1. Comparative statics analysis examines how optimal decisions change when underlying assumptions, like prices or income, change.
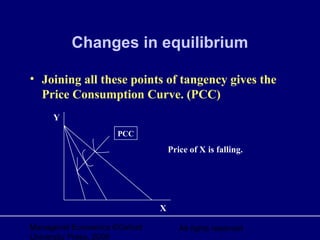
2. Changes in prices result in new budget constraints and equilibrium points where indifference curves are tangent to the new budget lines.
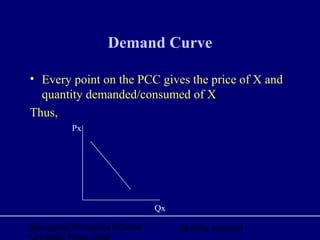
3. The price consumption curve is formed by joining all the new equilibrium points and used to derive the demand curve.
4. Similarly, changes in income result in parallel shifts to the budget line and new equilibrium points joined to form the income consumption curve.