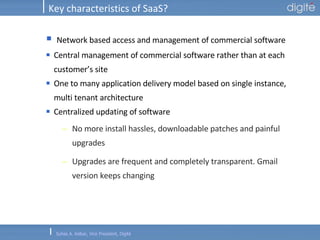
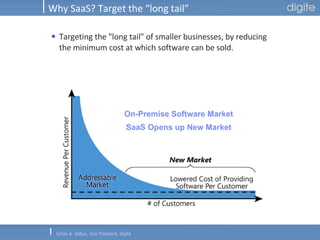
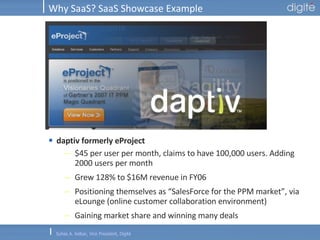
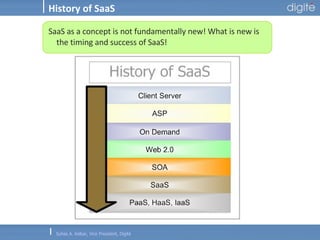
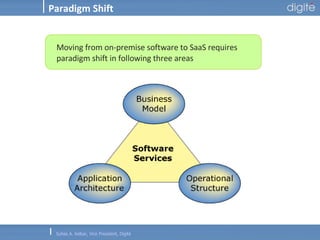
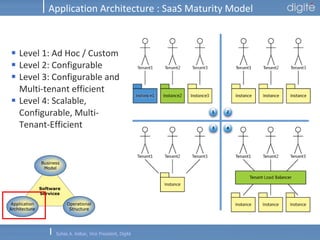
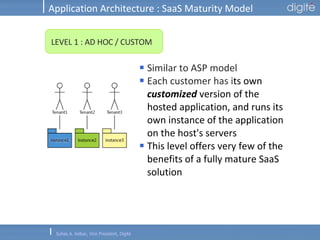
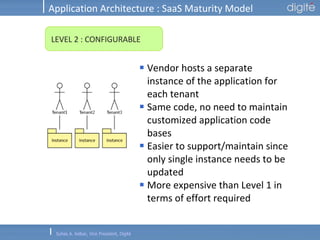
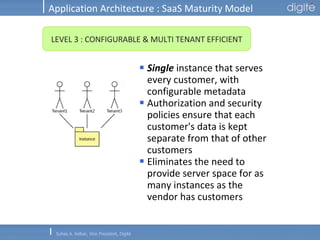
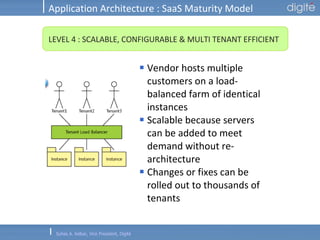
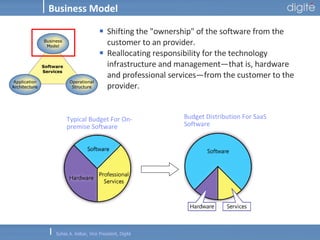
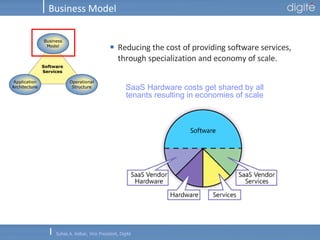
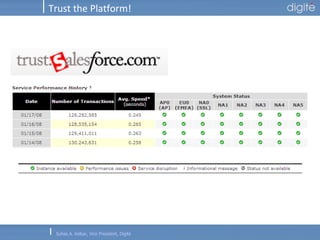
This document discusses Software as a Service (SaaS). It defines SaaS as software deployed as a hosted service and accessed over the Internet. Key advantages of SaaS include lower costs since users pay monthly subscription fees rather than large upfront licensing fees. The document outlines the history and growth of SaaS, describing how it has evolved from early ASP models. It also discusses the paradigm shifts required in application architecture and business models for SaaS, including moving to a multi-tenant architecture that is scalable and configurable. The speaker emphasizes that SaaS will have a major impact on the software industry and future IT professionals should closely track developments in SaaS.












![Thanks! [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saasscitpresentation-1221646549156167-8/85/SaaS-Presentation-at-SCIT-Conference-28-320.jpg)
