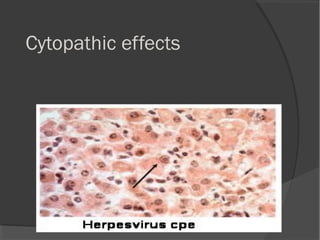
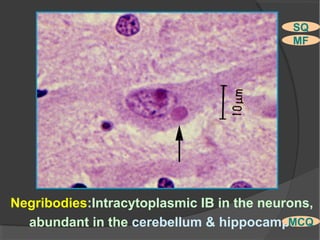
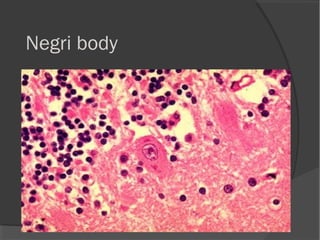
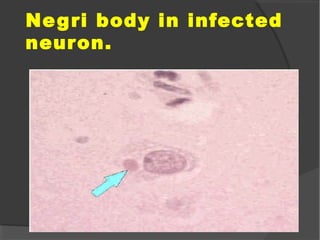
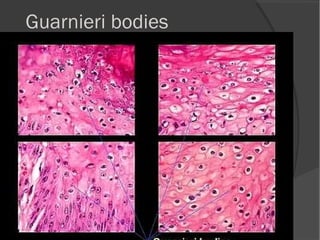
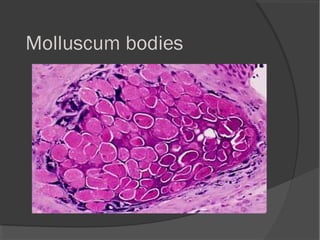
The document discusses the effects of viruses on host cells, including cytocidal effects, cellular proliferation, malignant transformation, and steady state infections. It details various cytopathic effects observed in tissues, such as inclusion bodies that are characteristic of specific viruses, along with their staining properties and classification. The types of inclusion bodies are explained, including intracytoplasmic and intranuclear types, with examples like Negri bodies and Guarnieri bodies.