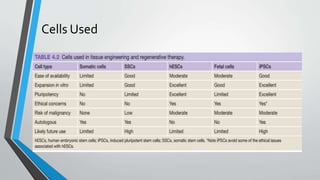
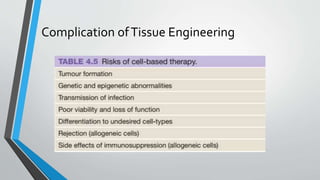
Tissue engineering involves implanting cells or scaffolds to promote tissue regeneration, with various sources including differentiated and stem cells. While it offers treatment for numerous diseases and potential lab-grown organs, concerns arise regarding the ethical implications of embryonic stem cell use and long-term effects. Scaffolds play a critical role, providing structural support and facilitating cellular interactions necessary for successful tissue engineering.