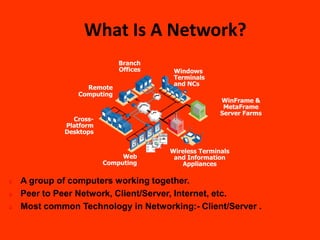
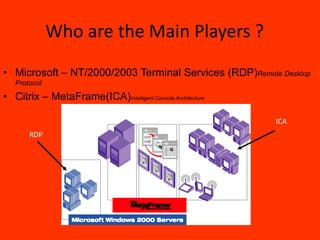
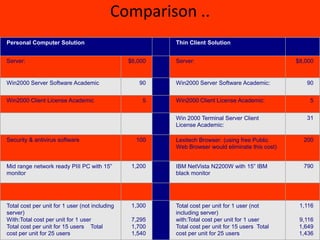
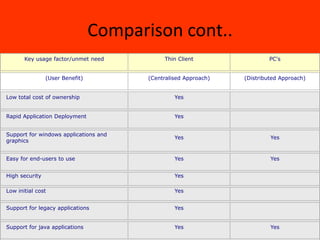
This document discusses thin client technology. It defines a thin client as a low-cost computing device that works in an application server environment and does not require powerful local processors or storage. A thin client network allows users to access applications, files, and other resources stored on centralized servers. Setting up a thin client system requires server hardware, terminal services software from Microsoft or Citrix, and low-powered thin client devices. Thin clients offer advantages over traditional PCs such as lower total cost of ownership and easier management and security. However, they may have disadvantages for multimedia or software that requires local processing power.