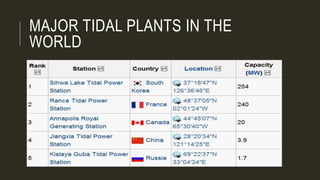
The document presents an overview of tidal energy, detailing its history, principles, components, and operational methods. It discusses both the advantages, such as being a renewable and predictable energy source, and disadvantages, including high construction costs and environmental impacts. Tidal energy is highlighted as a potential alternative to fossil fuels, necessary for future energy demands.