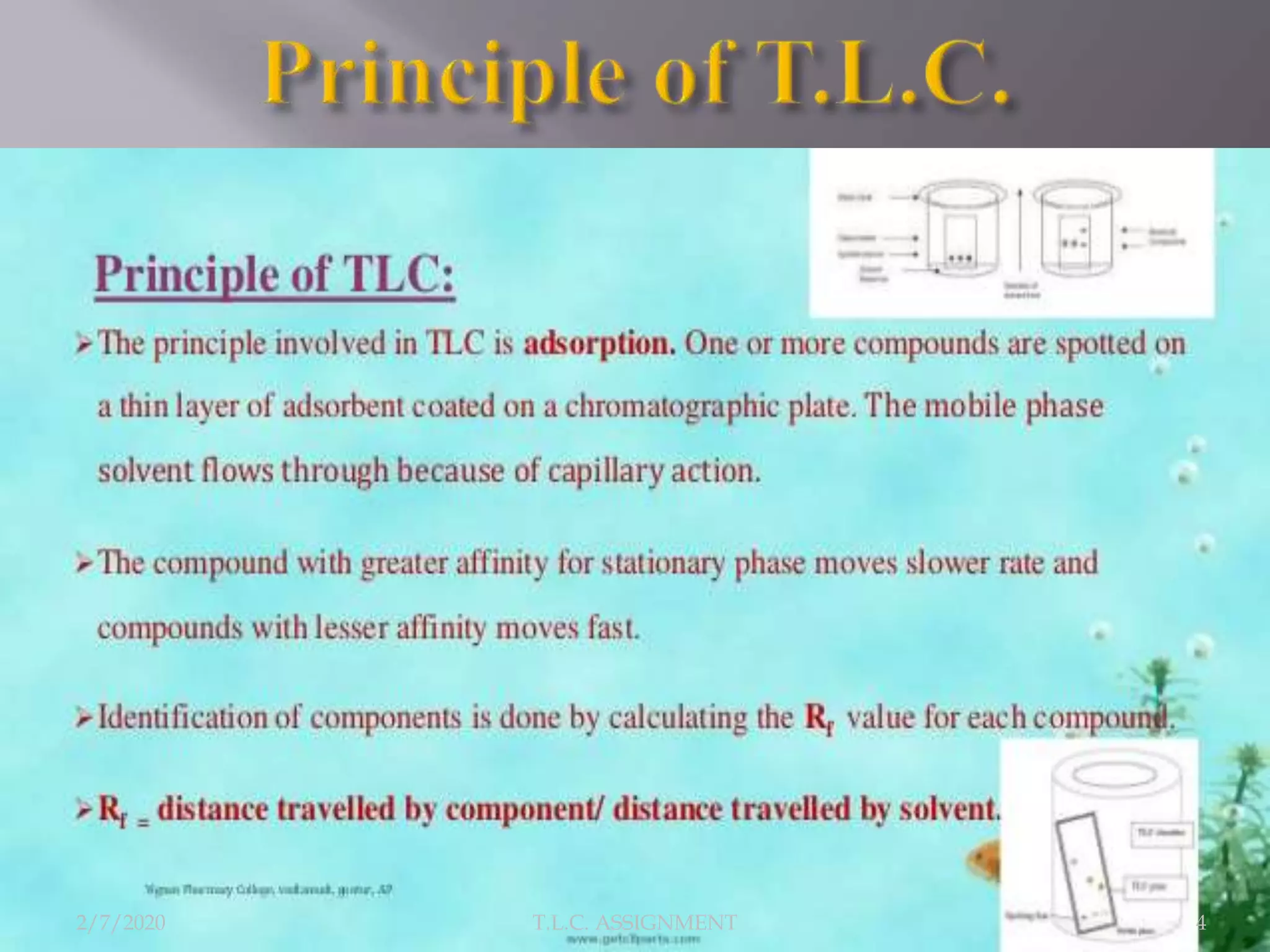
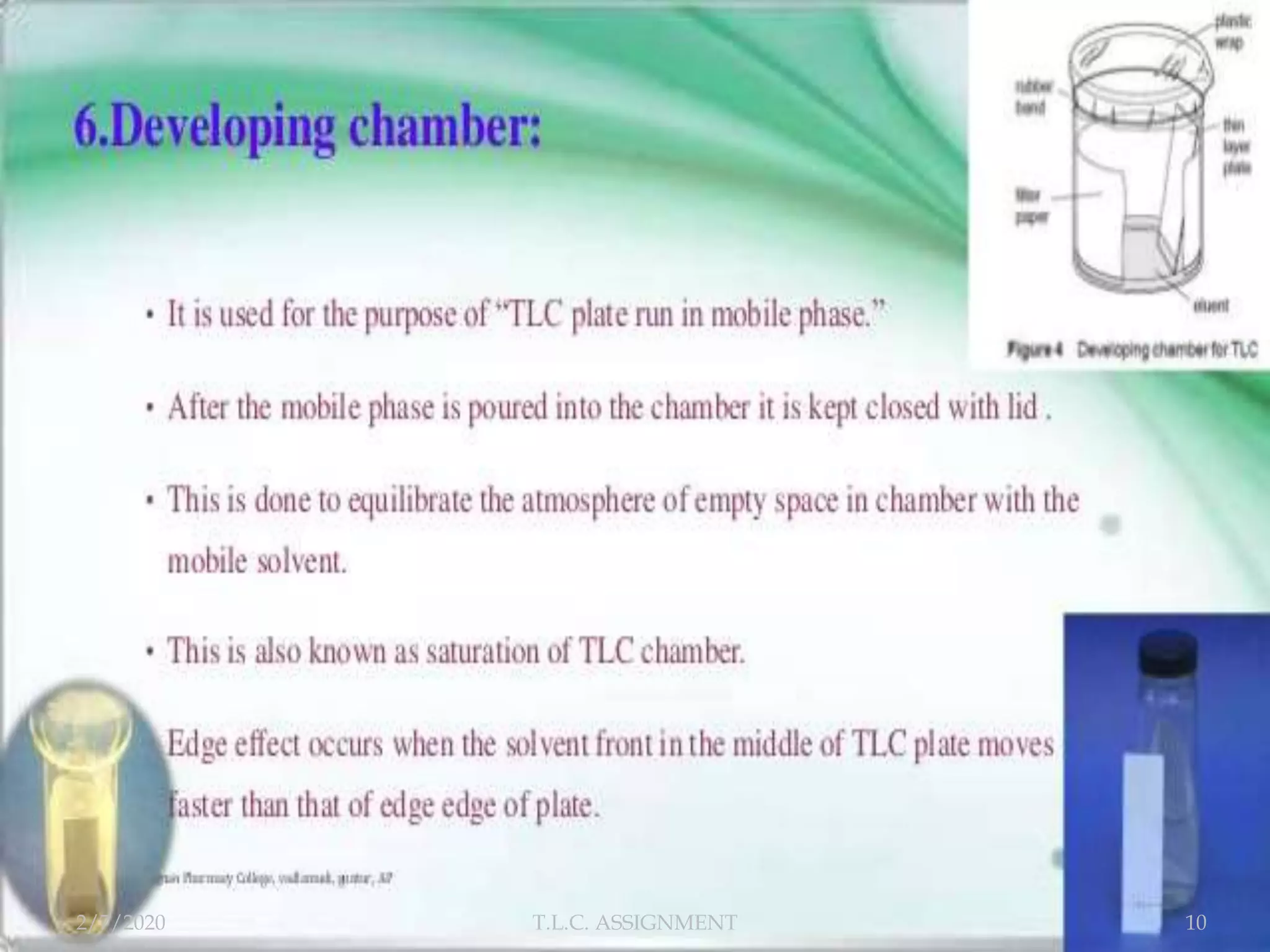
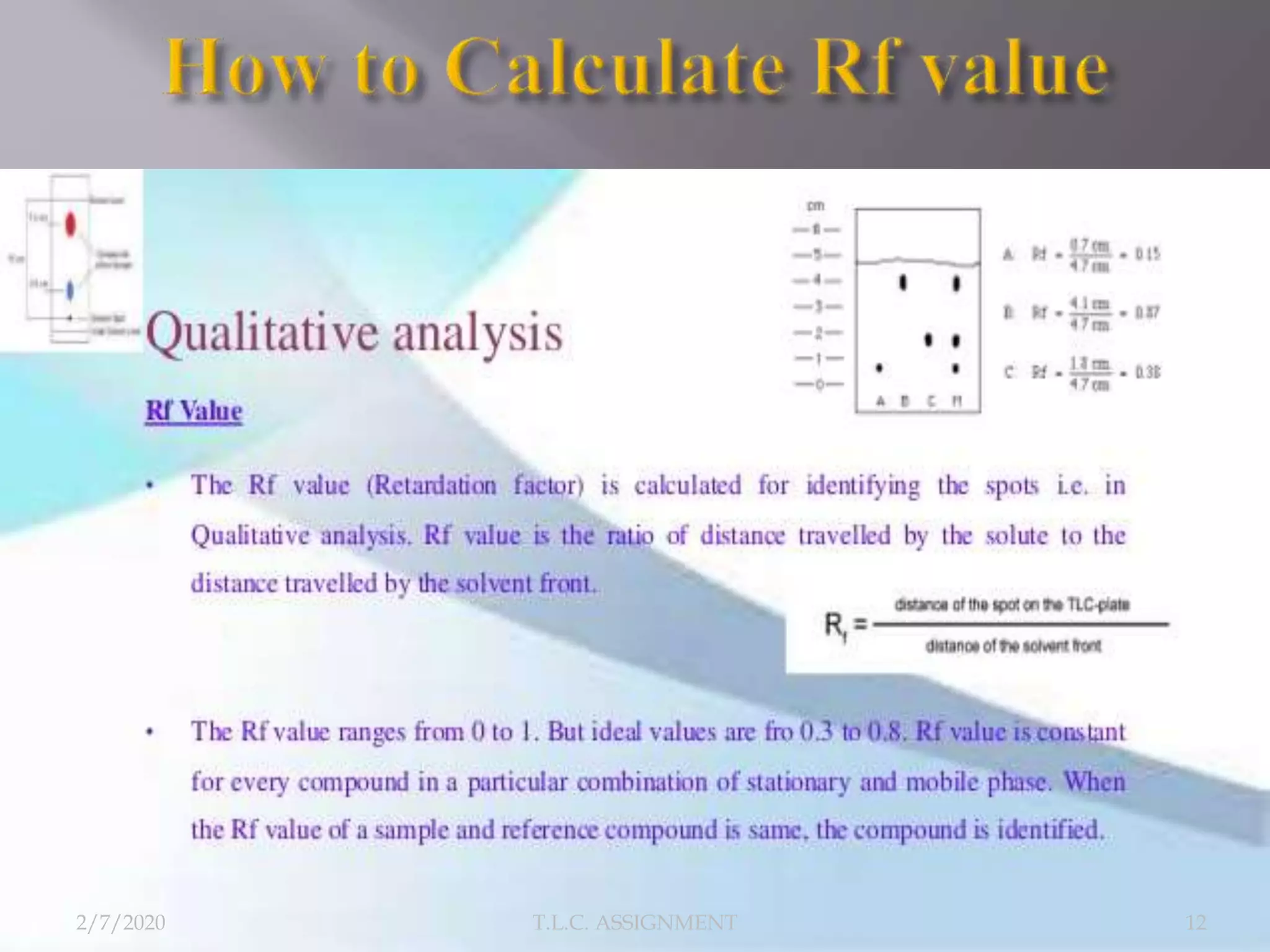
The document discusses thin layer chromatography (TLC), a technique used to separate mixtures based on differential partitioning between a mobile phase and stationary phase. TLC involves preparing a TLC plate by coating it with an adsorbent stationary phase. Samples are applied as spots and the plate is developed in a mobile phase, allowing separation. Visualization identifies the components, which are used to analyze samples and identify unknown compounds. TLC is useful for separating polar compounds like amino acids, sugars, and natural products.