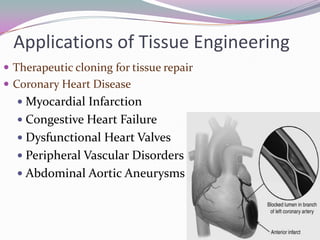
Tissue engineering involves using scaffolds and cells to regenerate tissues. There are various sources of cells, including embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Scaffolds provide structure for cells and must have properties like porosity and biodegradability. Common scaffold fabrication methods include solvent casting, gas foaming, and 3D printing. Tissue engineering has applications in healing burns, wounds, cartilage, and more. The global market is growing and projected to be worth $32 billion due to increasing demand for treatments of diseases like heart disease and diabetes. Challenges include standardization, ethics, and high costs.