The document discusses the history and evolution of client-server architecture, including:
1) Early centralized processing on mainframe computers.
2) The shift to distributed processing using multiple connected computers.
3) The current paradigm of cooperative processing where resources are shared transparently to users.

![Client/Server with Database Servers
Client Client Client
Application Application Application
insert/update/delete
Network
tuple(s)
Database
Server
3 At present the majority of existing client/server-based software is to be found in the area of
databases, and it is here that the greatest challenge to any corporation currently lies.
[Richard Finkelstein, President, Performance Computing]
3 Events (violation of integrity constraints, temporal conditions, errors) trigger event handlers
- implicit invocation, blackboards, events
3 A DBMS also offers features for recovery and concurrency control
! # $ % # 5 6 7 #
' ( ) 0 ( ' 1 2 3 4 ' 1 2 8 ( ' 9 @ A B ' C C C
Lawrence Chung
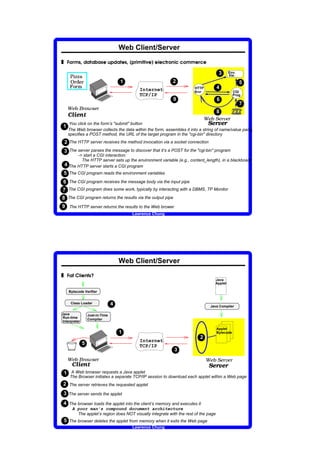
Client/Server Communication
Sockets - RPCs - MOMs and ORBs
Sockets
3 introduced in 1981 as the Unix BSD 4.2 generic interface
3 provide Unix-to-Unix communications over networks
3 The Windows socket API (Winsock): based on the Unix BSD 4.2 sockets interface
Net_id.Host_id
Internet Address Port Address
6 D E 6 G 5 % 6 % H 6 G 6 # % # Q
@ 2 @ B F ' @ B A 4 ( B F ' I 4 B ( P 2 B ) A 4 2 B ( B 4 A A 2 ( 4 2 4 ( B R
q
3 Principal transport service calls
d ` X Y ` X T U V p ` Y
S T T U V
Socket (addr format, type: connection-oriented/connectionless, protocol:TCP/IP/...)
W X Y ` X a S T V W W a X b ` Y U X c d ` e W U f T g h V d ` X Y ` i T U V p ` Y
q d ` X Y
Bind(...) ` X r f ` f ` s U d T Y U d W a t W a V U b W a t V U a a ` V Y W U a d ` r f ` T Y T u v g U V p W a t w a U a x v g U V p W a t y
€ ` b U
Listen(...) e ` X V U a a ` V Y W U a d ` r f ` T Y s d U b Y ` r f ` f ` U d ‚ X W Y s U d U a ` u v g U V p W a t w a U a x y
ƒ a W Y W X
Accept(...) Y ` X V U a a ` V Y W U a ‚ W Y X d ` b U Y ` T U V p ` Y
„ ` d b
Connect(local_socket, remote_socket)
W a X Y ` Y ` V U a a ` V Y W U a U a X T U V p ` Y
… ` a i
Shutdown(local_socket, remote_socket) X b ` T T X t ` Y d f X t U e ` a T U V p ` Y
€ ` V `
Send(local_socket, remote_socket, buffer, bytes)
W e ` X b ` T T X t ` Y d f X t U e ` a T U V p ` Y
q ` V
Recv(local_socket, remote_socket, buffer, bytes)
p X T ` Y U s T U V p ` Y T Y U T ` ` W s X a h V X a v ` d ` X i U d ‚ d W Y Y ` a u v g U V p W a t y
Select(...)
Lawrence Chung](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csarchitecture-120721074712-phpapp02/85/Cs-architecture-3-320.jpg)
![Client/Server with Transaction Processing
Client Client Client
Application Application Application
transactions
(banking, Network
reservation,...)
TP Monitor
Database
Server
3 Transaction changeAddress (p: String, newAddress: Address)
begin
oldAddress - retrieve address from Person where name = p
if oldAddress = newAddress then return error1
else update Person where p = name
with address - newAddress
end
3 Transaction increaseSalary (increment: Dollar)
begin
...
end
Lawrence Chung
Client/Server with Transaction Processing
3 Transactions are a way to make ACID operations a general commodity
[Transaction Processing Concepts and Techniques, Jim Gray and Andreas Reuter, 1993]
Ë Atomicity
t a transaction is an indivisible unit of work
t an all-or-nothing proposition
t all updates to a database, displays on the clients’ screens, message queues
t e.g., salary increase for all 1 million employees or none
Ë Consistency
t a transaction is an indivisible unit of work
t S - [T | abort] - S
t integrity constraints (e.g., mgr.salaray salary)
Ë Isolation
t a transaction’s behavior not affected by other transactions running concurrently
t e.g., reserve a seat
t serialization techniques
Ë Durability
t persistence
t a transaction’s effects are permanent after it commits.
† ‡ ˆ ‰ ‘ ’ “ ” • – — ˜ ” ™ ˜ – – d e f d e g g ’ ” g ” h ˆ — i ‘ f ” j ” ‘ ‘ e ™ k l e f d k – m j e f i — ˜ e n ” — – – • m j ˜ – o — h
p q r ” f – m s ˜ g ™ ” e j ˜ f s h
Lawrence Chung](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csarchitecture-120721074712-phpapp02/85/Cs-architecture-5-320.jpg)
![Client/Server with Transaction Processing
v Two-Phase Commit Protocol
3 To synchronize updates on different machines so that they either all fail or all succeed
3 centralize the decision to commit but giving each participant the right of veto
3 like a Christian marriage
Commit Coordinator Subordinate Subordinate
(Root) Node Node
Prepare-to-commit Prepare-to-commit Prepare-to-commit
Phase 1
Record in Log Ready-to-commit Ready-to-commit
Commit Commit Commit
Phase 2
Complete Complete Complete
t If the subordinates have spawned pieces of the transaction on other nodes,
they must propagate the prepare-to-commit-command in the first phase
- a transaction tree
t If any of the participants returns a transaction failure,
the root node tells all its subordinates to perform a rollback
Lawrence Chung
Client/Server Groupware
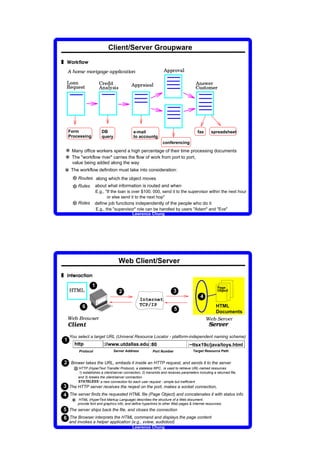
3 Why?
support for business reengineering: bcfh - maximize profit
change the way people communicate with each other
helps manage (and track) the product thru its various phases
computer-supported cooperative work (CSCW)
collaborative/workgroup computing
return on investment: 16% to 1666% on a median investment of $100K
[a study of 65 Notes users in 1994]
3 Five foundation technologies t u v w x y z y z { | } u ~ z v v { y } € z ‚ u ƒ } | y z { z } „ € … z } ƒ { … t
„
› ‘ ‘
š ‹ œ ” ™ ™ ‡ • š ” “ œ “ – ” ” “ œ
from electronic imaging (scanning, digitization, display, storage and retrieval)
to document (component types: text, image, graphics, faxes, mail, voice clips, BBs)
„ † ‡ ˆ ‰ Š ‹ ‡ Œ
„
Ž ‘
‹
„
‘
‡ “ Š ” ˆ ” “ • “ –
’
thru microphones, video windows, electronic whiteboards,
controlled access to shared document
„
‘
— • ˜ ” ™ š ‹ “ –
electronic scheduling of meetings, sharing calendars and to do lists, triggering events
e Why not just DBMS?
DBMS: highly structured data
Groupware: highly unstructured data document database
e Why not just TP Monitors?
TP Monitors: transaction processes
Groupware: (currently) not transaction-oriented in the ACID sense
Lawrence Chung](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csarchitecture-120721074712-phpapp02/85/Cs-architecture-6-320.jpg)