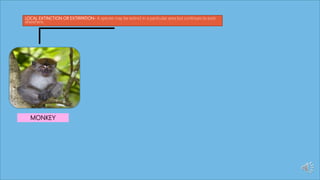
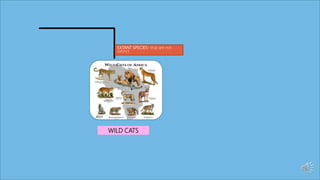
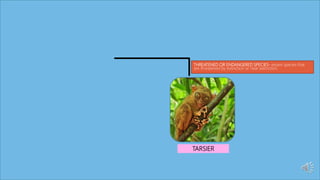
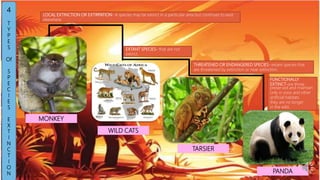
This document discusses species extinction and identifies four types: local extinction, extant species, threatened or endangered species, and functionally extinct species. It provides examples for each type. There are two main causes of extinction: natural causes like climate change and asteroids and anthropogenic causes like habitat destruction and pollution. Protecting biodiversity is important, especially protecting habitats, as species cannot survive without natural homes. The document ends with assessment questions about causes of extinction.