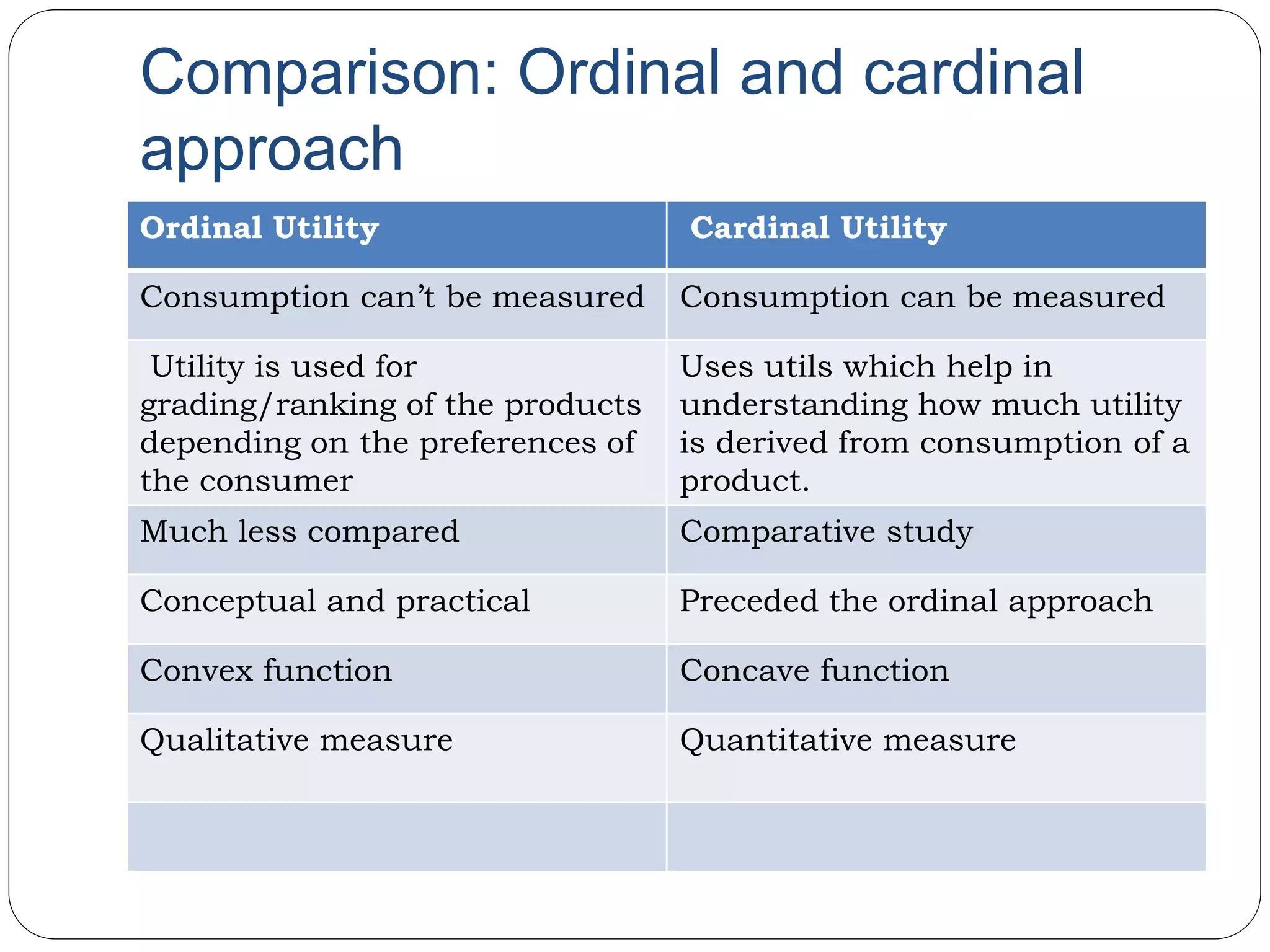
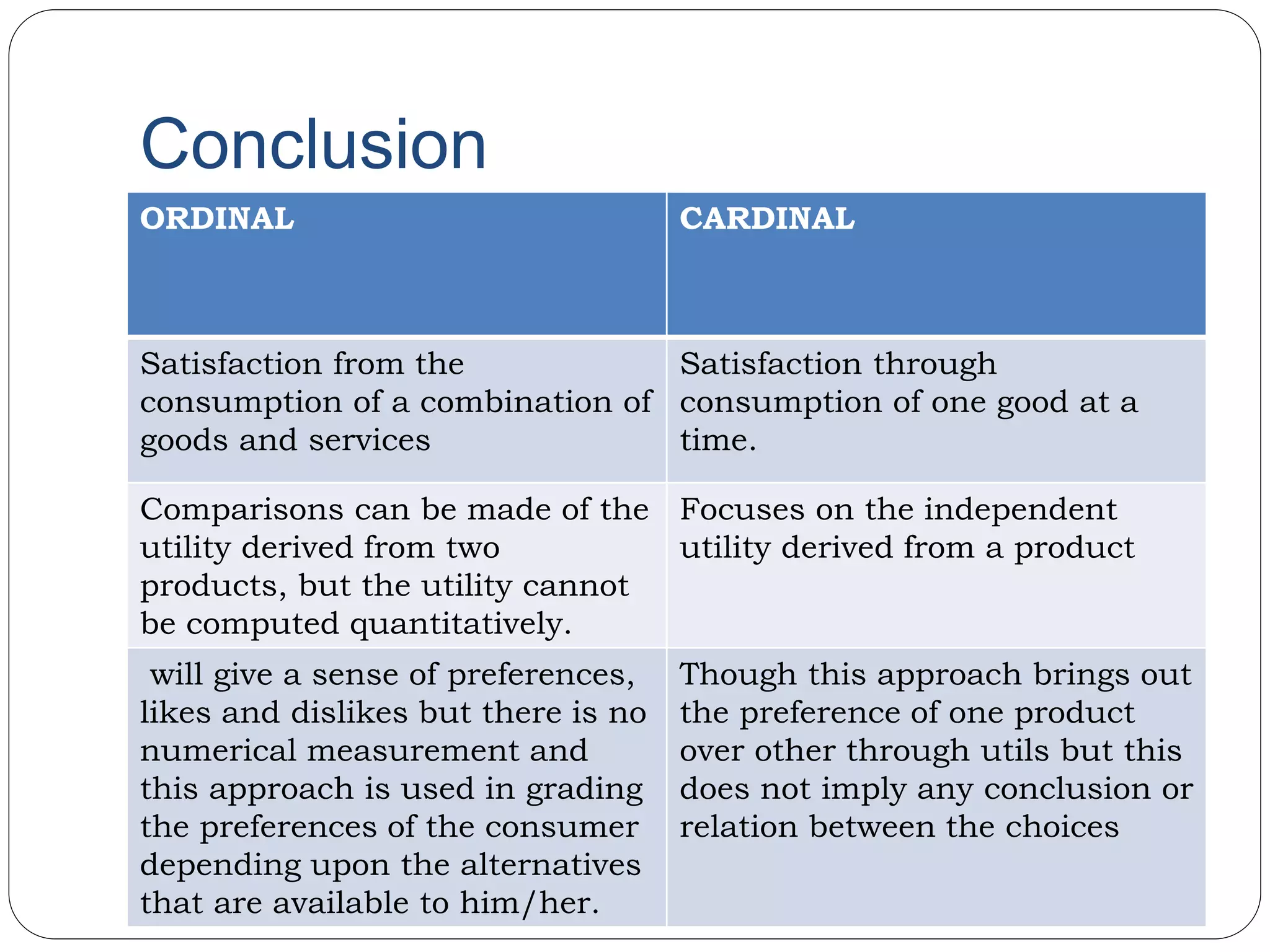
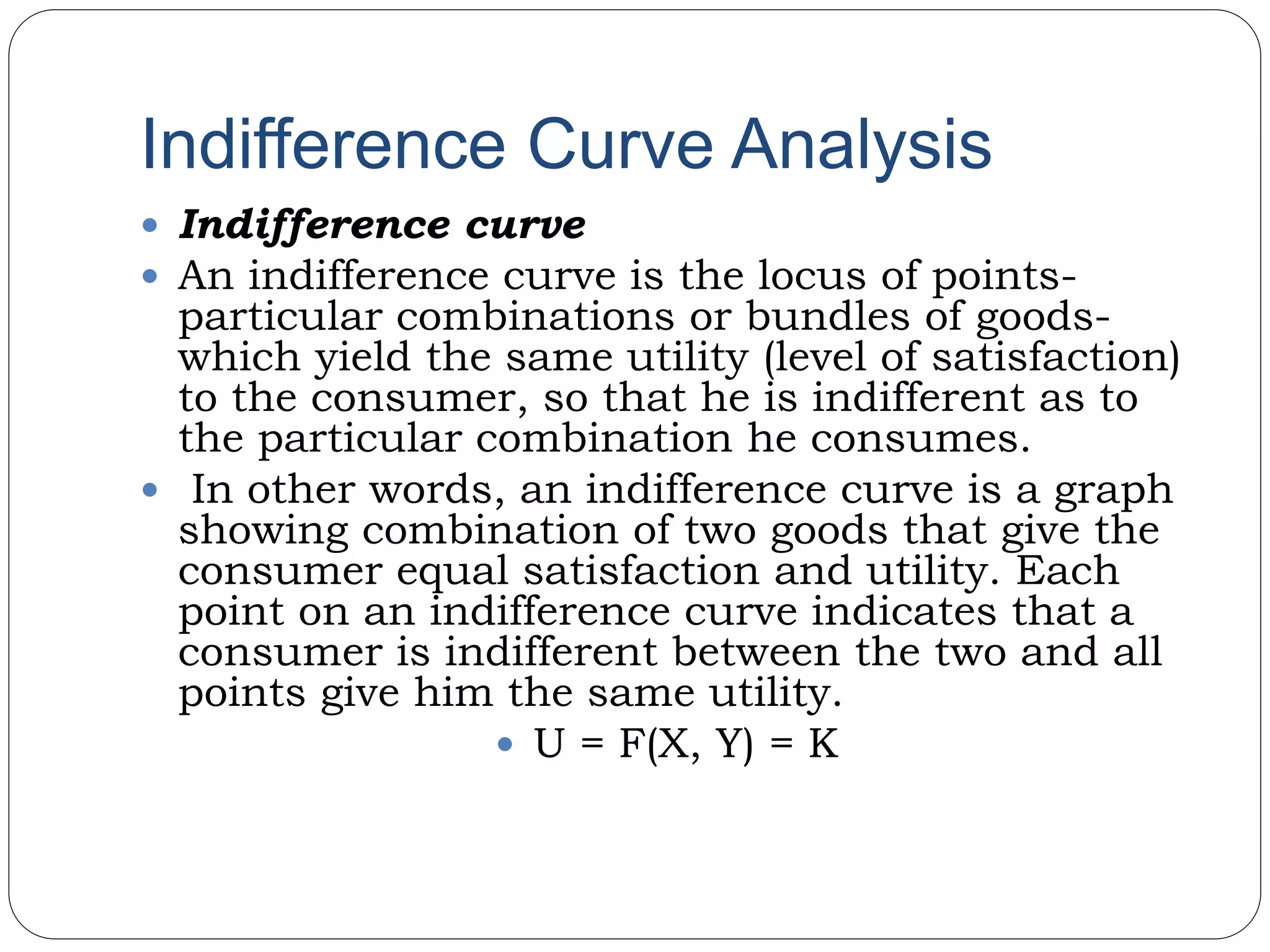
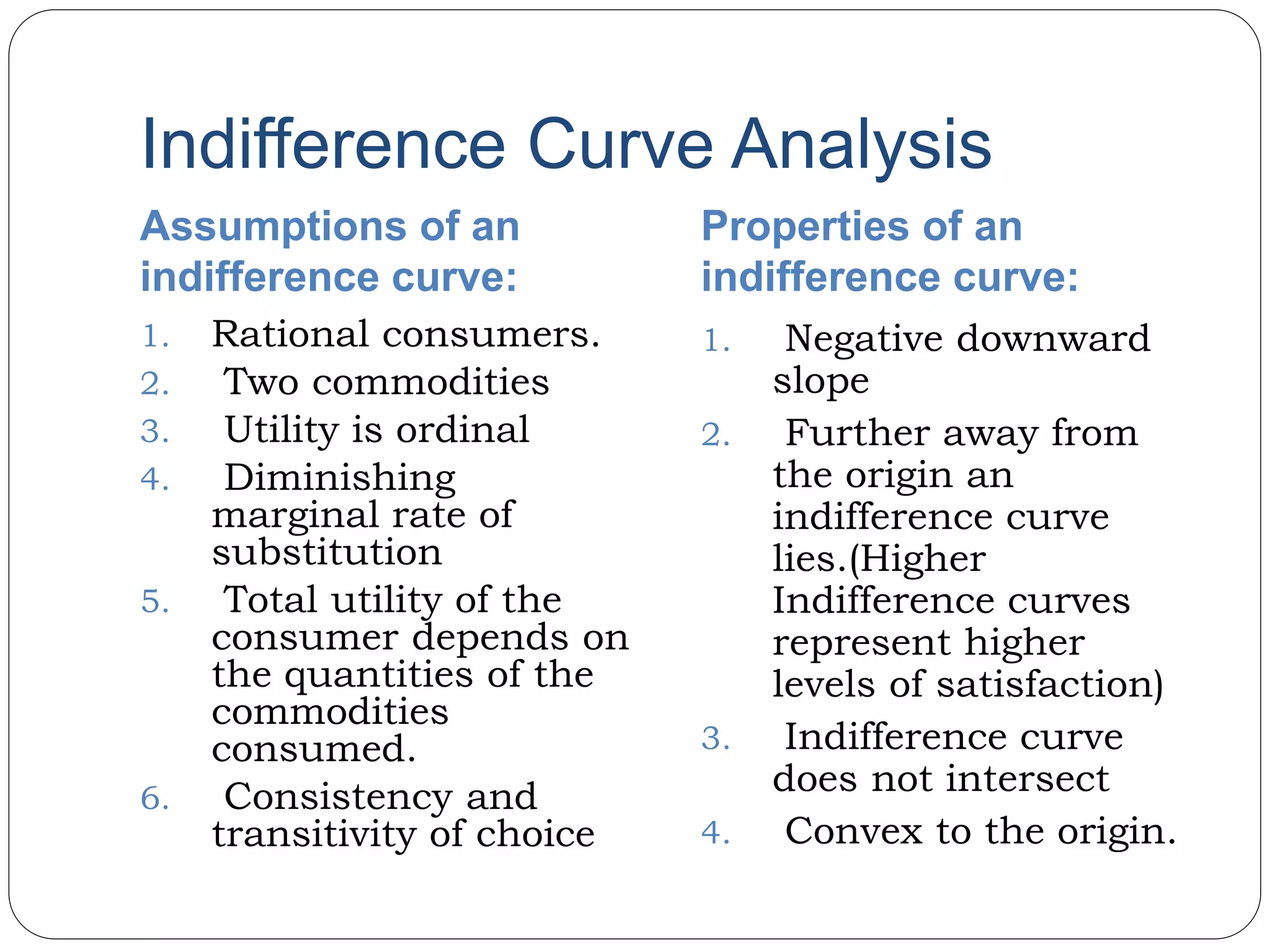
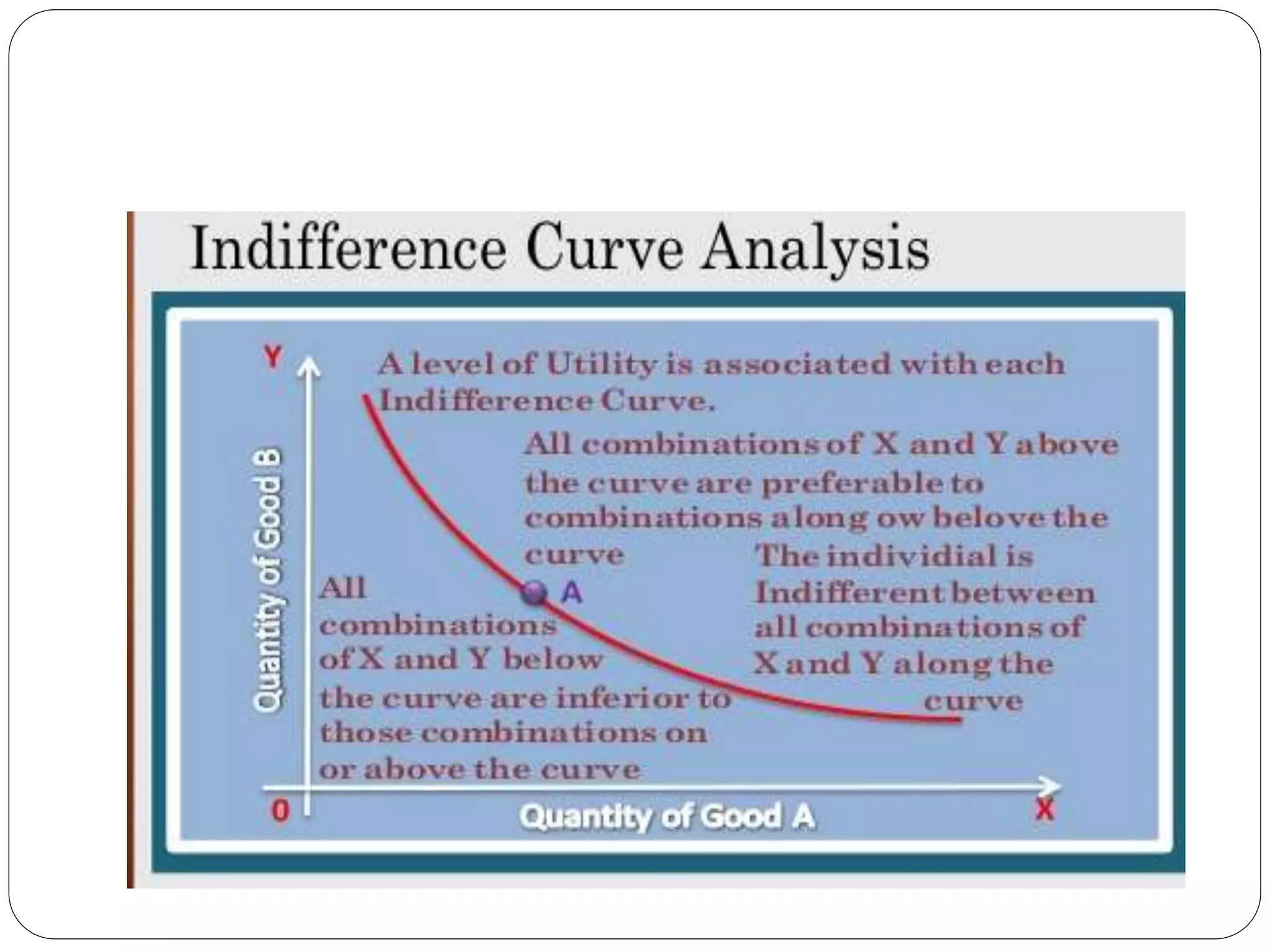
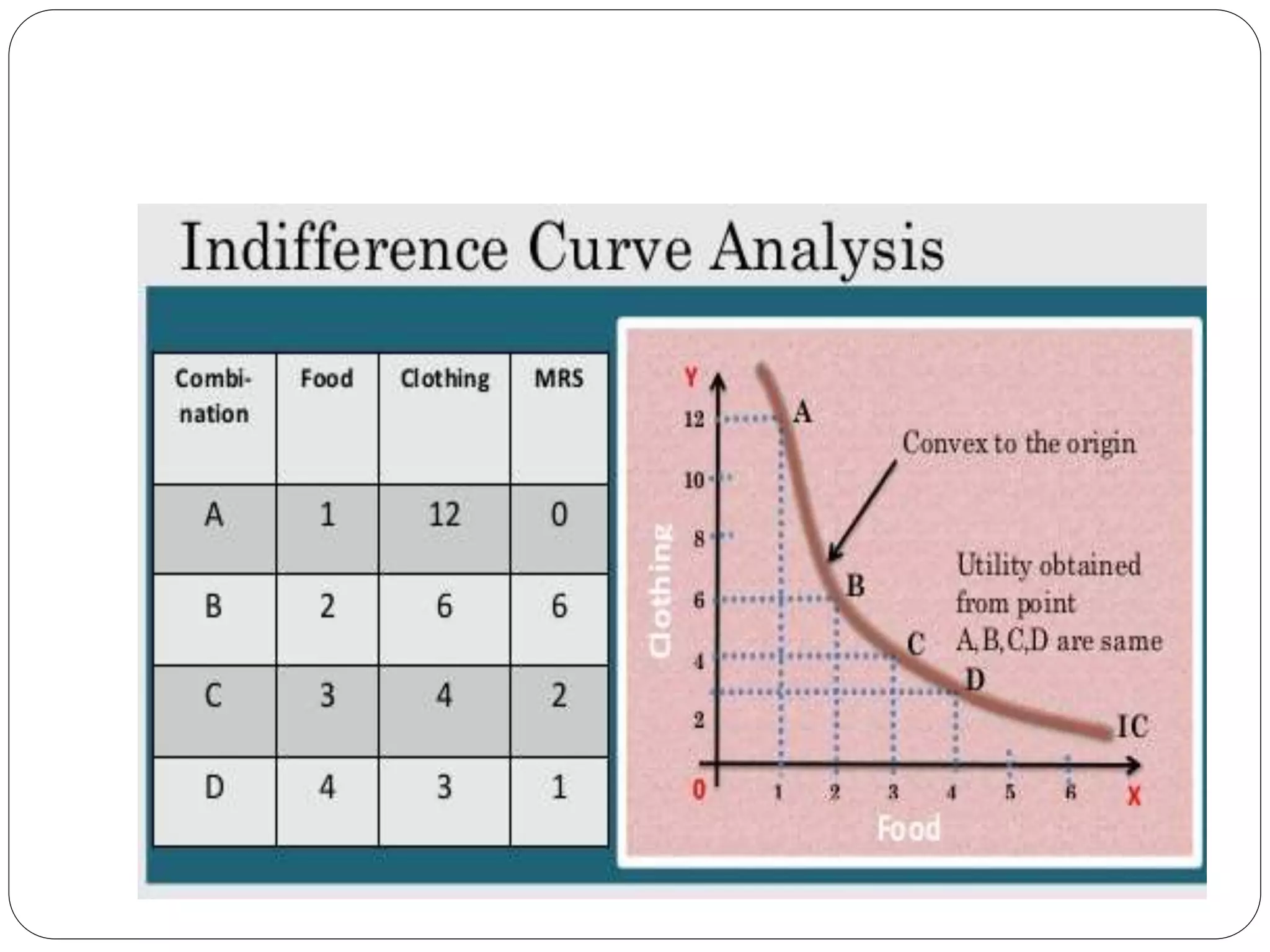
This document provides an overview of consumer behavior theory and concepts. It discusses the determinants of demand, marginal utility analysis including the law of diminishing marginal utility, and the ordinal and cardinal approaches to measuring utility. It defines key terms like utility, marginal utility, and total utility. It also covers indifference curve analysis and the budget line/budget set that represent the consumption possibilities and constraints for a consumer. The purpose is to understand the various factors that influence how consumers make choices to maximize satisfaction given prices and income.