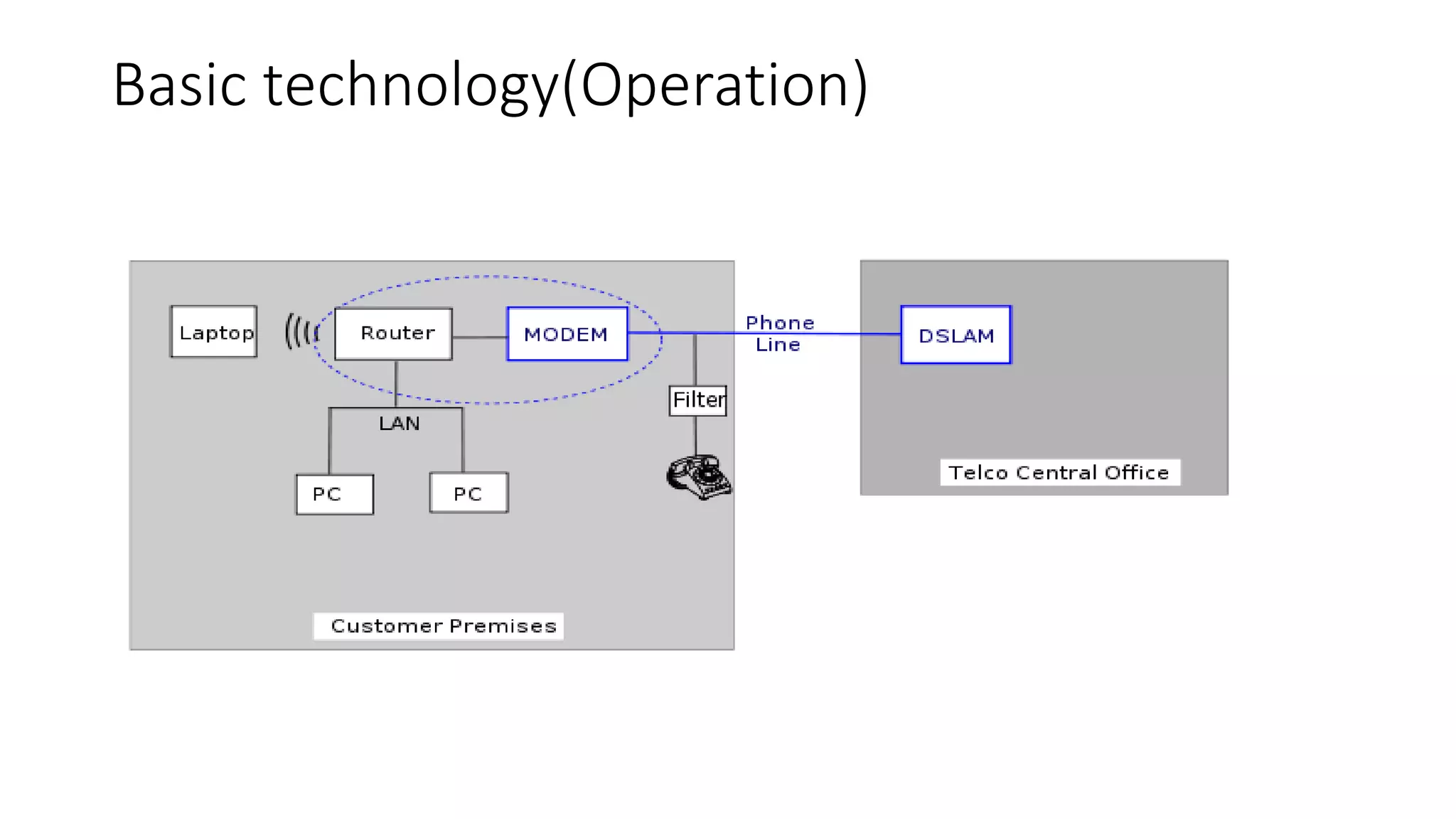
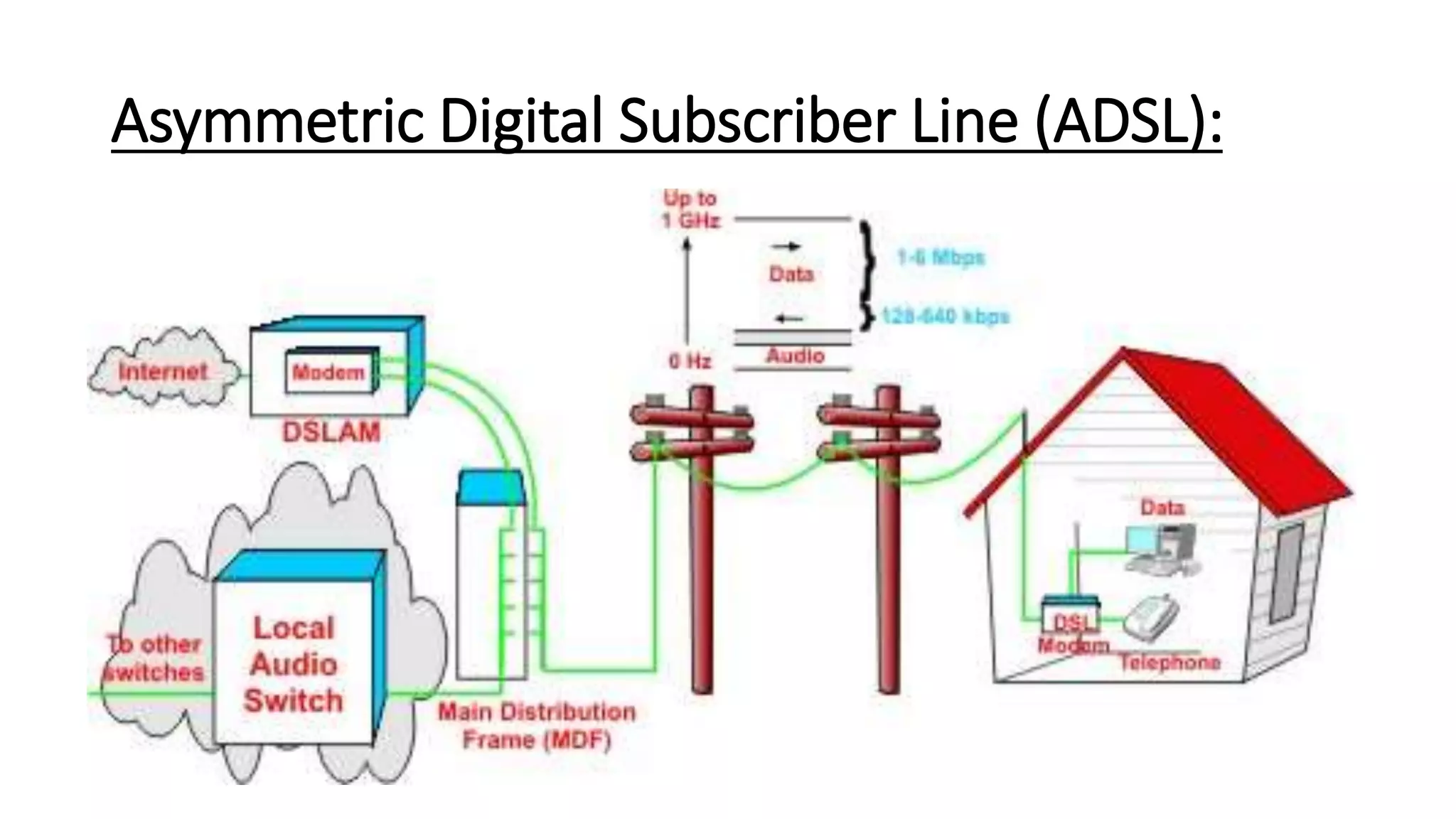
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is a technology that provides high-speed internet access over ordinary copper telephone lines. It allows digital data transmission and voice calls to occur simultaneously. There are different types of DSL that provide varying speeds depending on distance from the telephone exchange. DSL works by using a separate frequency spectrum from voice calls to transmit digital data at speeds much faster than a dial-up modem.