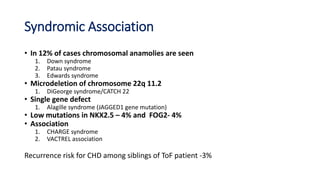
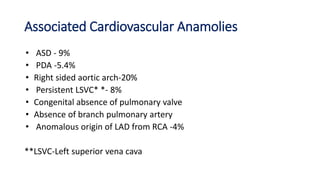
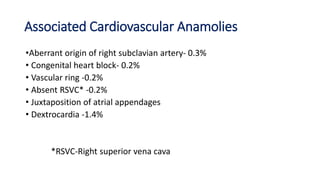
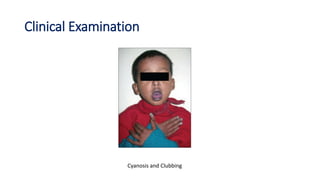
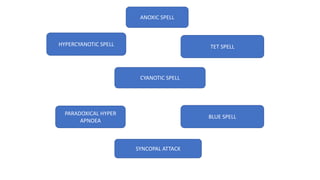
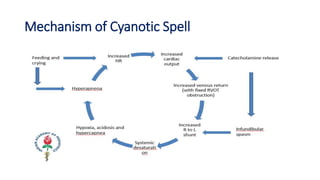
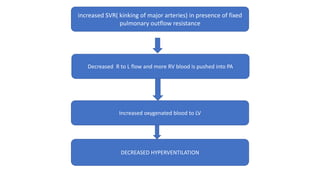
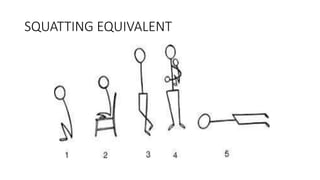
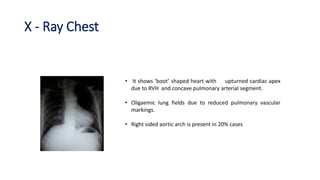
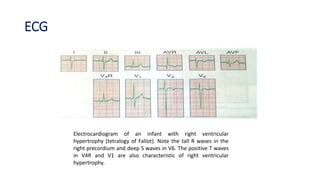
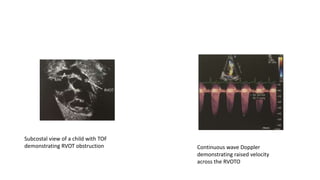
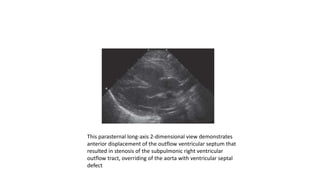
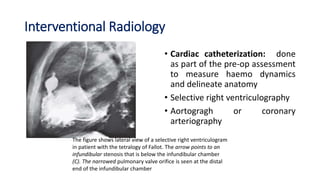
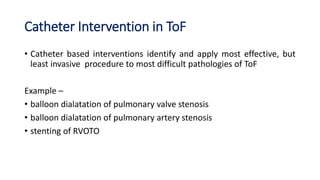
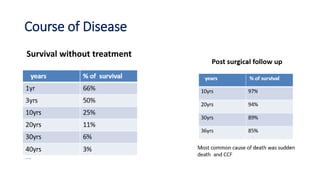
Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital heart defect characterized by four anatomical abnormalities: pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect, overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy. It is one of the most common cyanotic congenital heart diseases. Presentation varies from cyanosis and failure to thrive in infants, to exertional dyspnea in older children and adults with milder cases. Diagnosis involves echocardiography, chest x-ray, and cardiac catheterization. Management includes oxygen supplementation, medications to relieve cyanotic spells, and ultimately complete repair surgery.