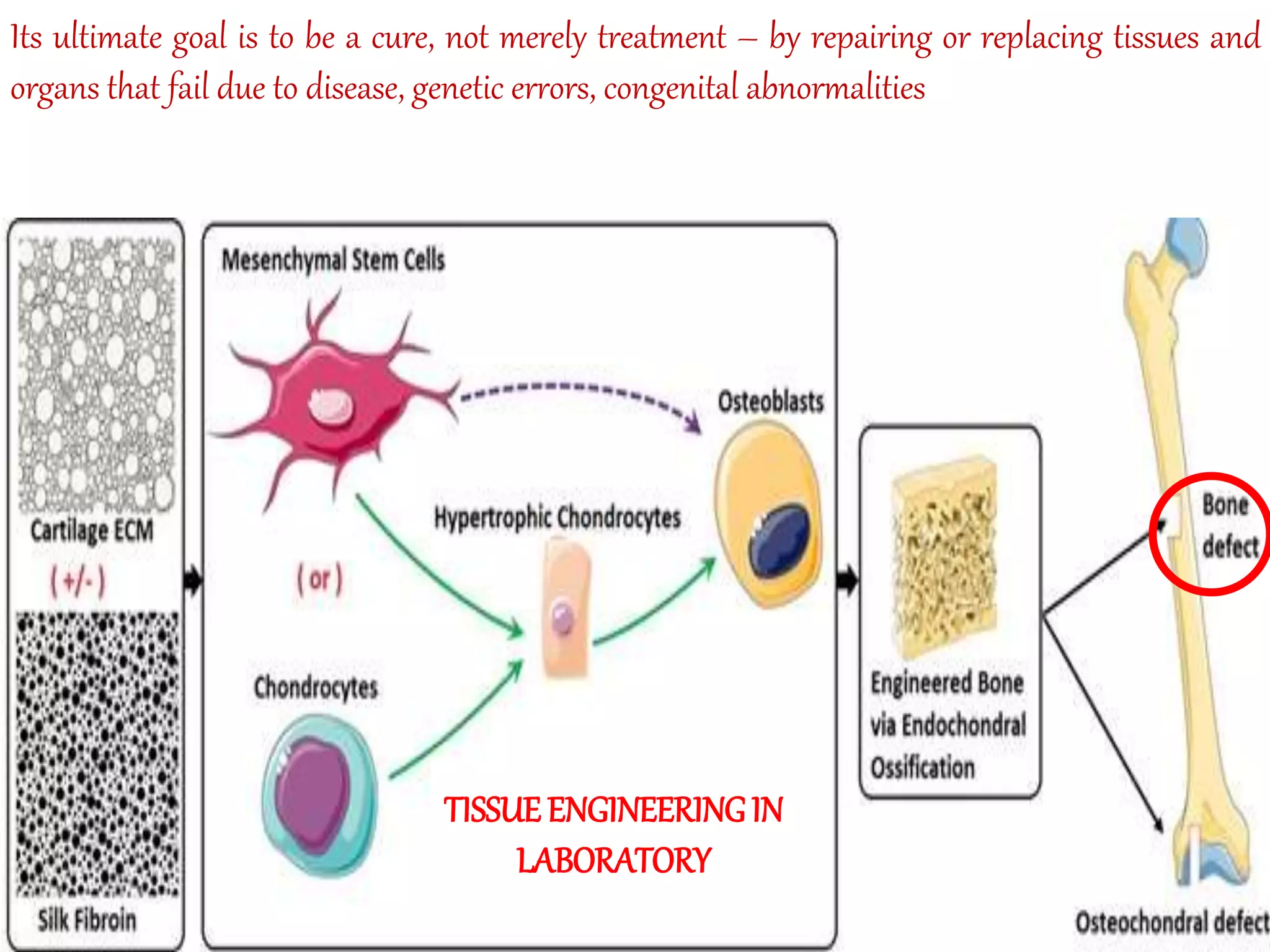
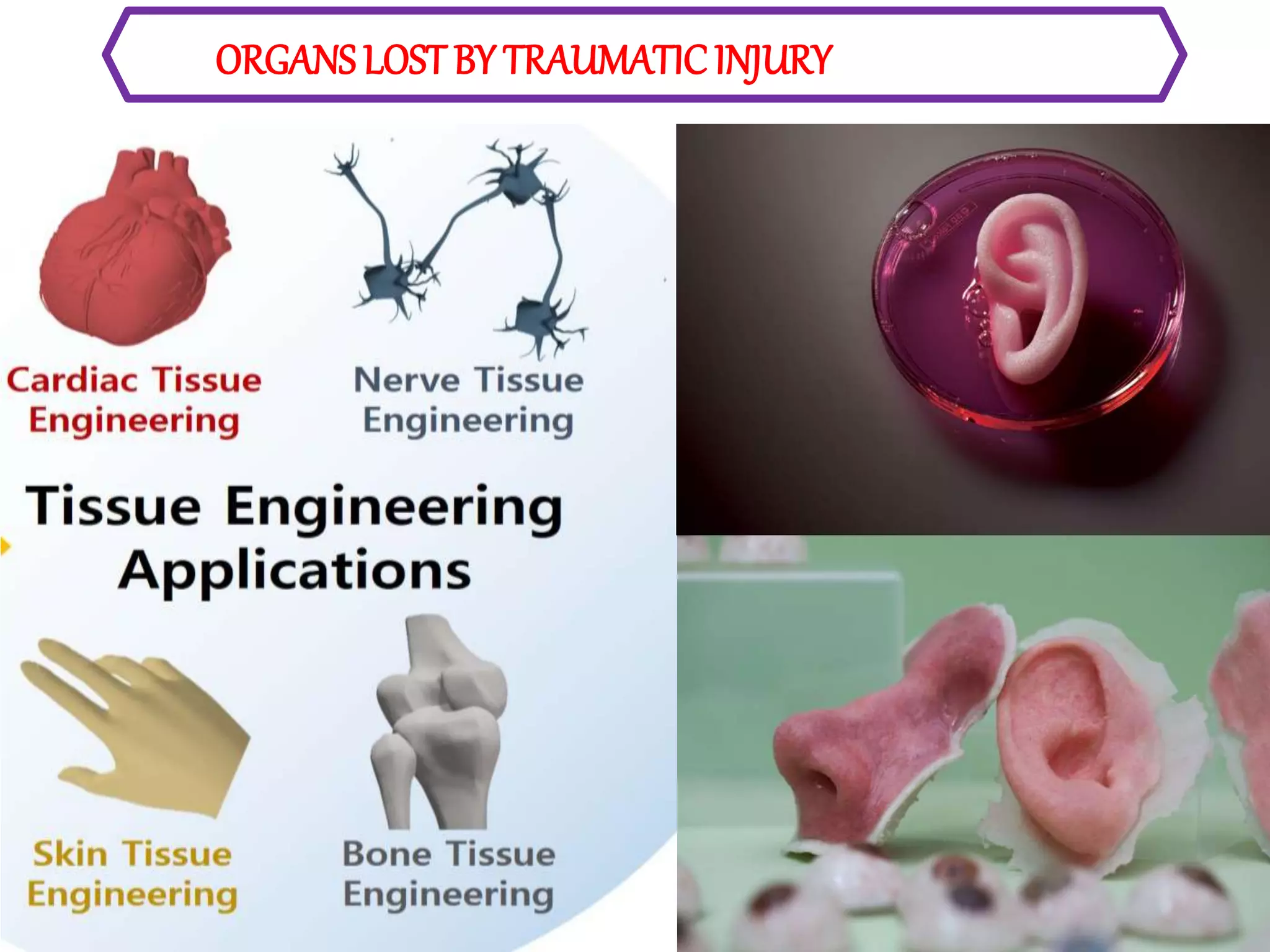
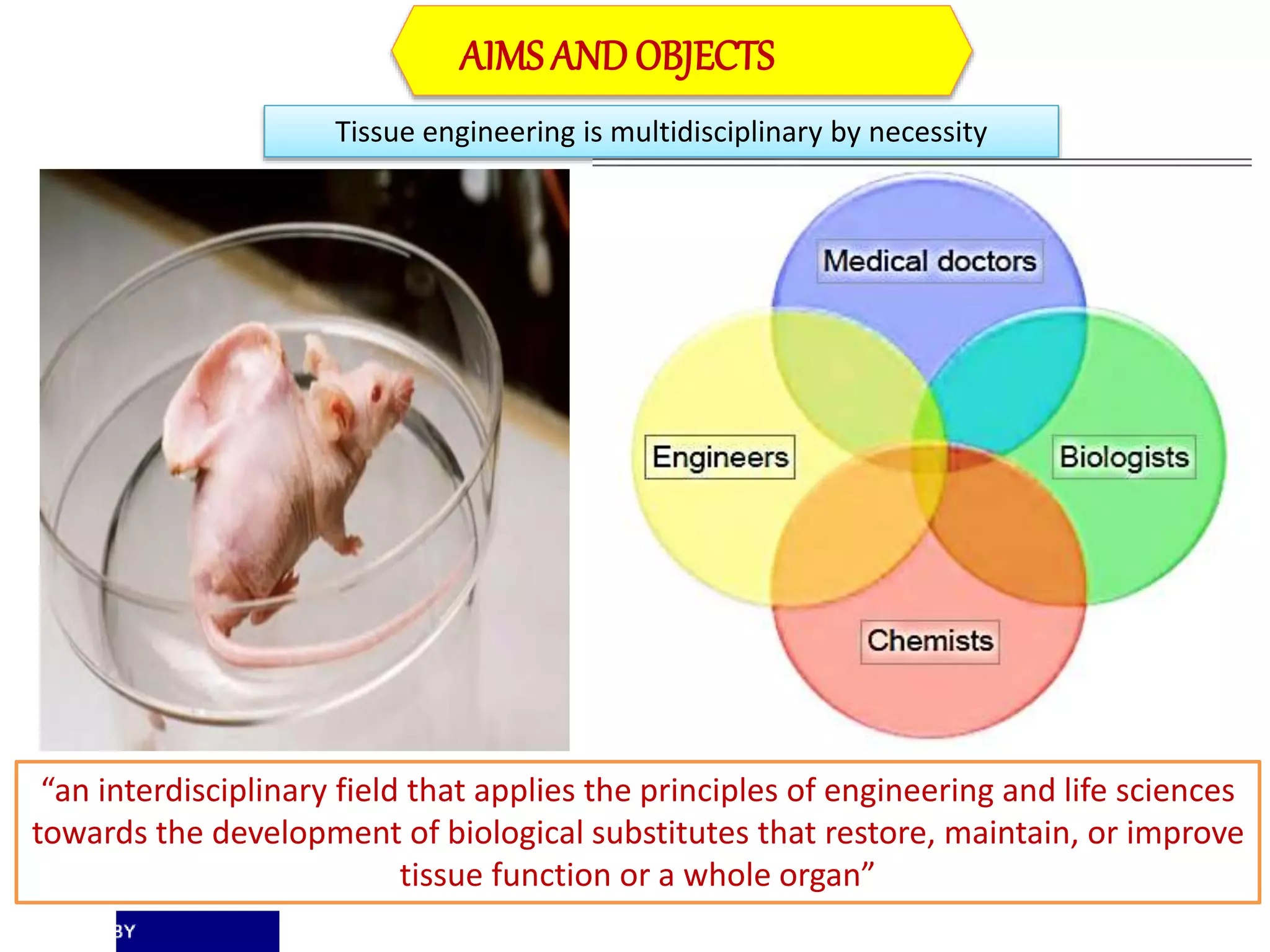
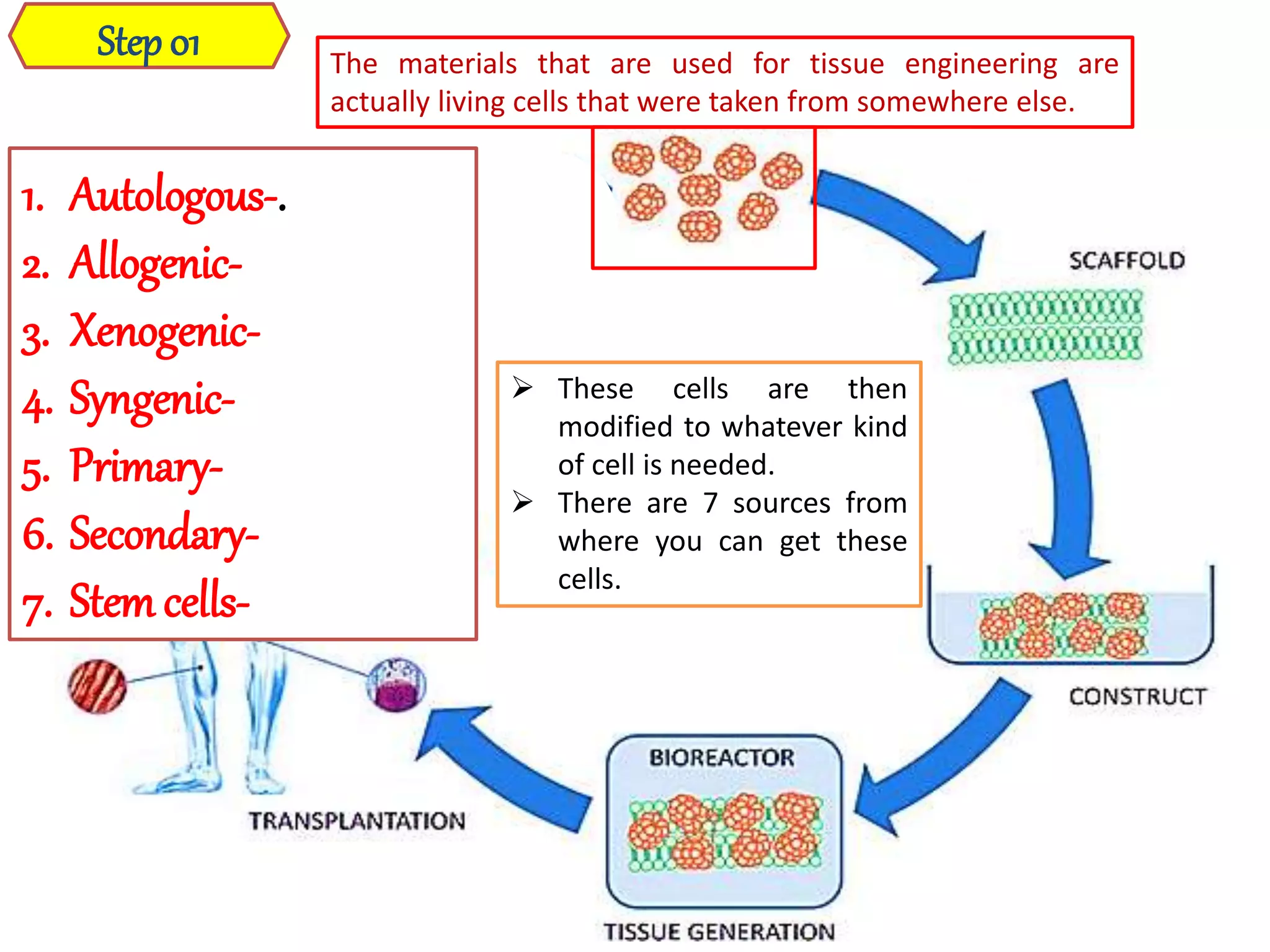
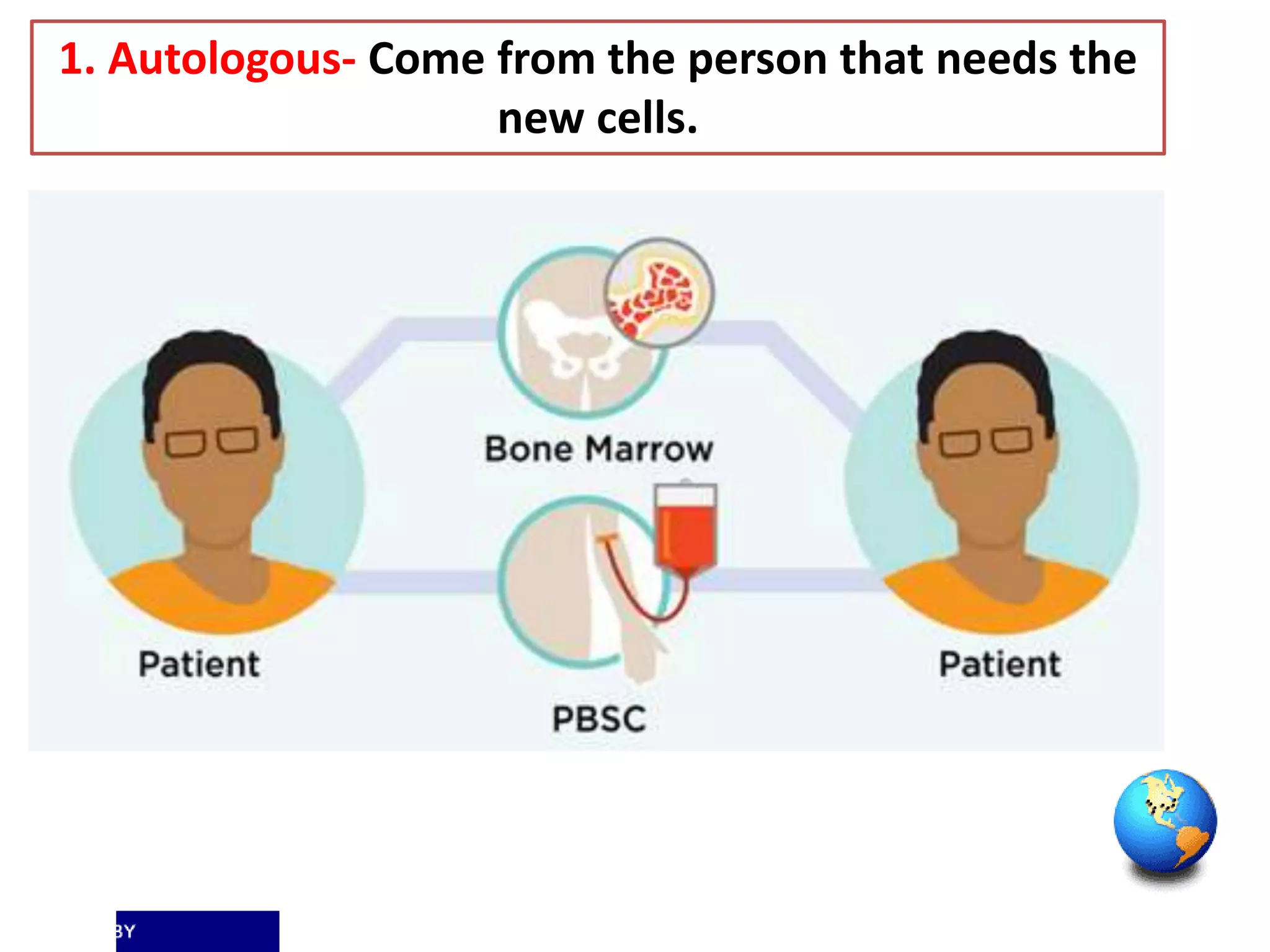
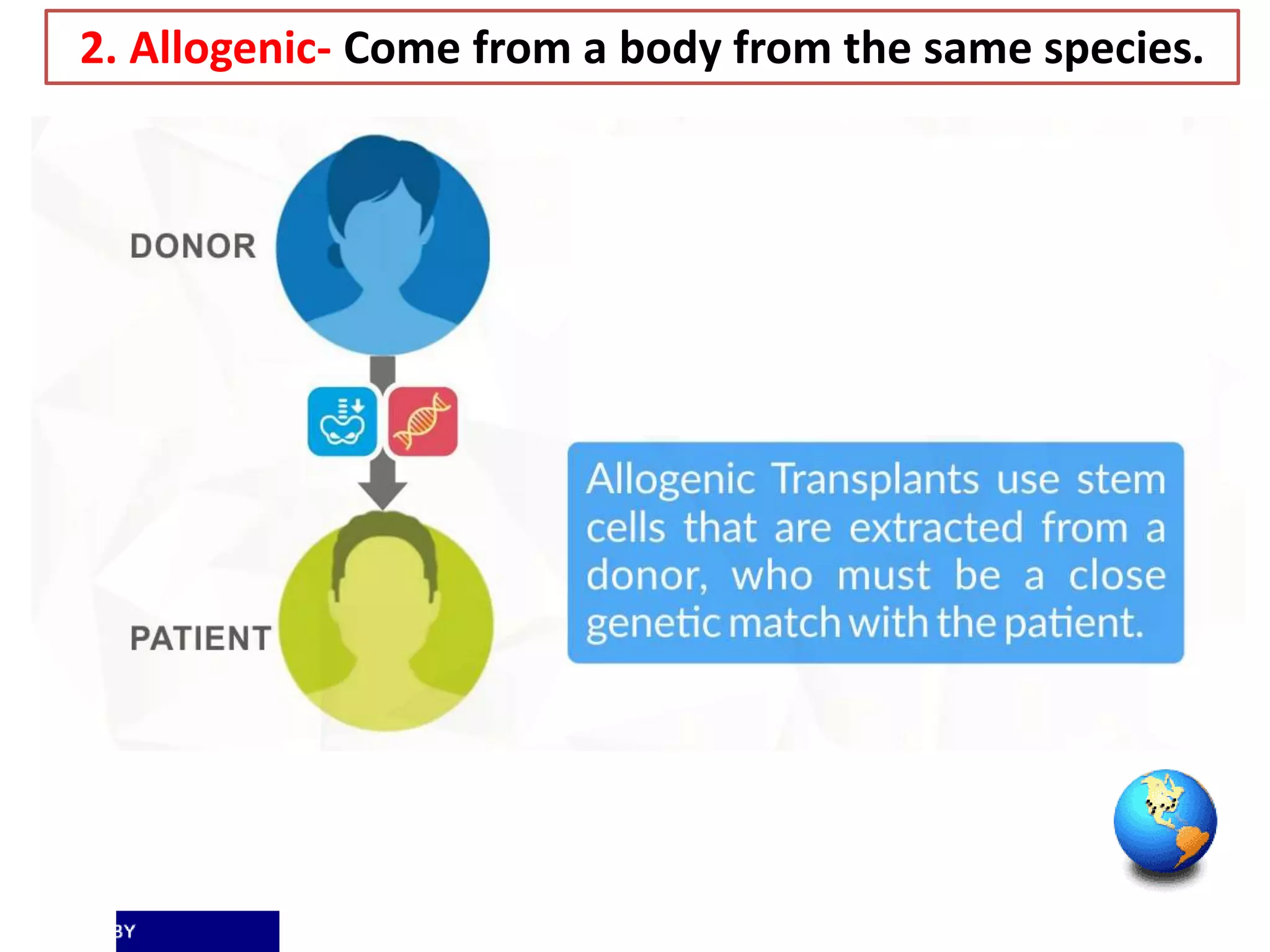
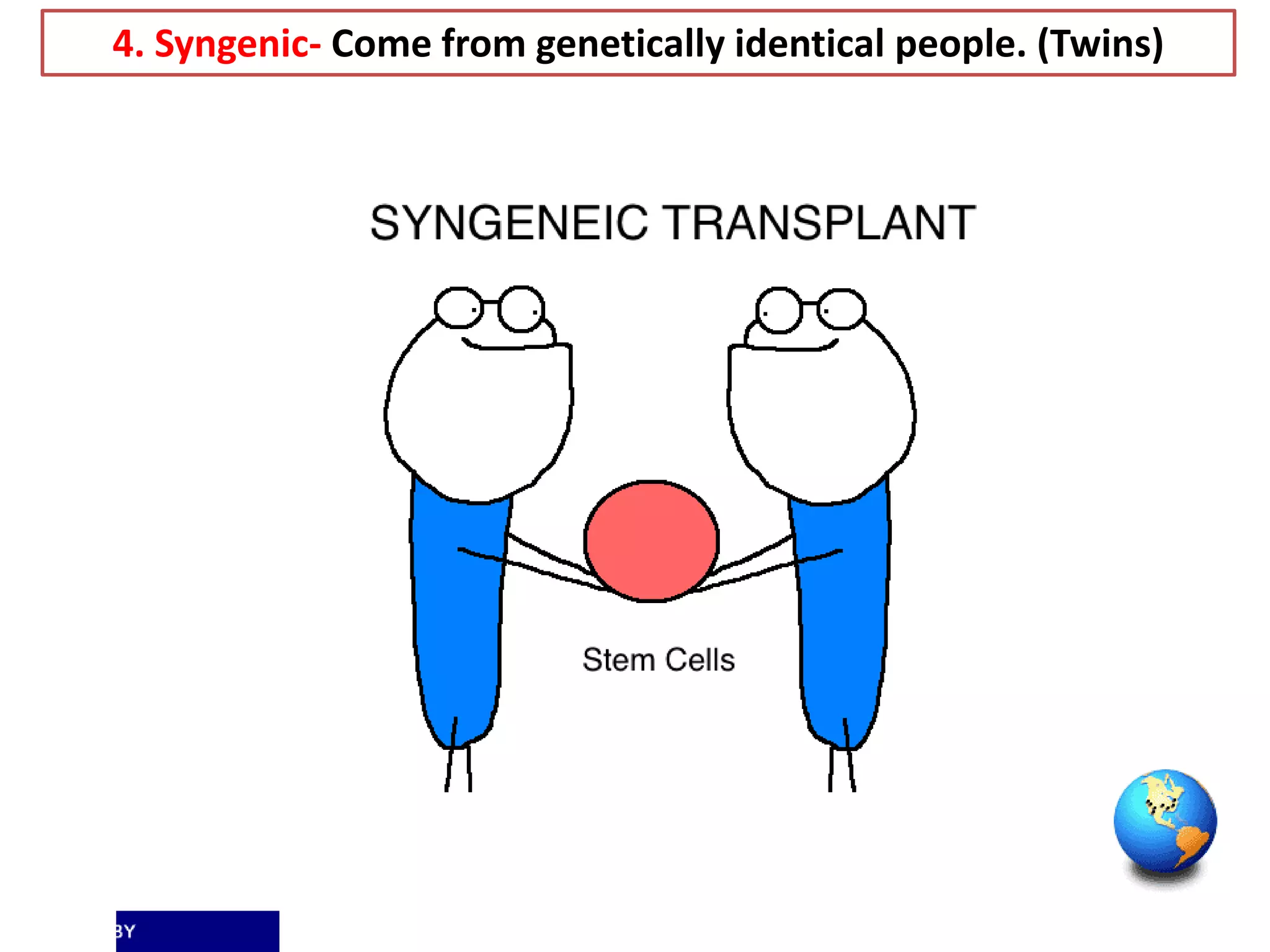
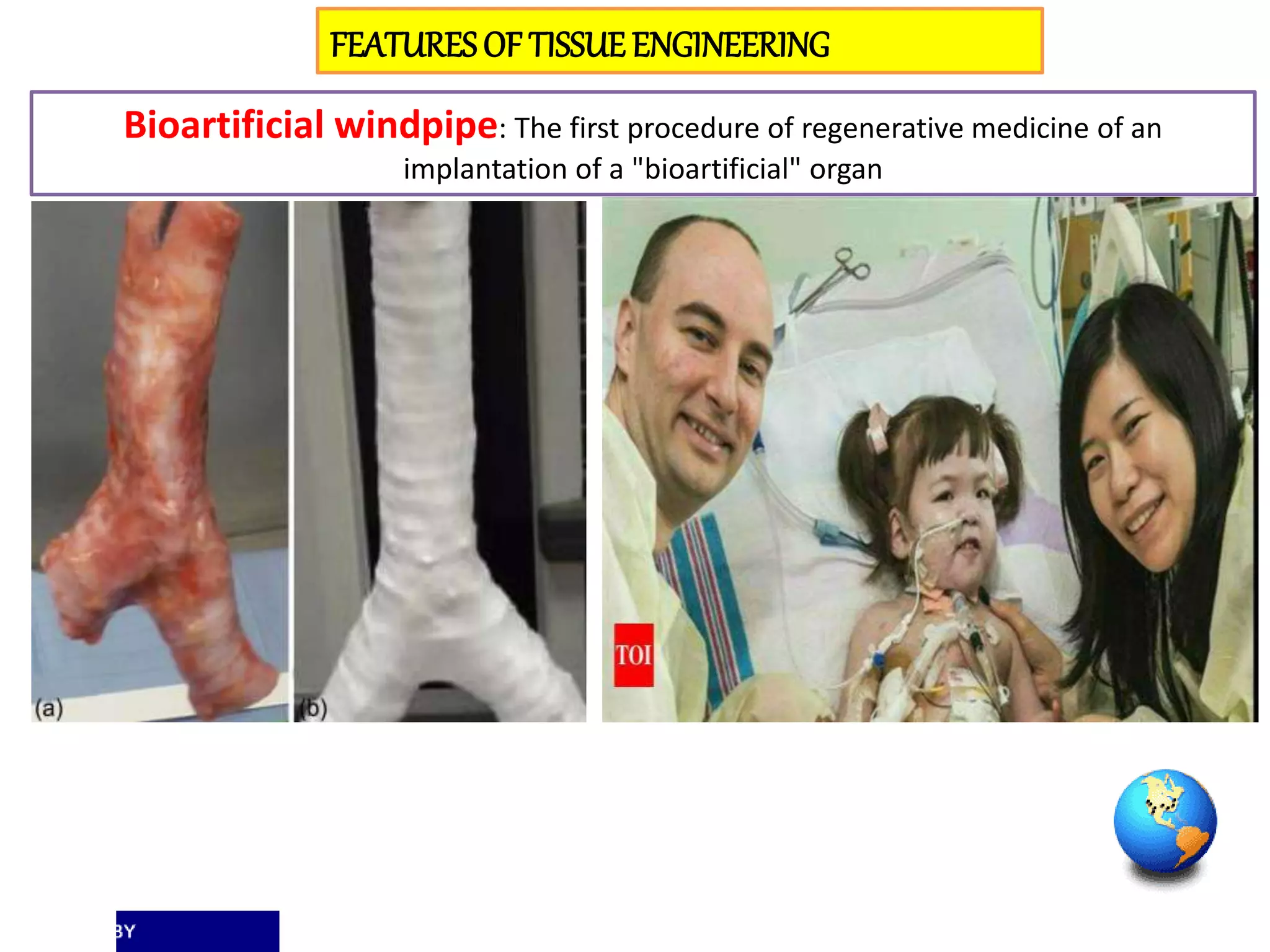
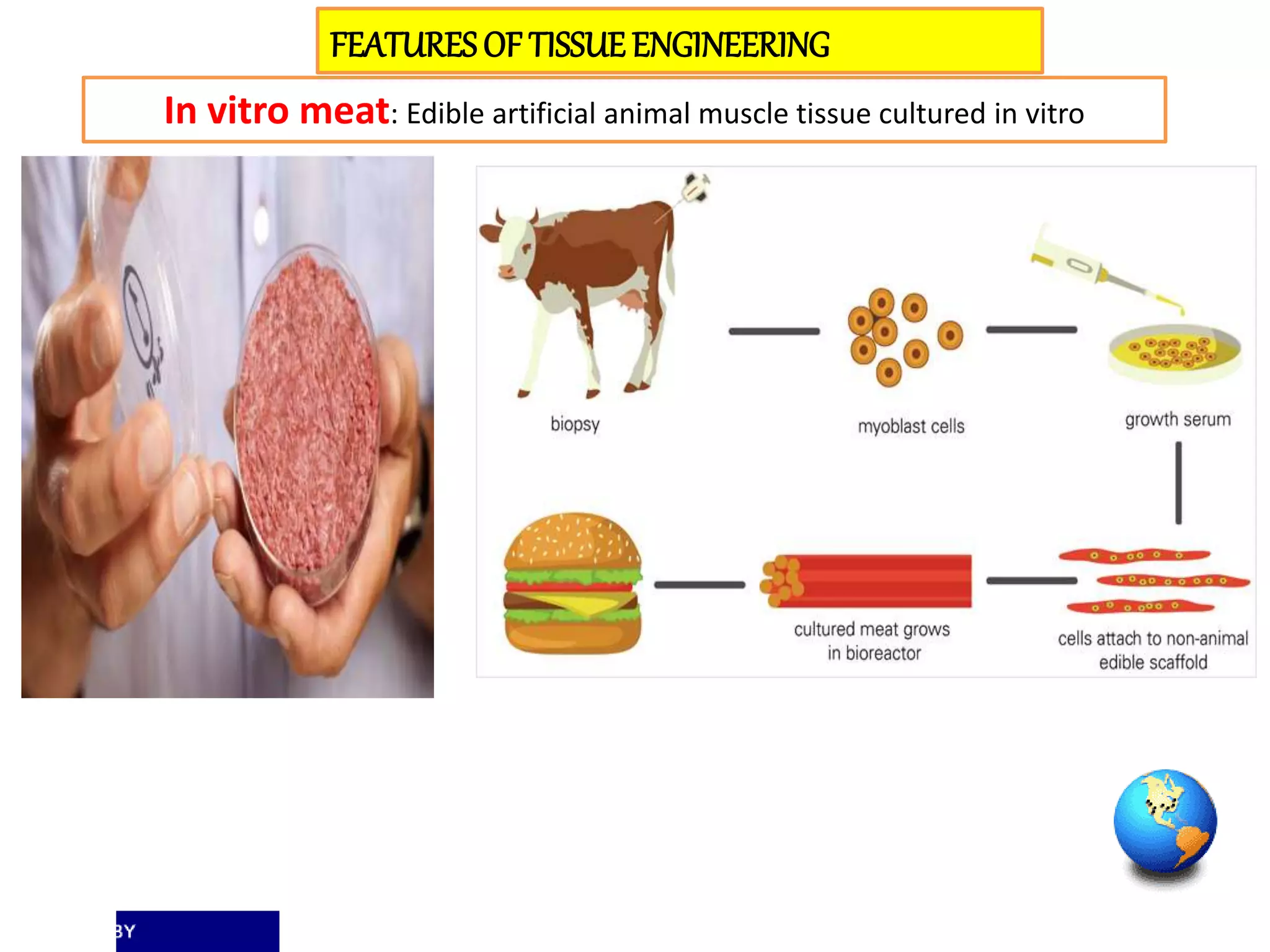
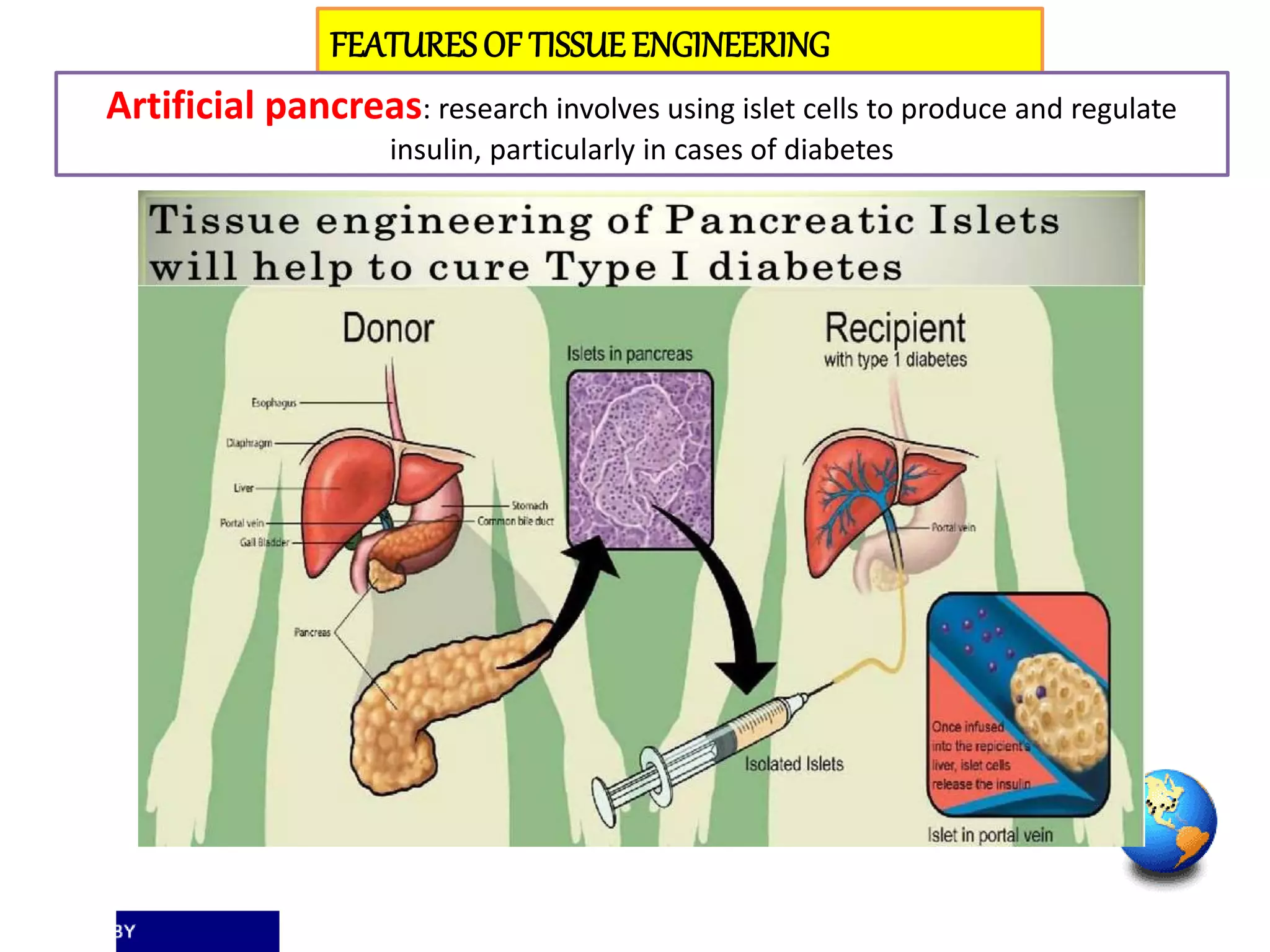
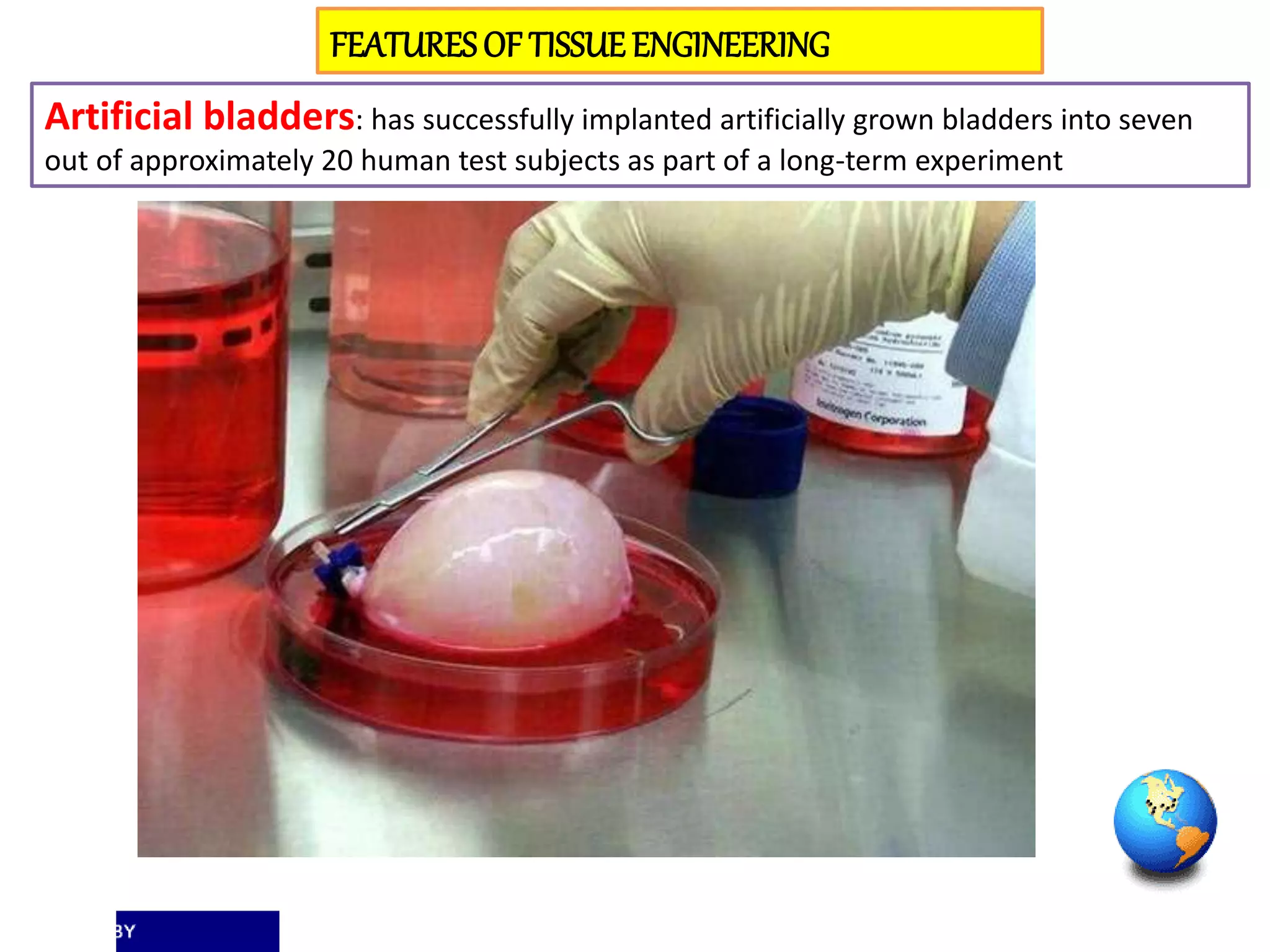
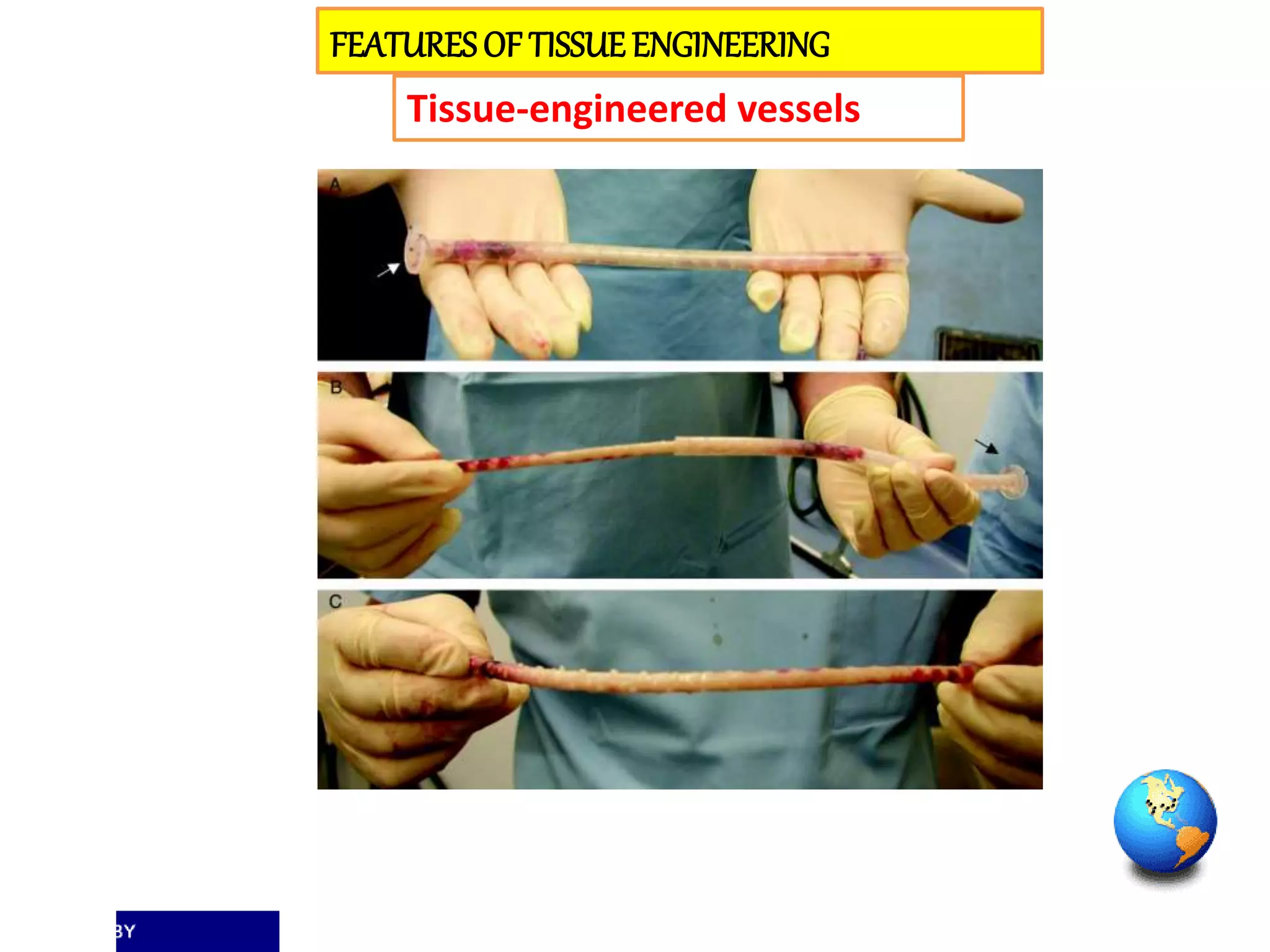
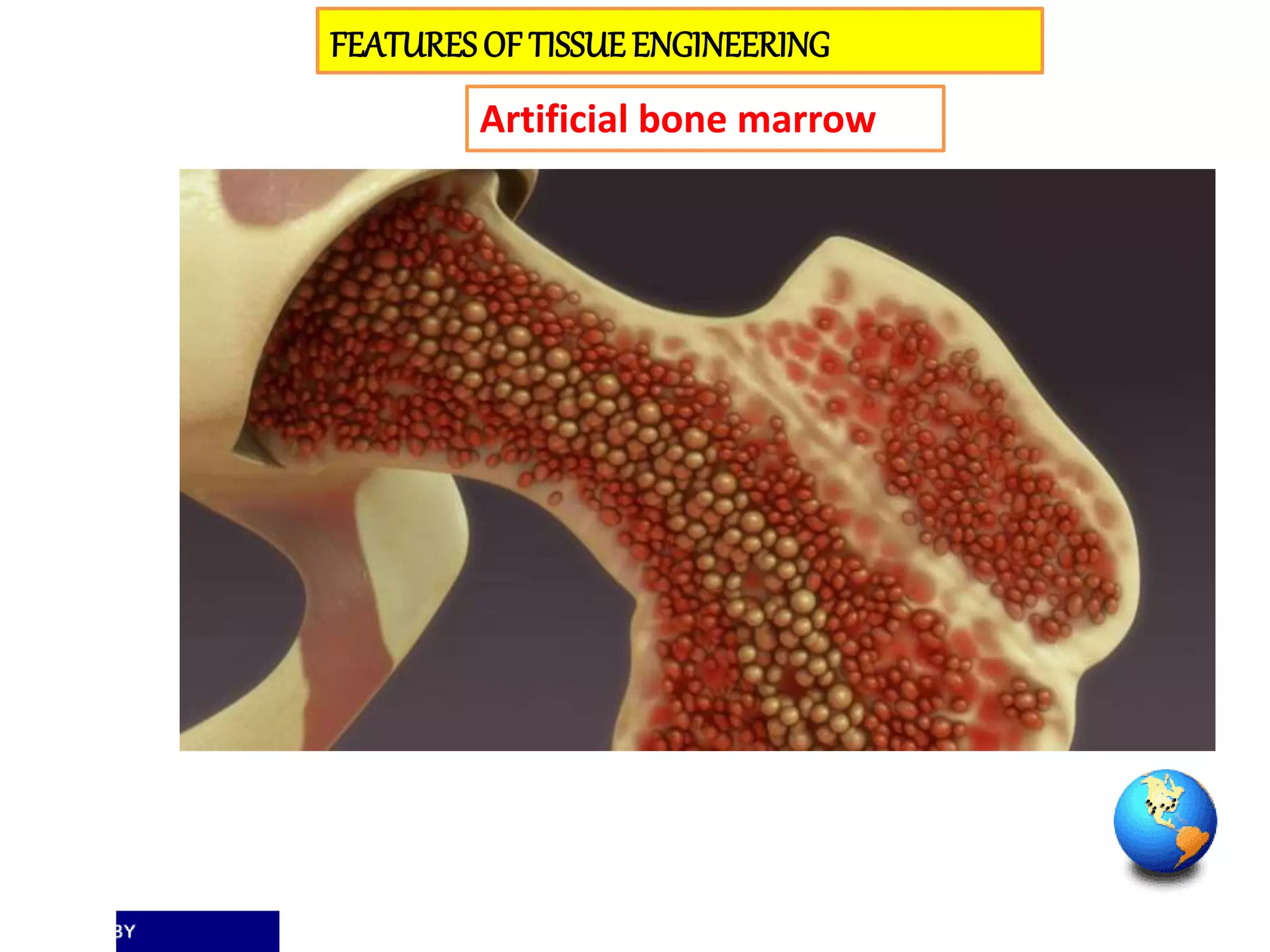
Tissue engineering aims to create functional human tissues for repair or replacement of damaged organs. It involves obtaining cells, expanding them in culture, seeding them onto a scaffold to grow new tissue, and implanting the construct. Stem cells offer potential due to their ability to differentiate and self-renew. Research applications include creating artificial organs like livers, pancreases, and bladders. Challenges remain in vascularizing tissues and preventing immune rejection, but tissue engineering offers hope for treating diseases.