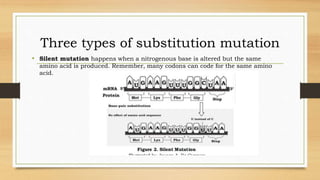
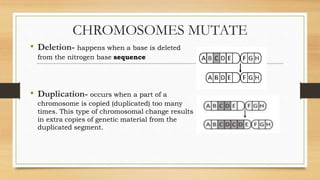
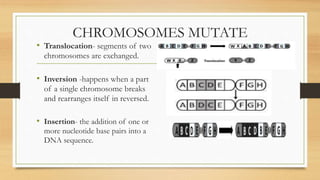
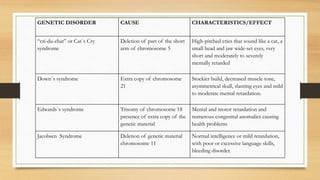
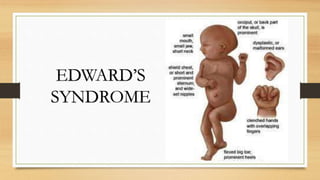
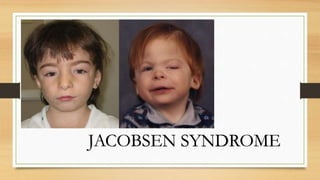
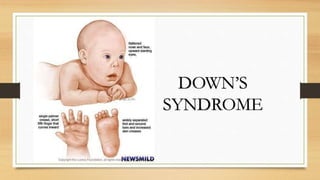
Mutations are changes to an organism's genetic material that can be caused by errors in DNA replication or exposure to mutagens like radiation or chemicals. There are two categories of mutations: germline mutations, which occur in gametes and can be inherited, and somatic mutations, which occur in other body cells and are not inherited. Some mutations have beneficial effects and contribute to evolution, while others may cause genetic disorders or cancer.