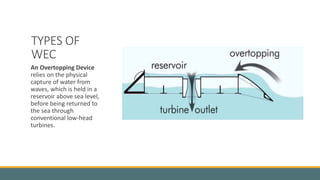
This document discusses wave energy as a renewable source of energy. It explains that wind energy transfers to ocean waves, and wave energy machines like turbines and buoys can capture this energy from waves and tides to generate pollution-free electricity. While wave energy technology is still developing, it is estimated that fully utilizing wave energy could satisfy around 40% of the world's total energy needs. The main ways to capture wave power are surface devices, underwater devices, and reservoirs. The document also describes different types of wave energy converters including attenuators, point absorbers, submerged pressure differential devices, overtopping devices, and oscillating wave surge converters.











![REFERENCES
[1]: https://renewablenw.org/node/wave-tidal-energy-technology
[2]: https://www.conserve-energy-future.com/different-energy-sources.
[3]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JOP33yCKmNw
[4]: https://www.ducksters.com/science/environment/wave_and_tidal_energy.php
[5]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave_power
[6]: https://www.schiffundhafen.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Publikationen/ShipOffshore/2010-
04/Offshore_Principles_of_wave_energy.pdf
[7]:https://energiatalgud.ee/img_auth.php/2/23/Drew,_B.,_Plummer,_A.R.,_Sahinkaya,_M.N._A
_review_of_wave_energy_converter_technology._2009.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waveenergyslides-181203215904/85/Wave-Energy-13-320.jpg)