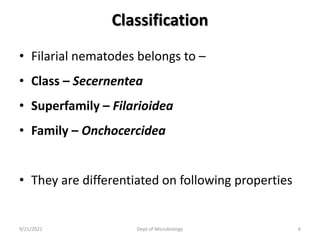
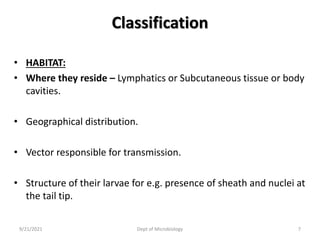
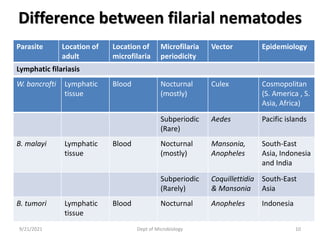
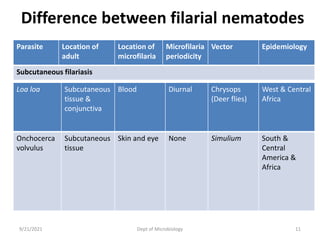
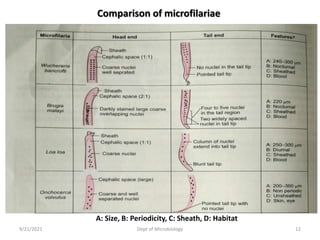
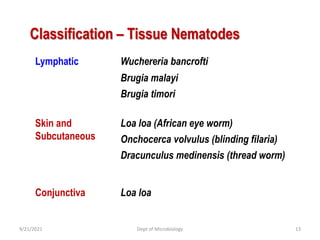
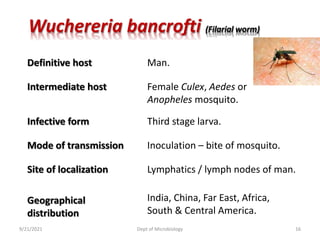
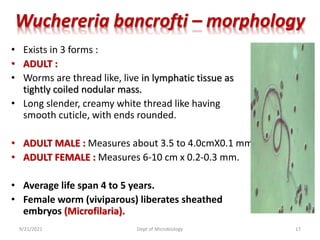
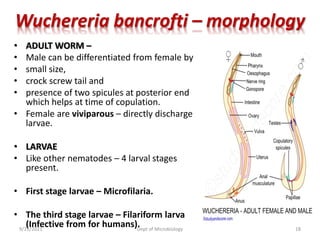
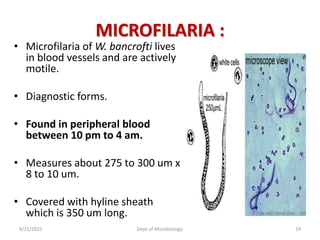
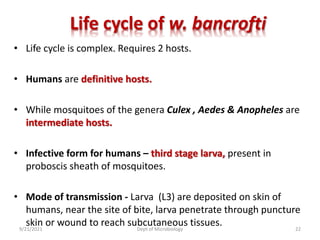
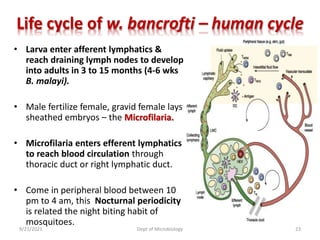
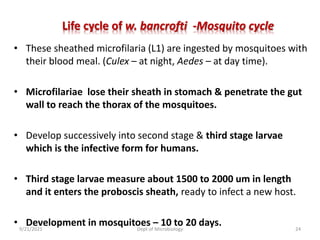
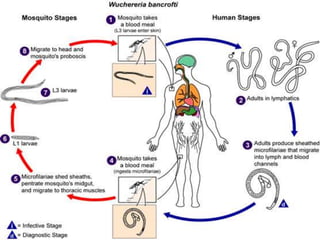
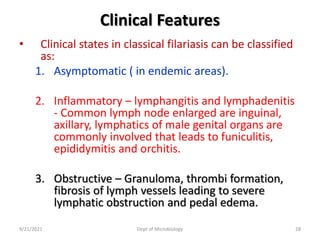
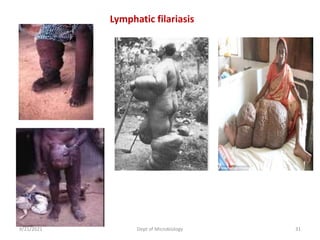
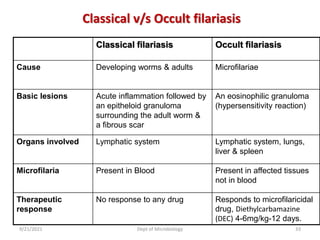
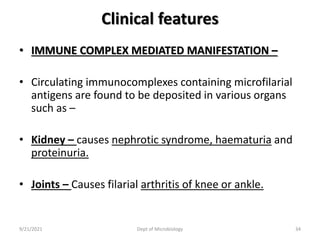
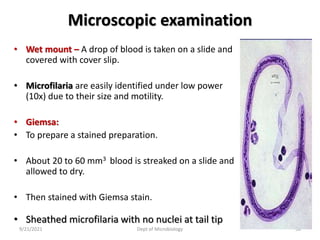
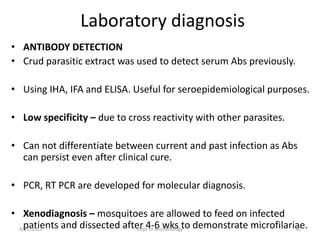
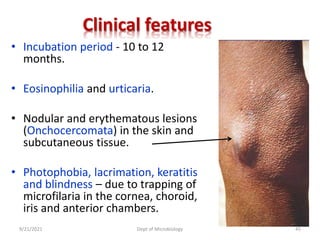
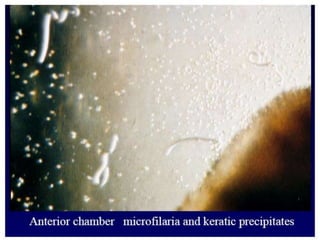
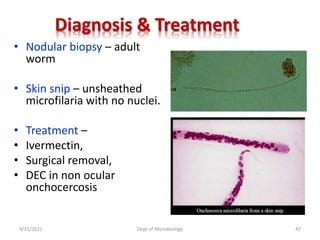
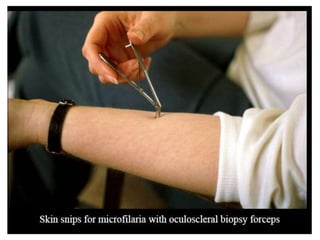
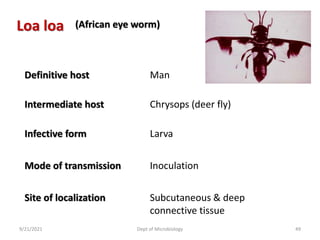
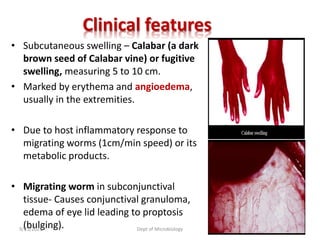
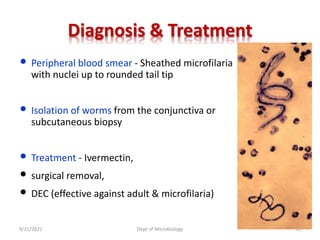
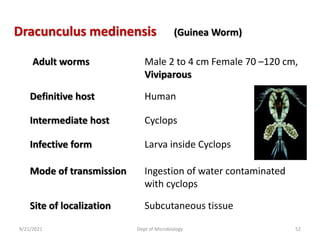
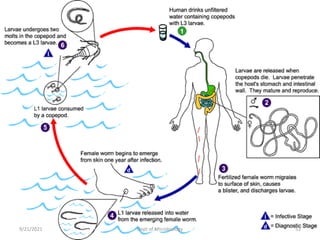
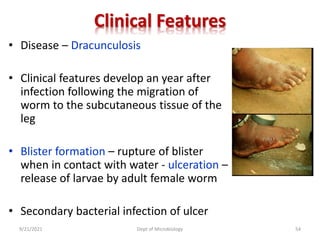
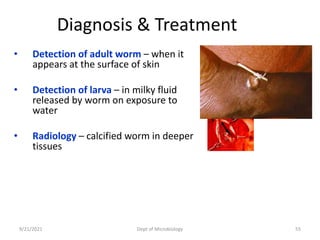
The document provides an overview of somatic (tissue) nematodes, focusing on their classification, life cycle, pathogenesis, and laboratory diagnosis, particularly for species such as Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia species, Loa loa, Onchocerca volvulus, and Dracunculus medinensis. It details their general properties, habitat, morphological characteristics, transmission vectors, and the clinical manifestations associated with infections they cause. Diagnostic methods are also outlined, emphasizing the importance of blood sampling and various laboratory techniques to identify and study these parasites.