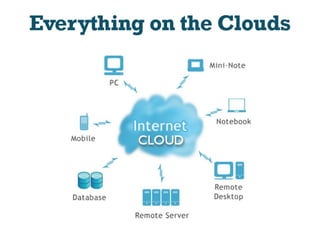
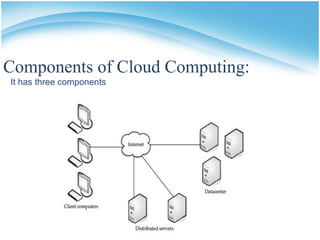
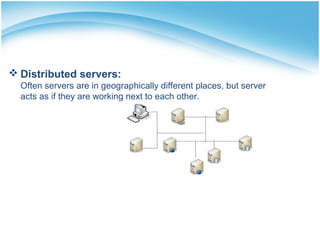
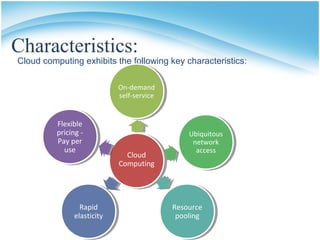
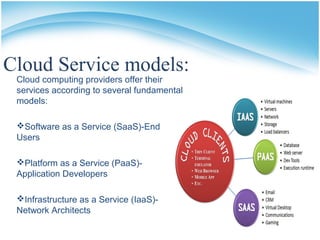
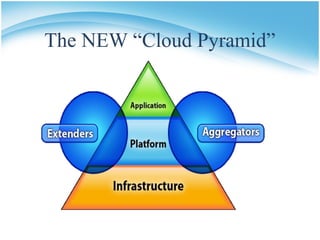
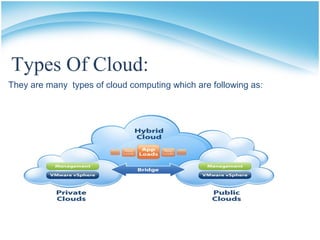
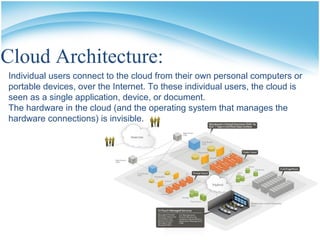
The document presents a presentation on cloud computing. It begins with an outline of topics to be covered, including definitions of cloud computing, the history of cloud computing, components and characteristics of cloud computing, cloud service models, types of clouds, cloud architecture, properties, security, operating systems, applications, and advantages and disadvantages. It then goes on to define cloud computing and describe its various components, characteristics, service models including SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. It also discusses types of clouds, properties, security considerations, operating systems, applications, and the advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing.