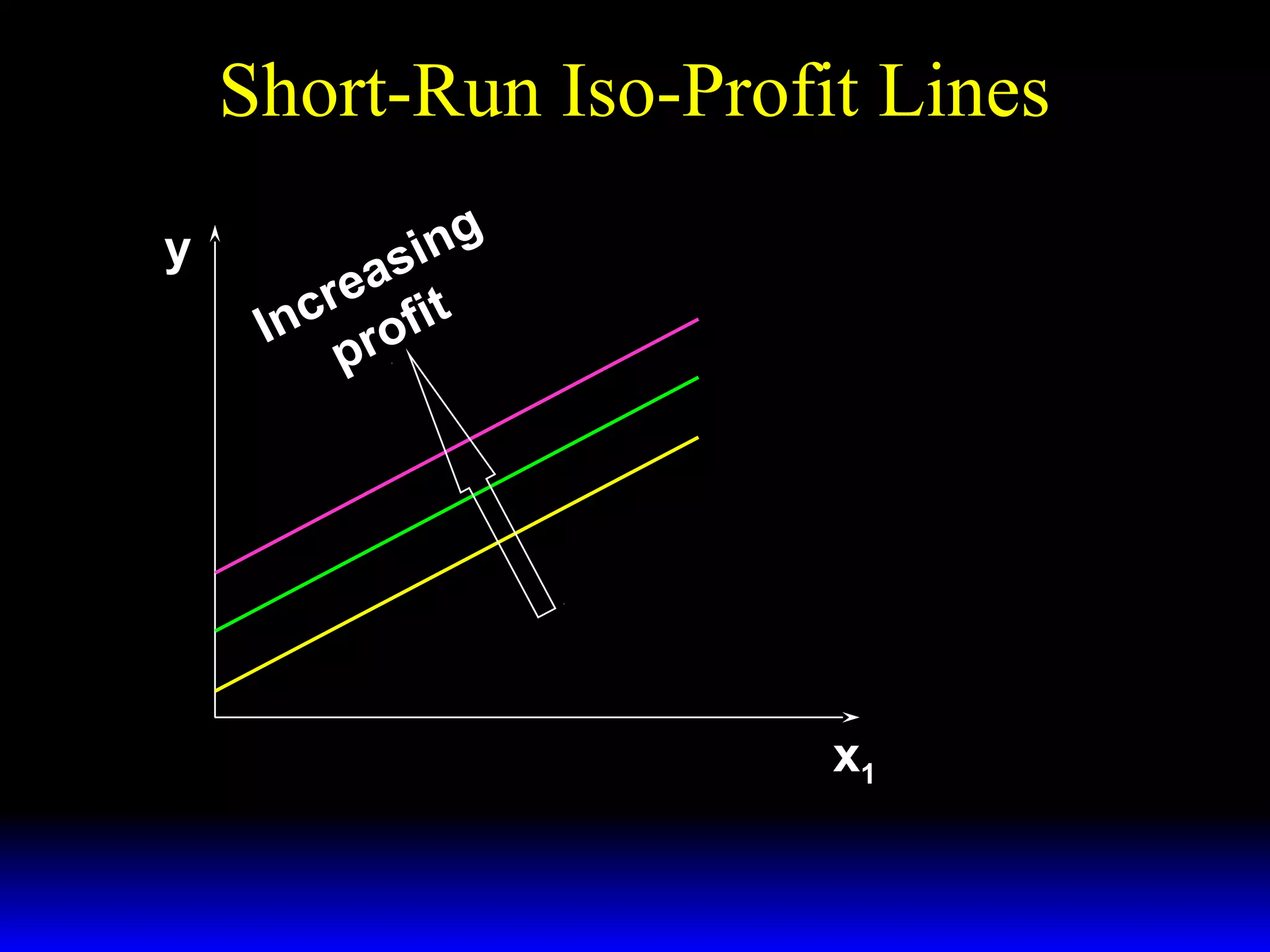
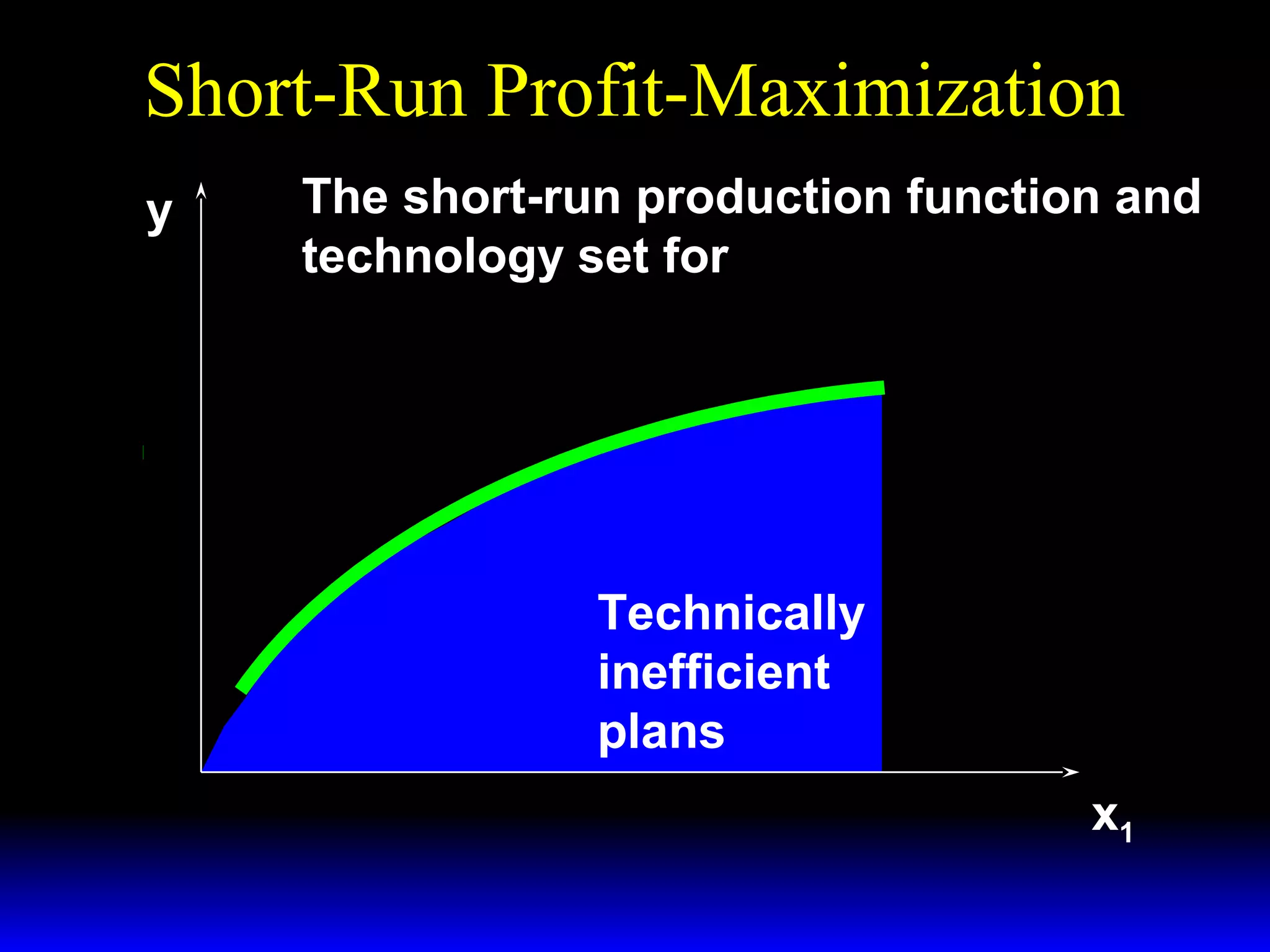
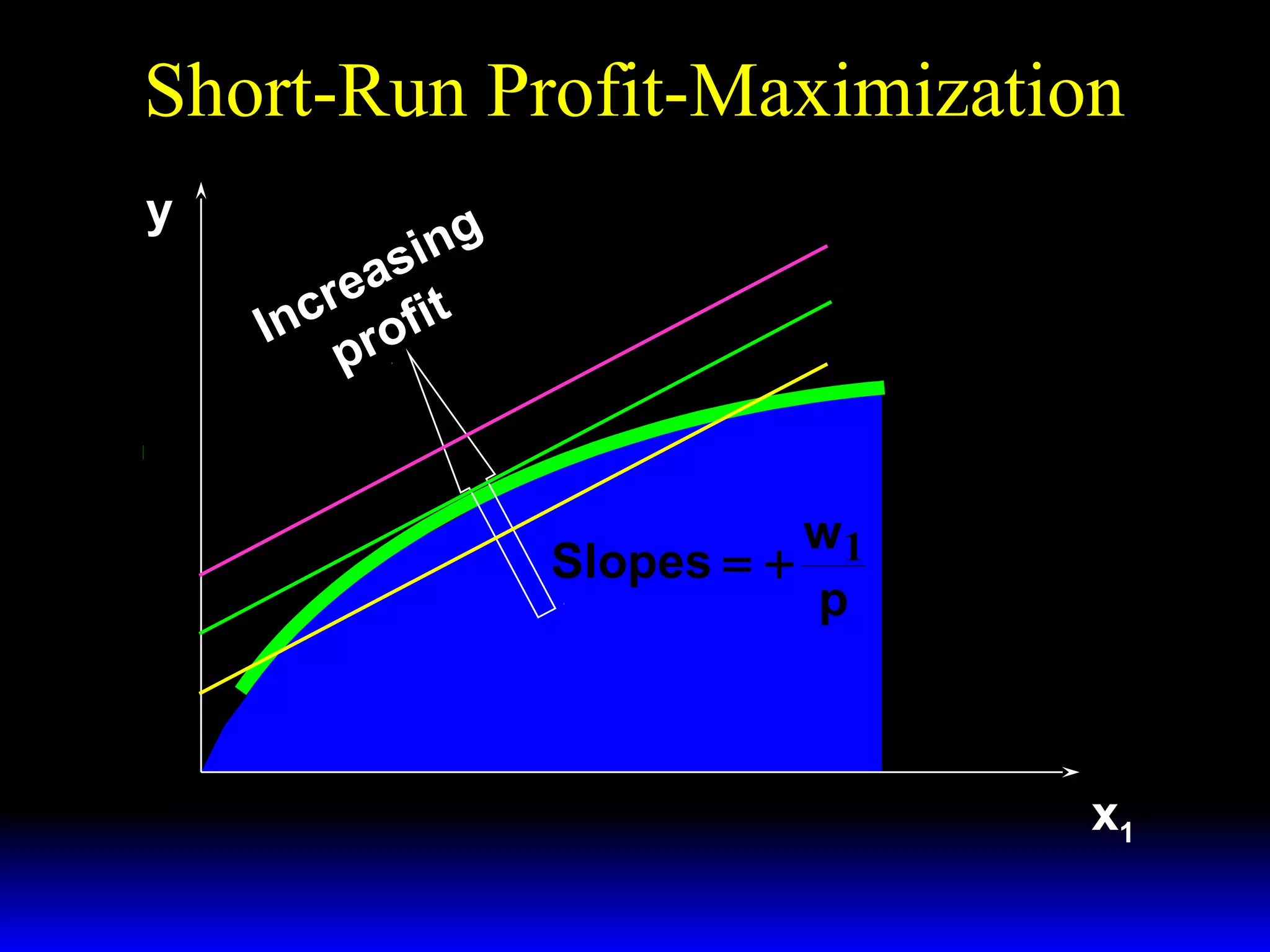
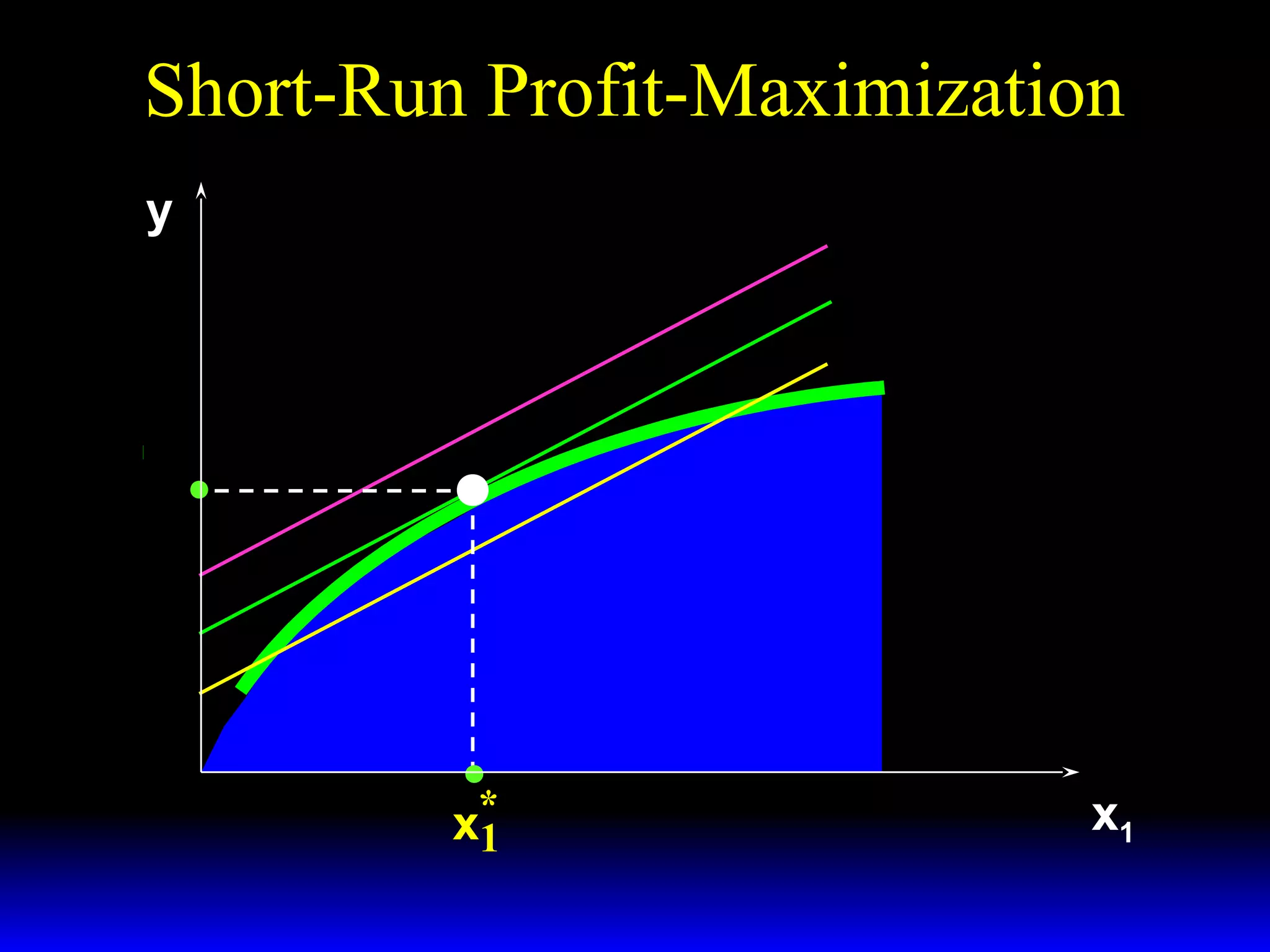
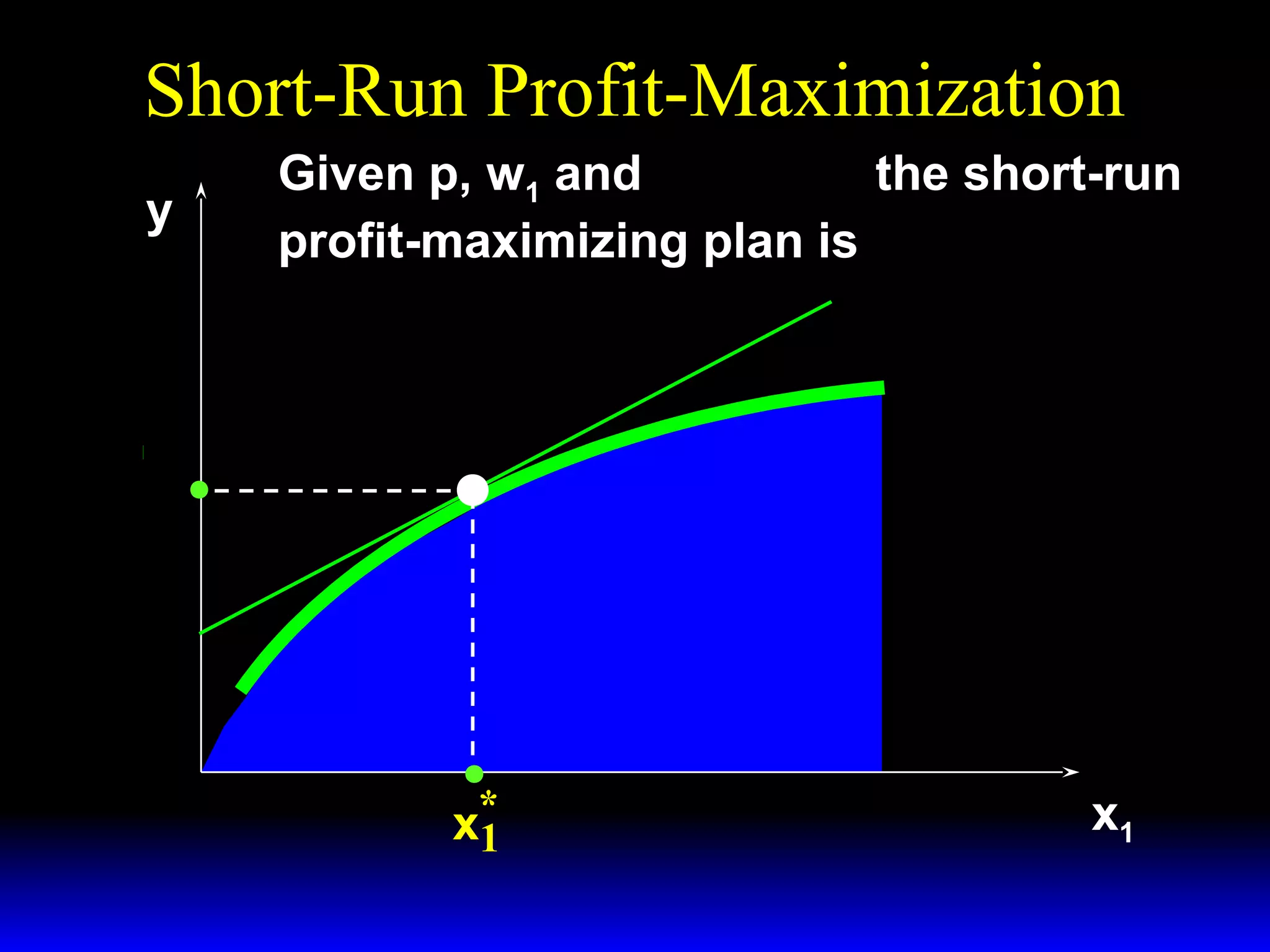
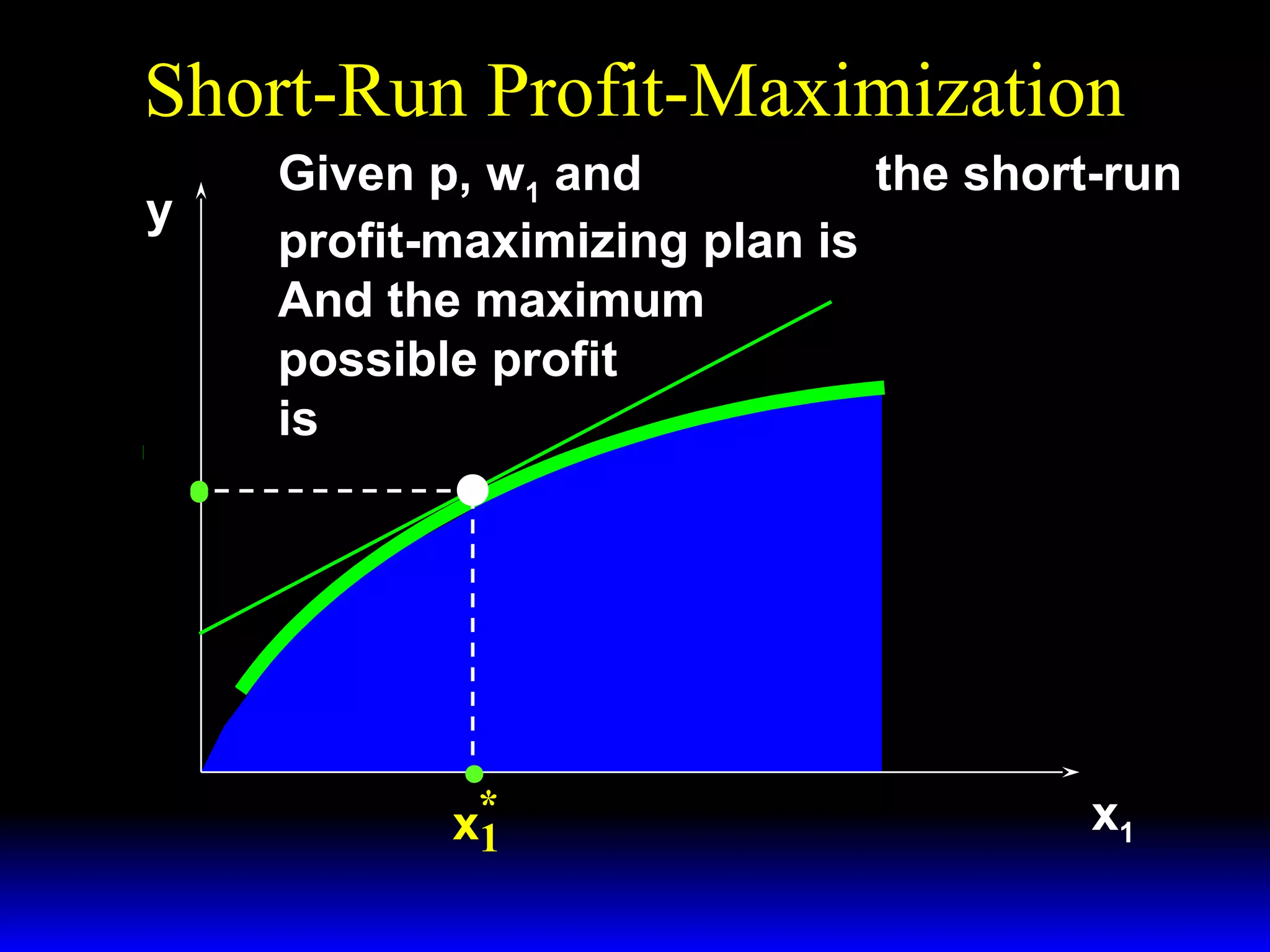
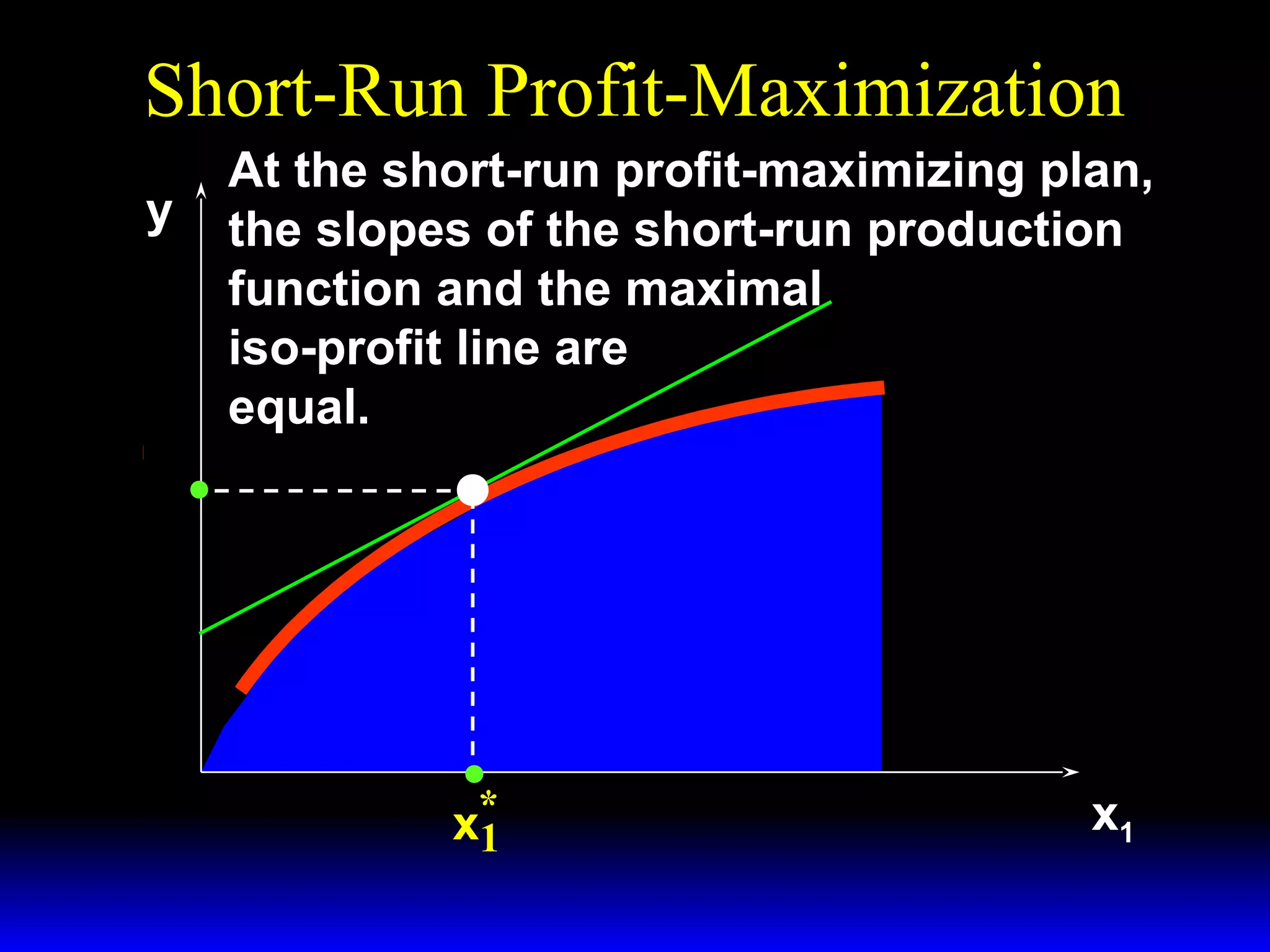
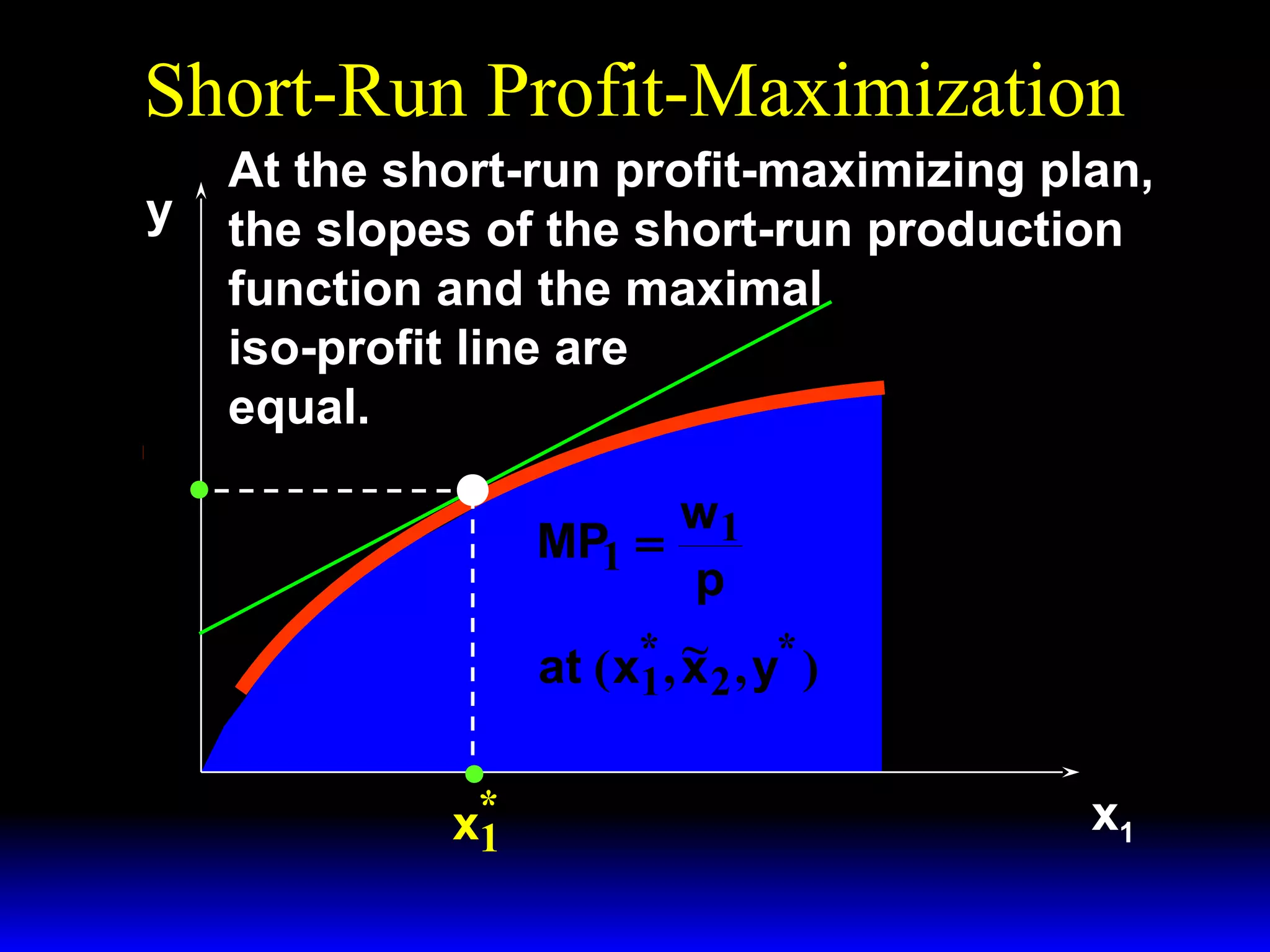
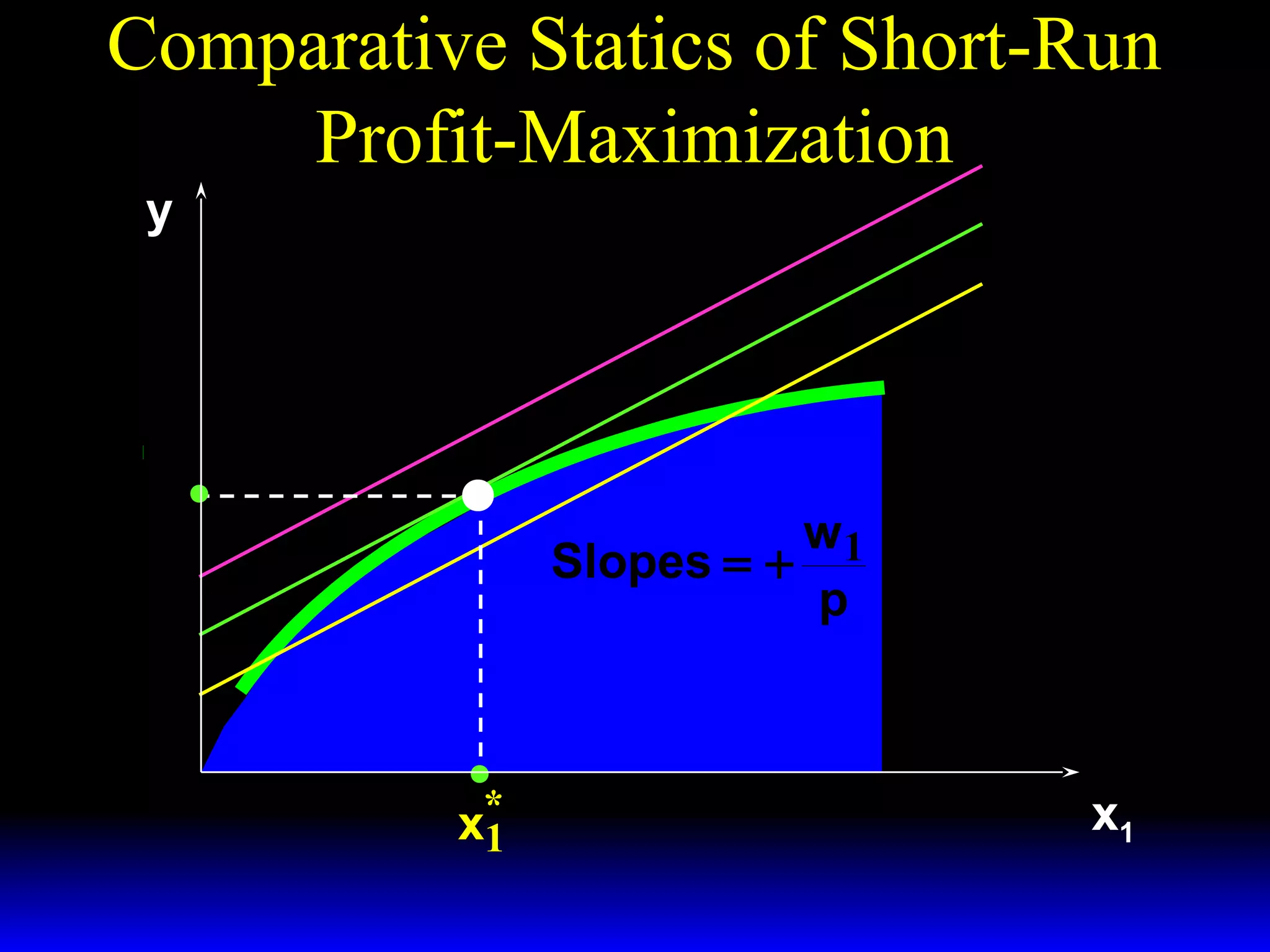
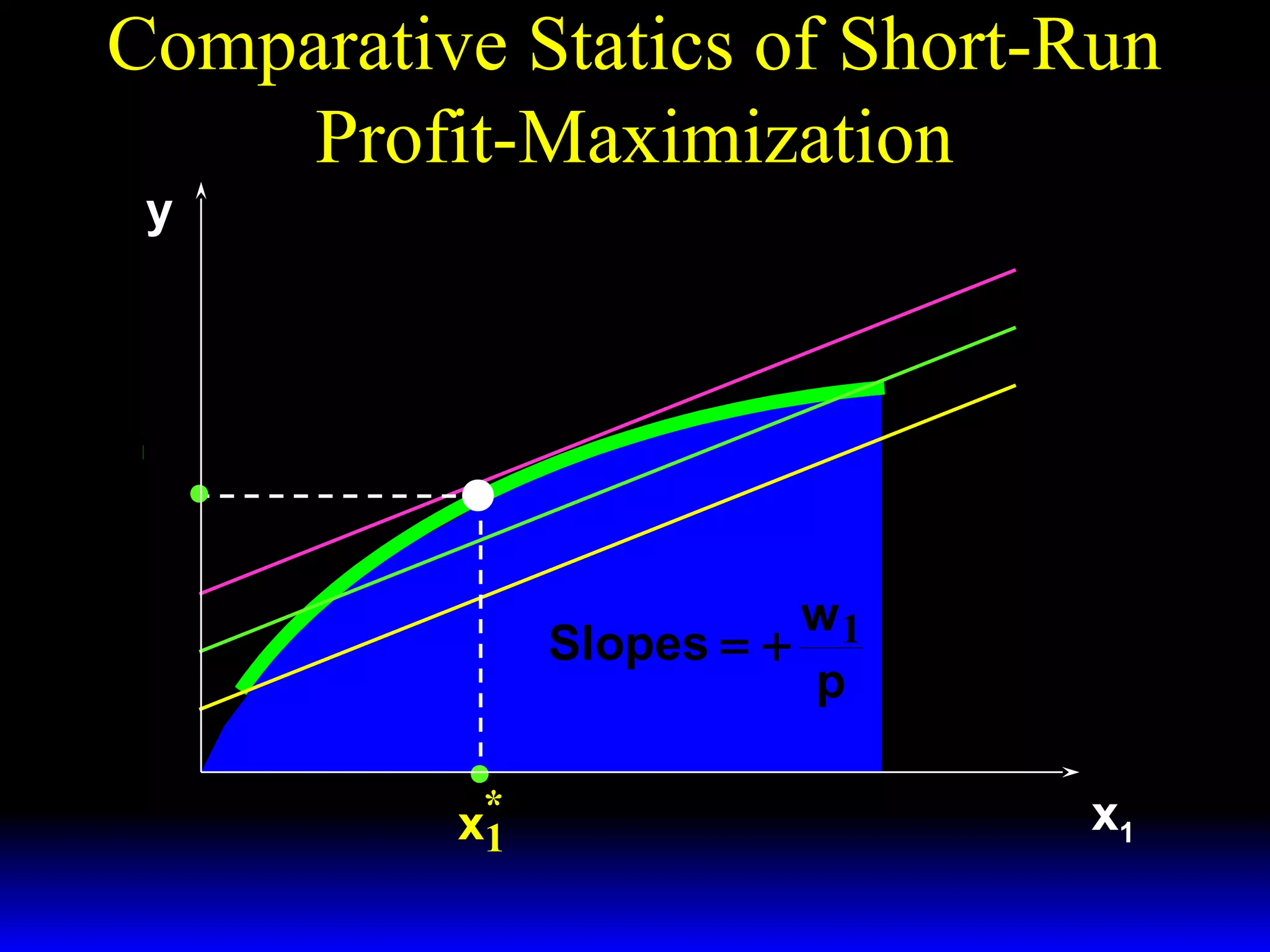
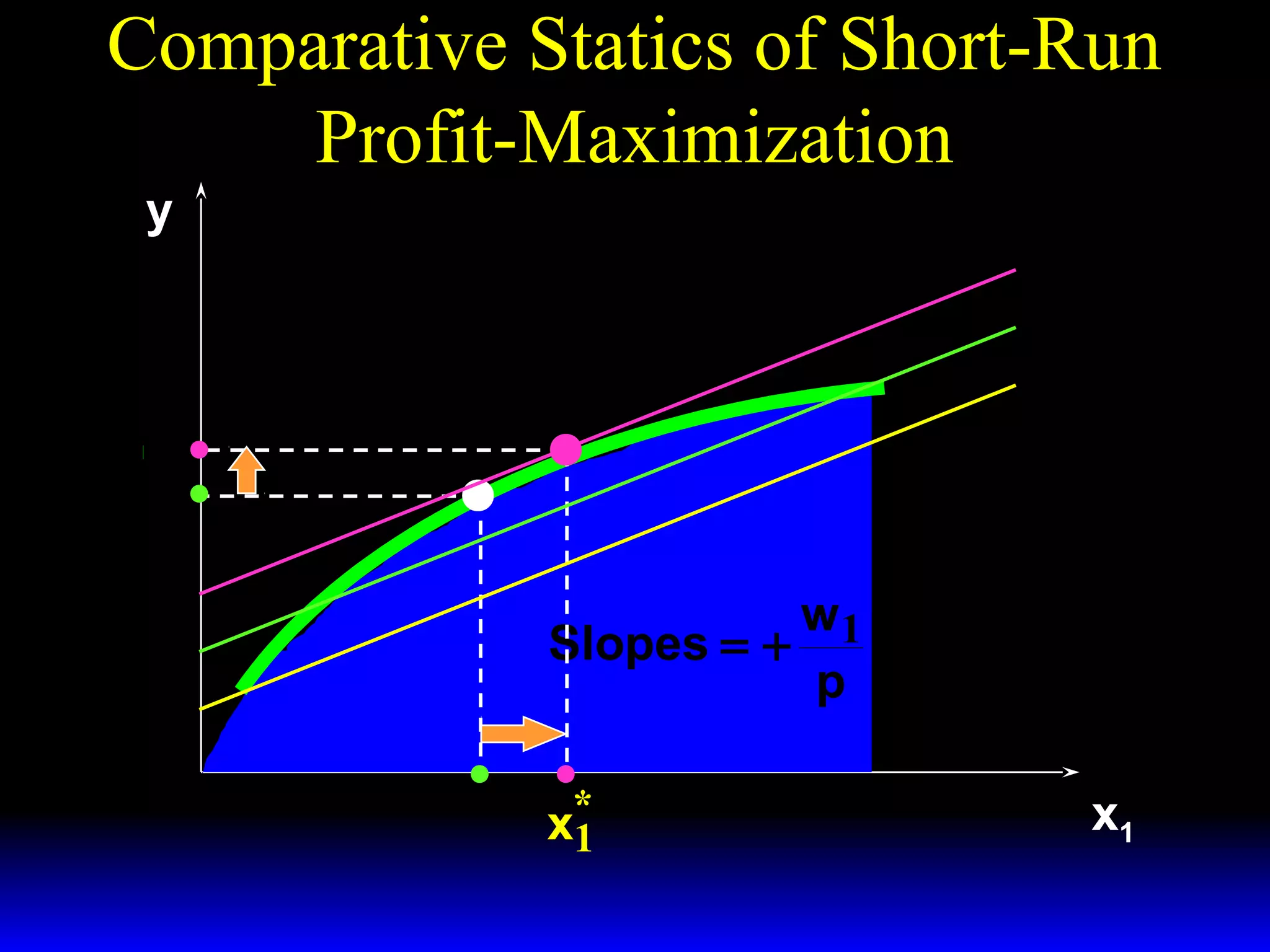
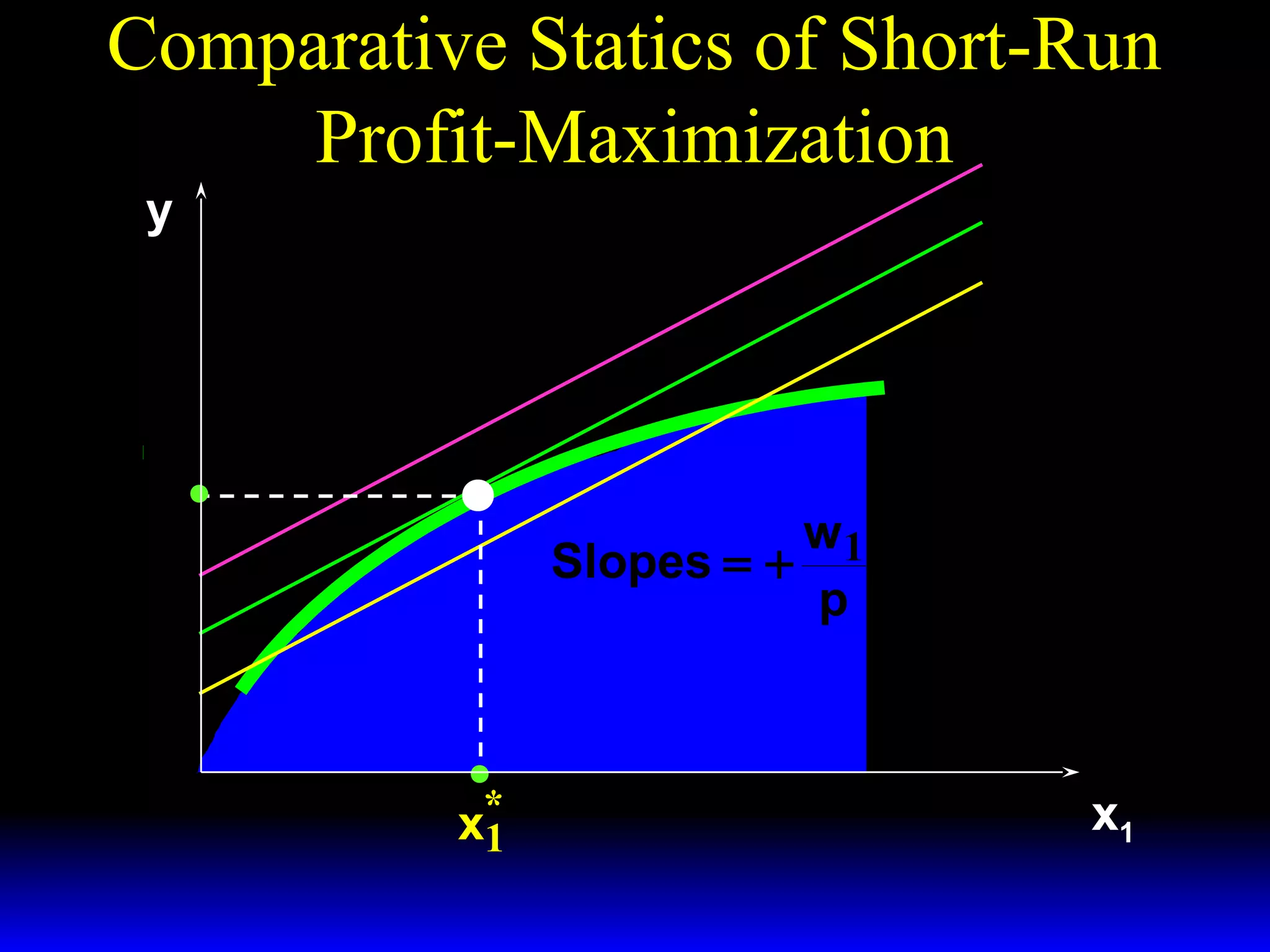
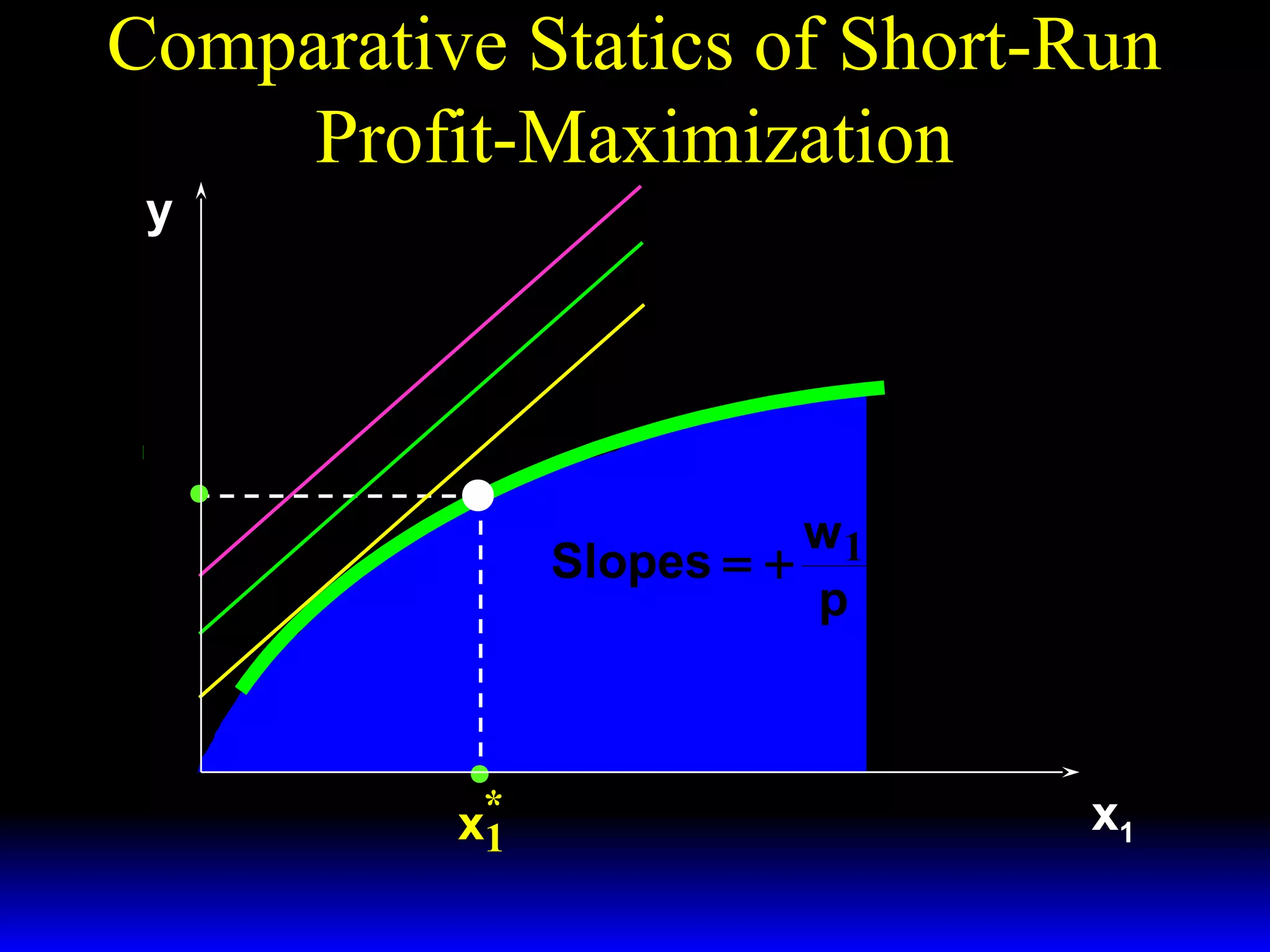
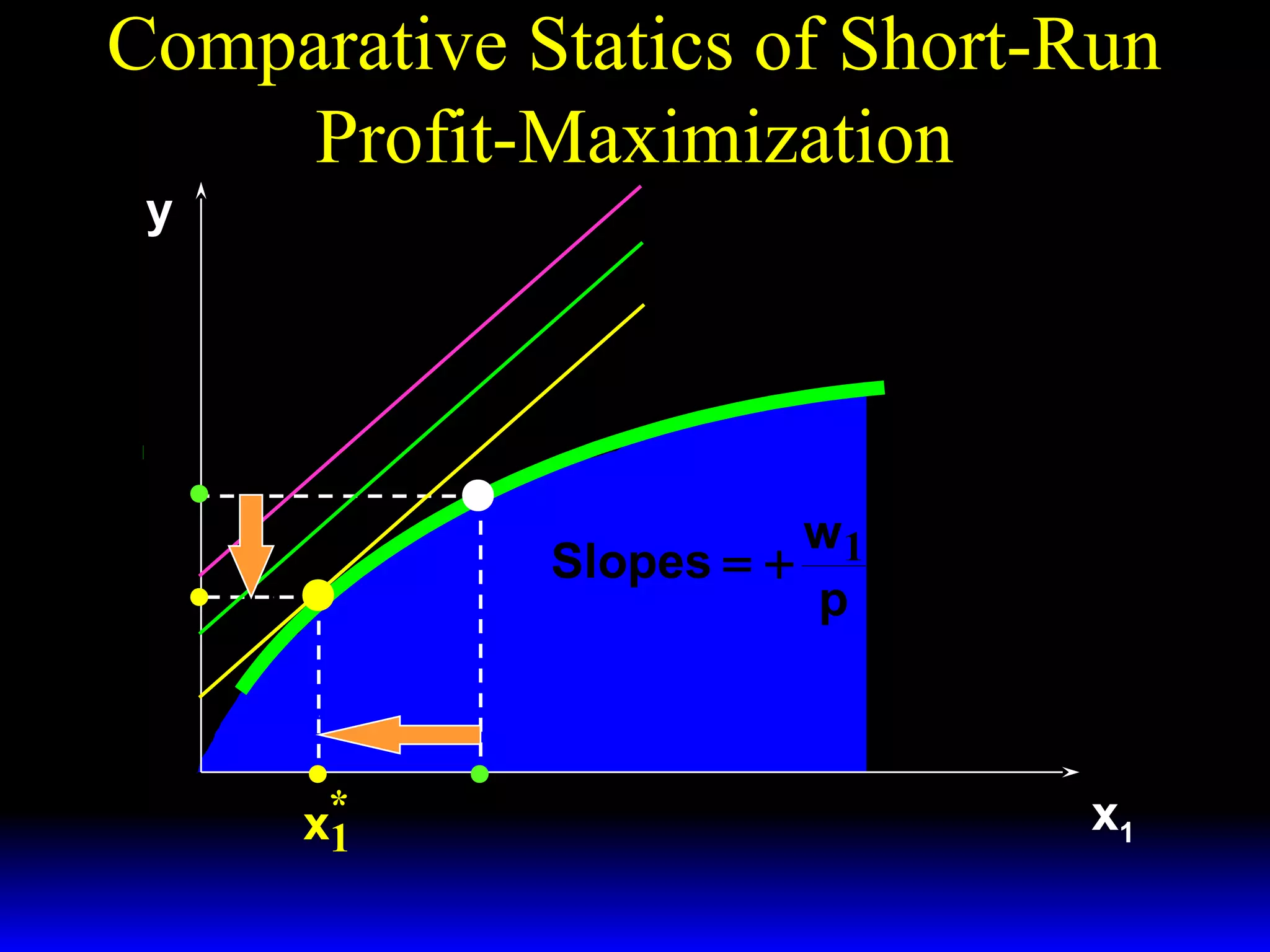
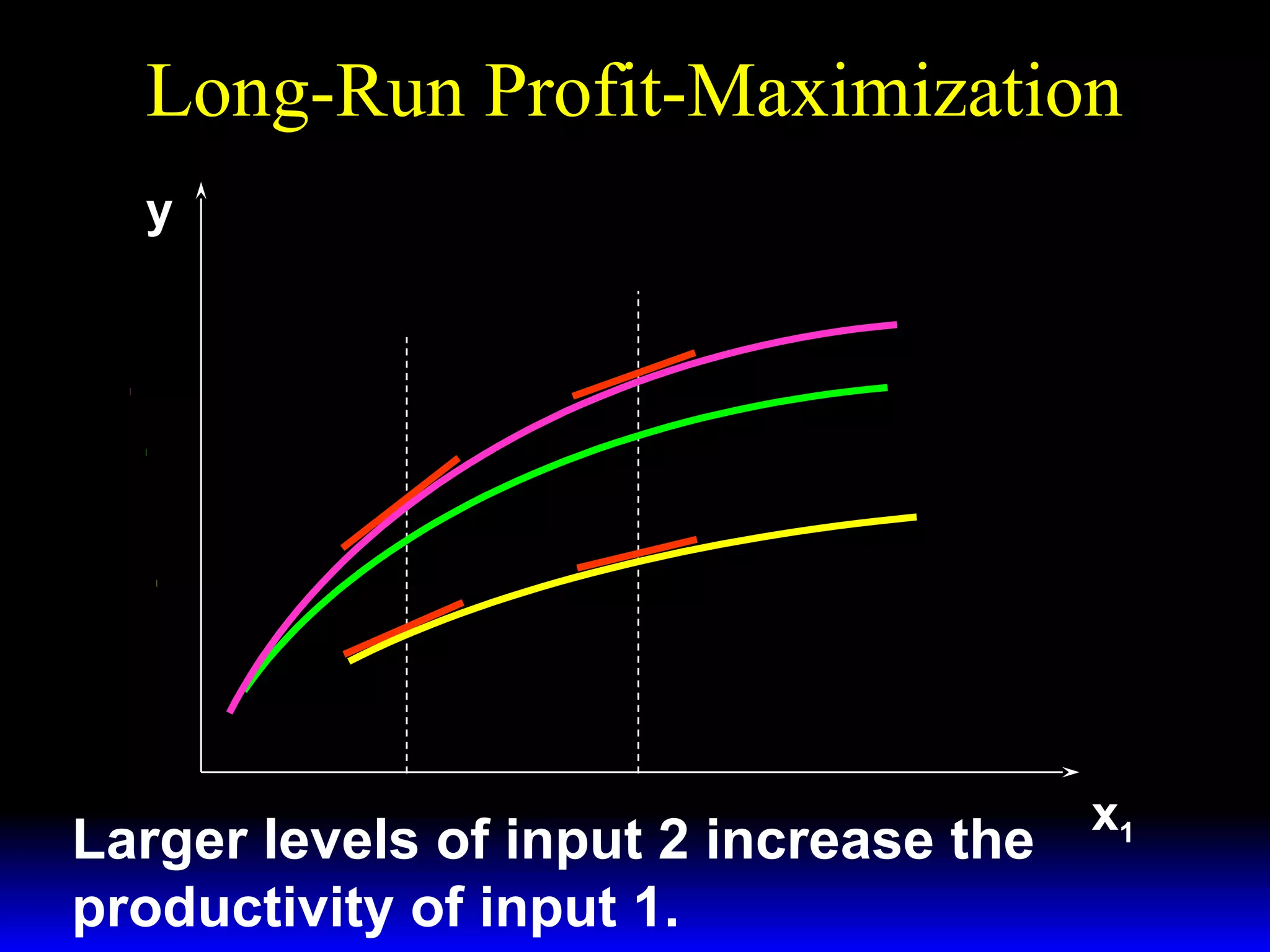
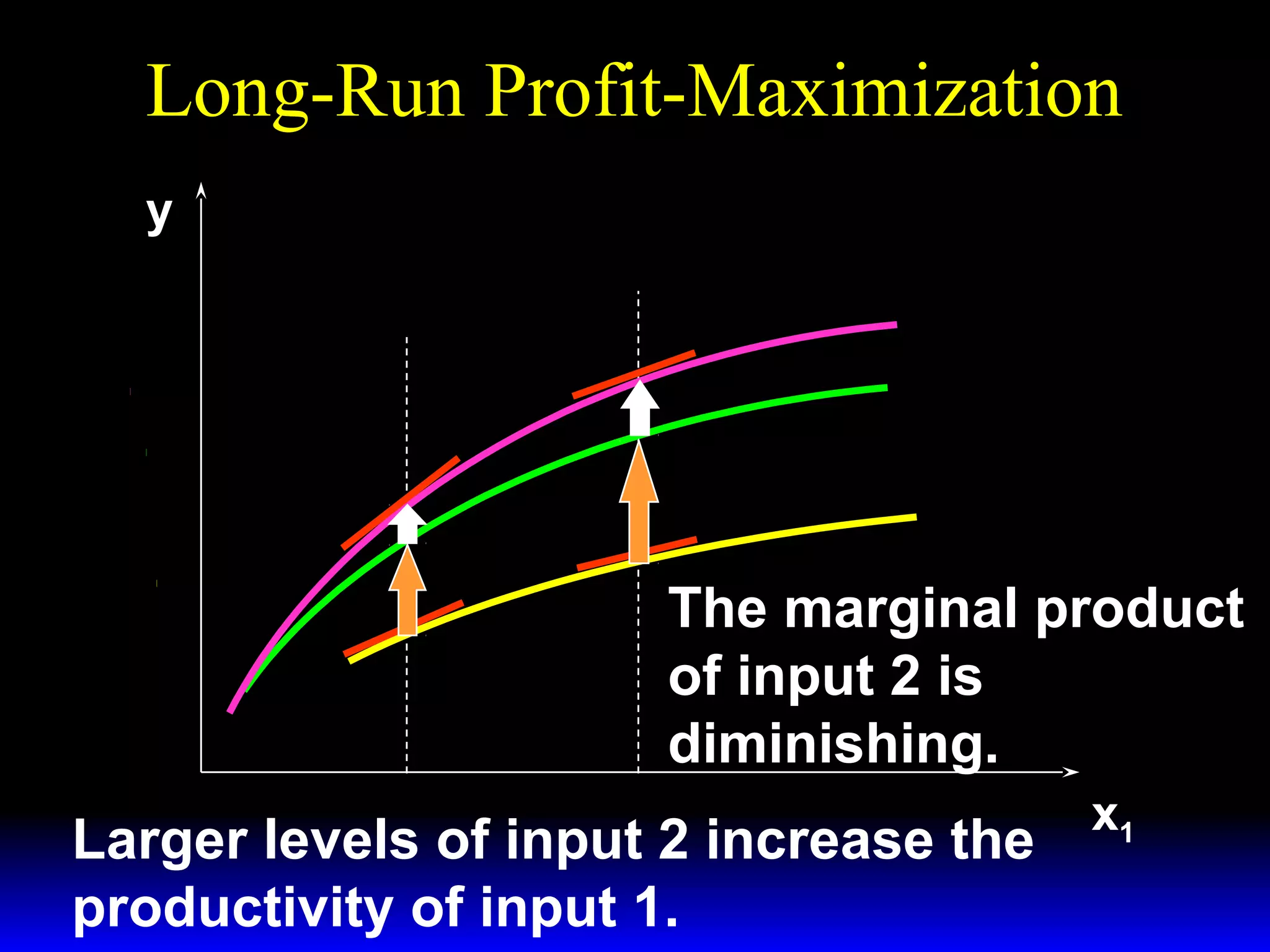
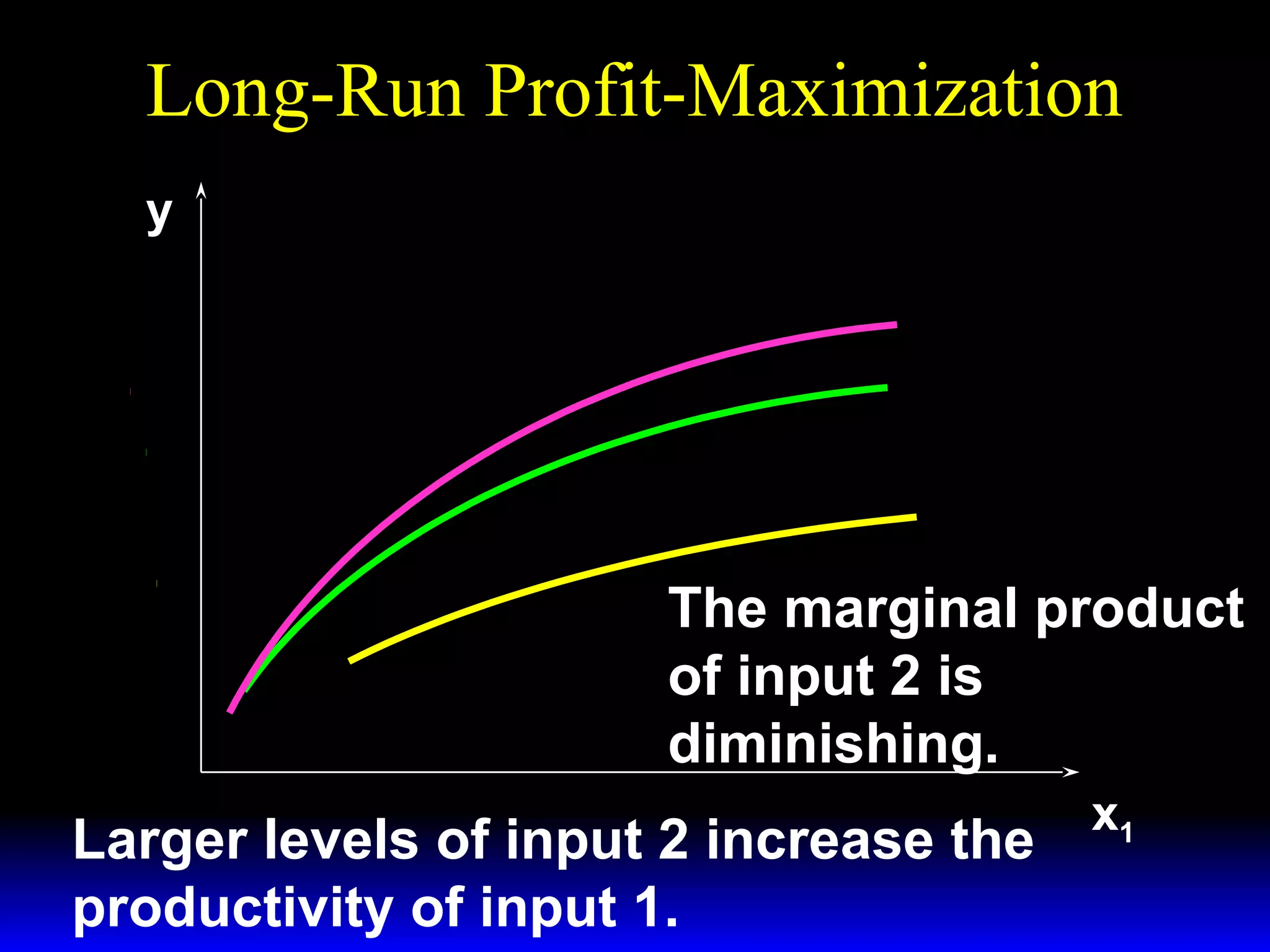
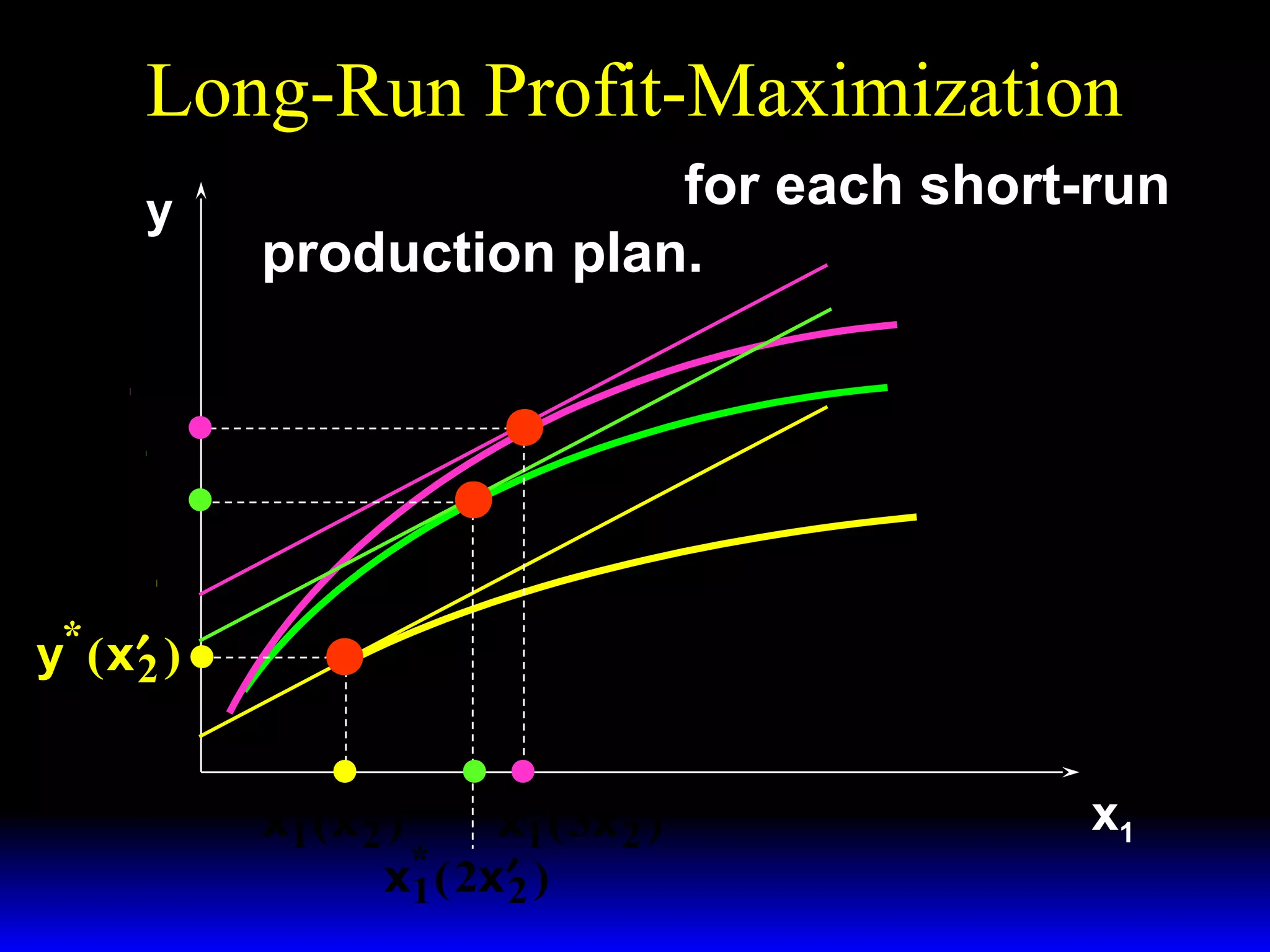
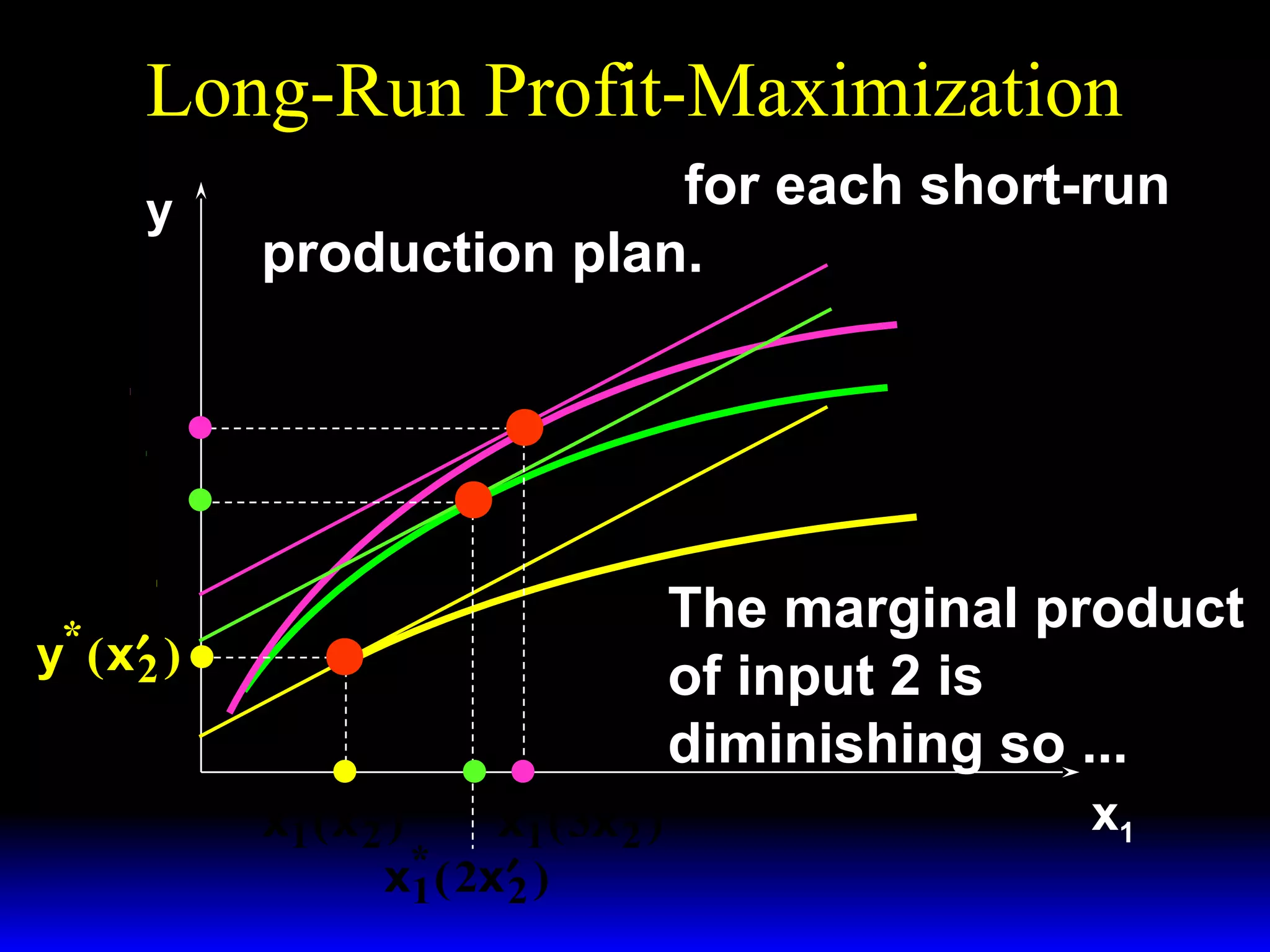
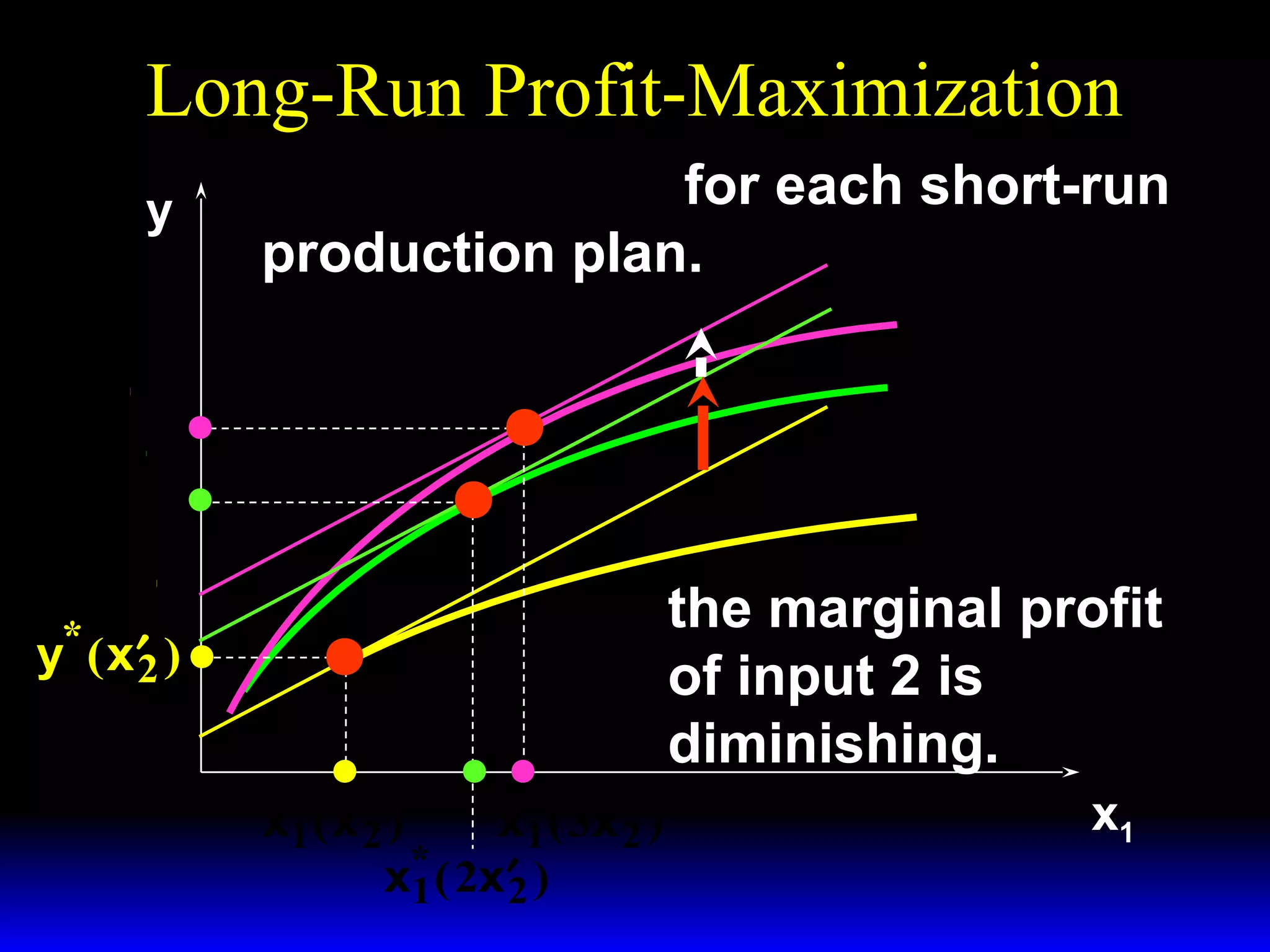
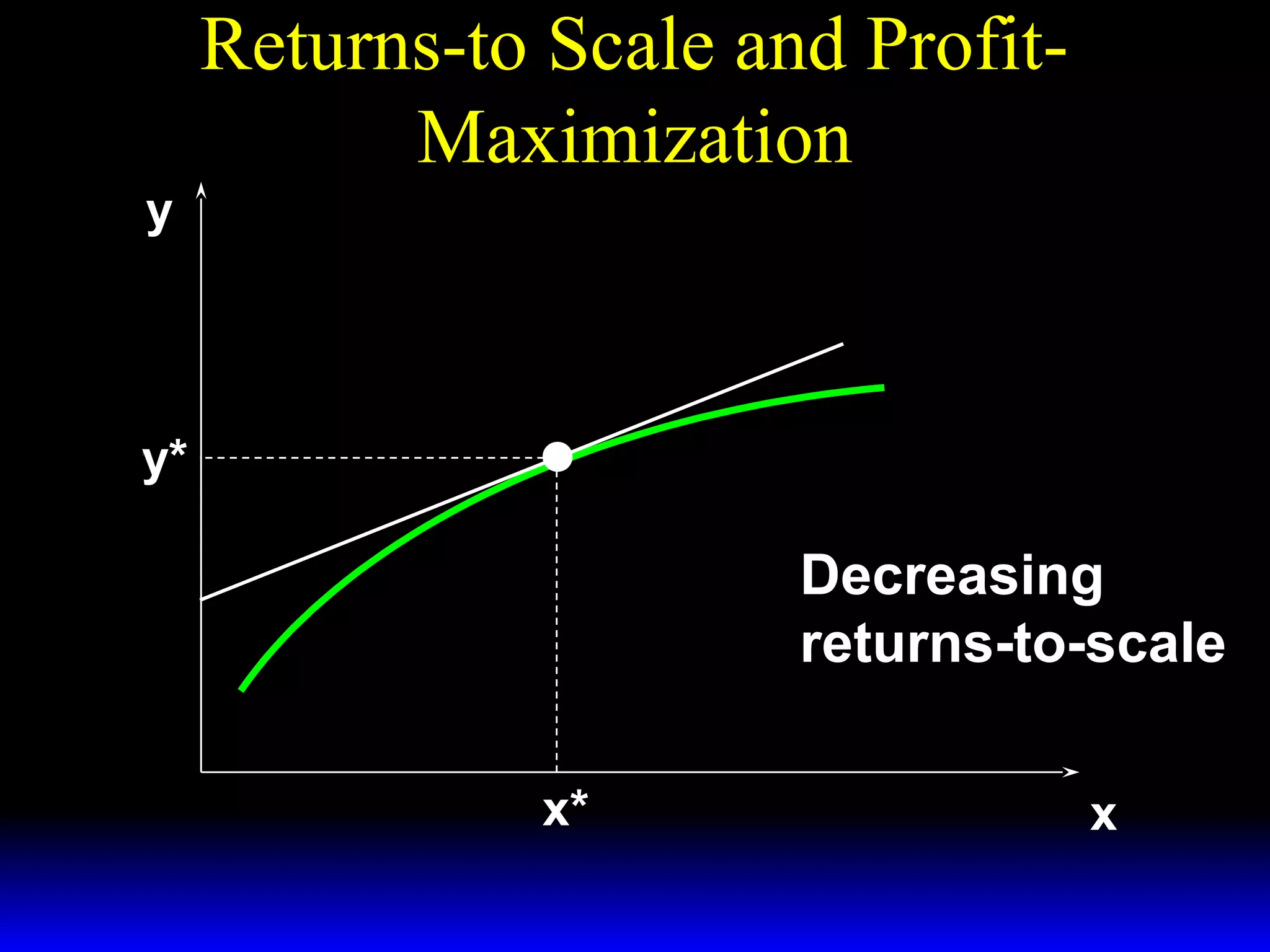
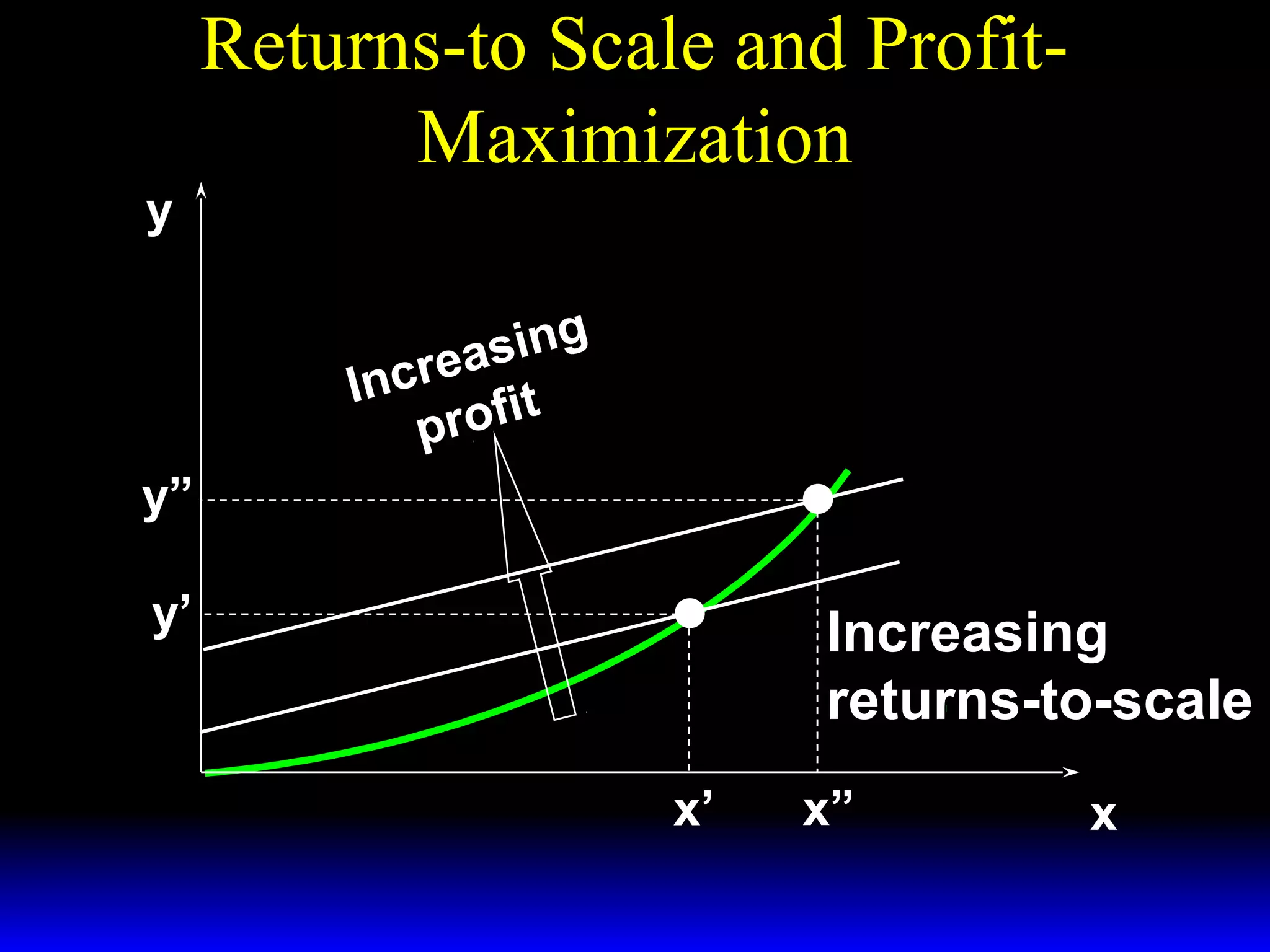
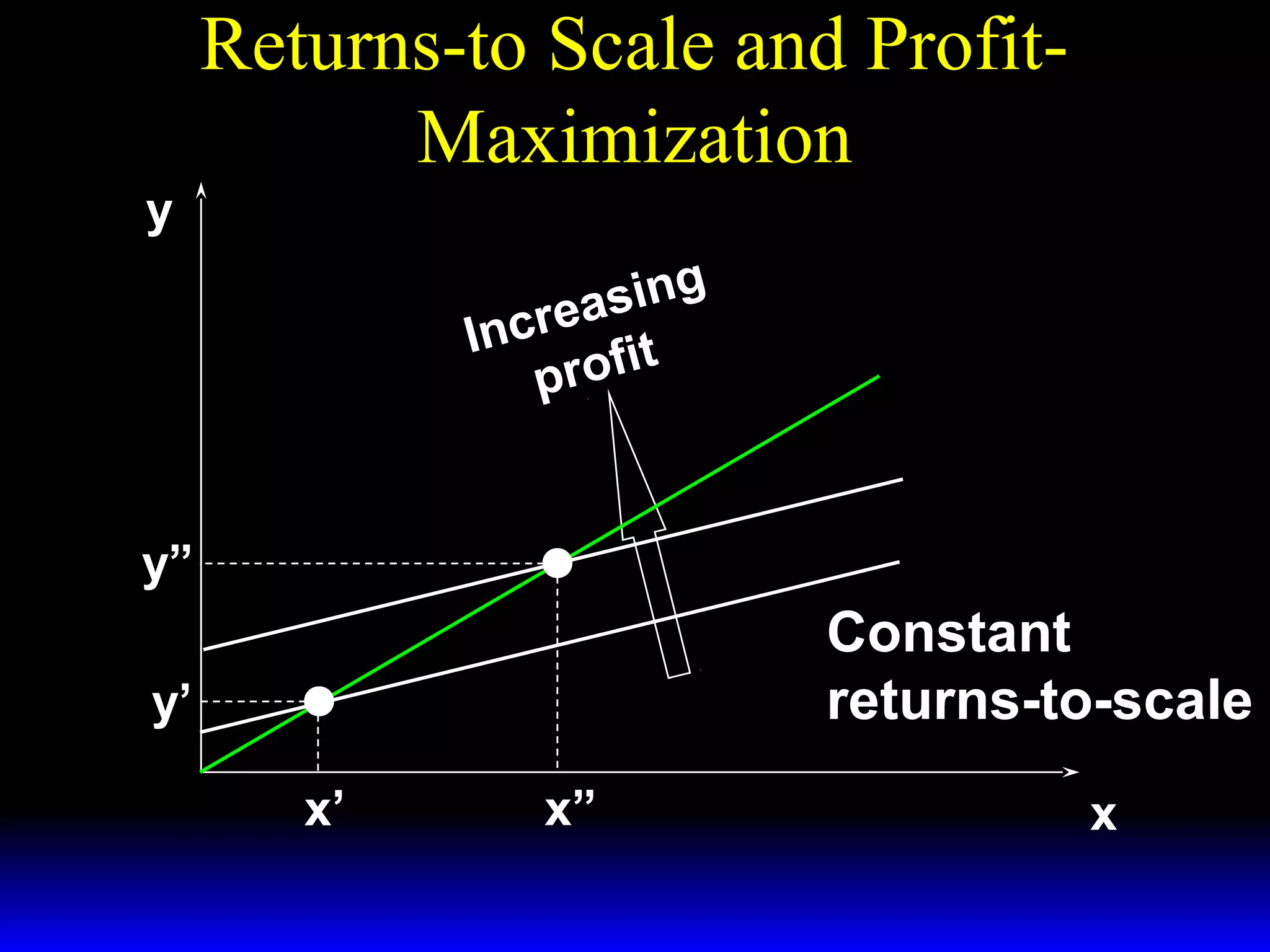
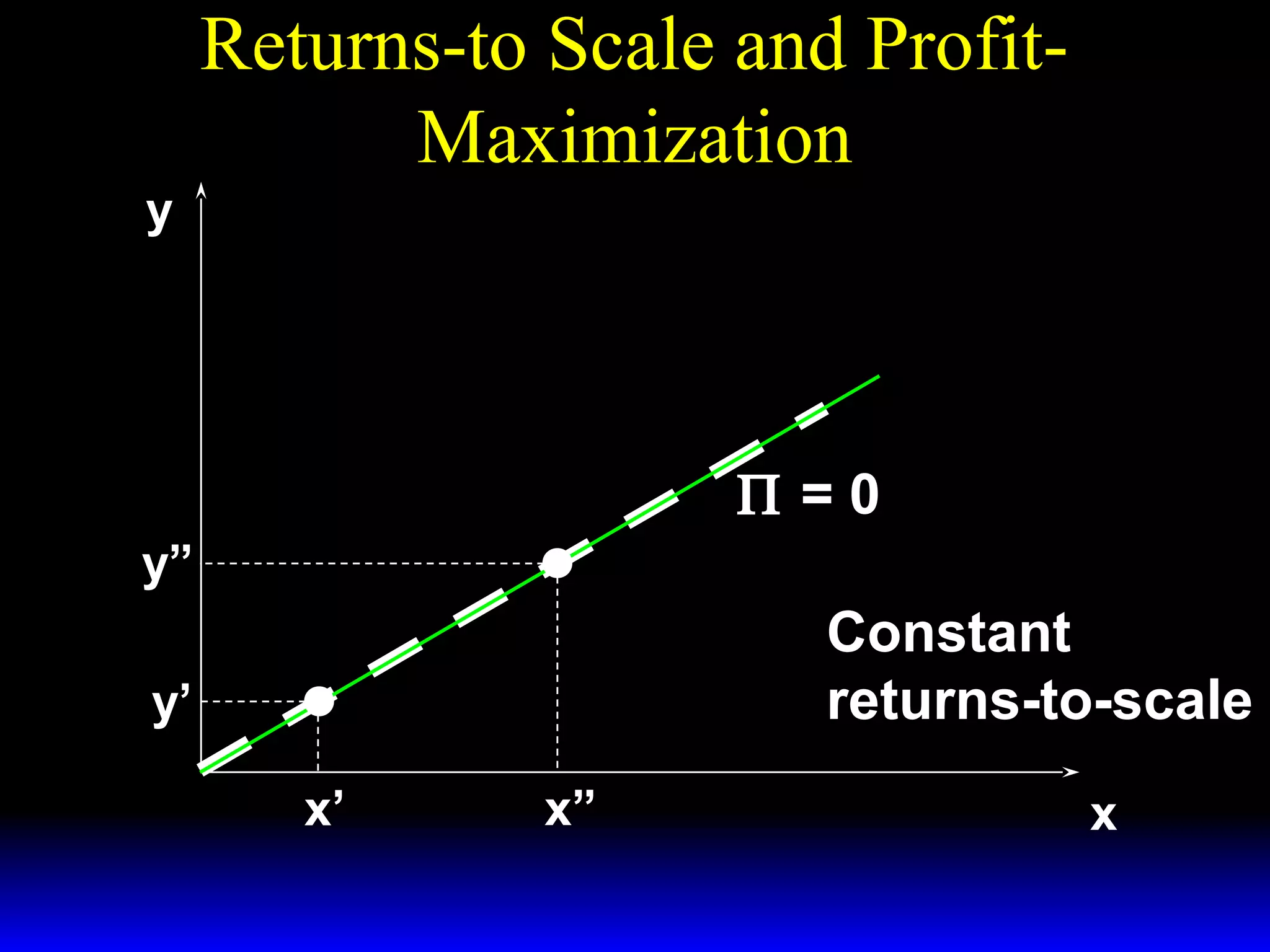
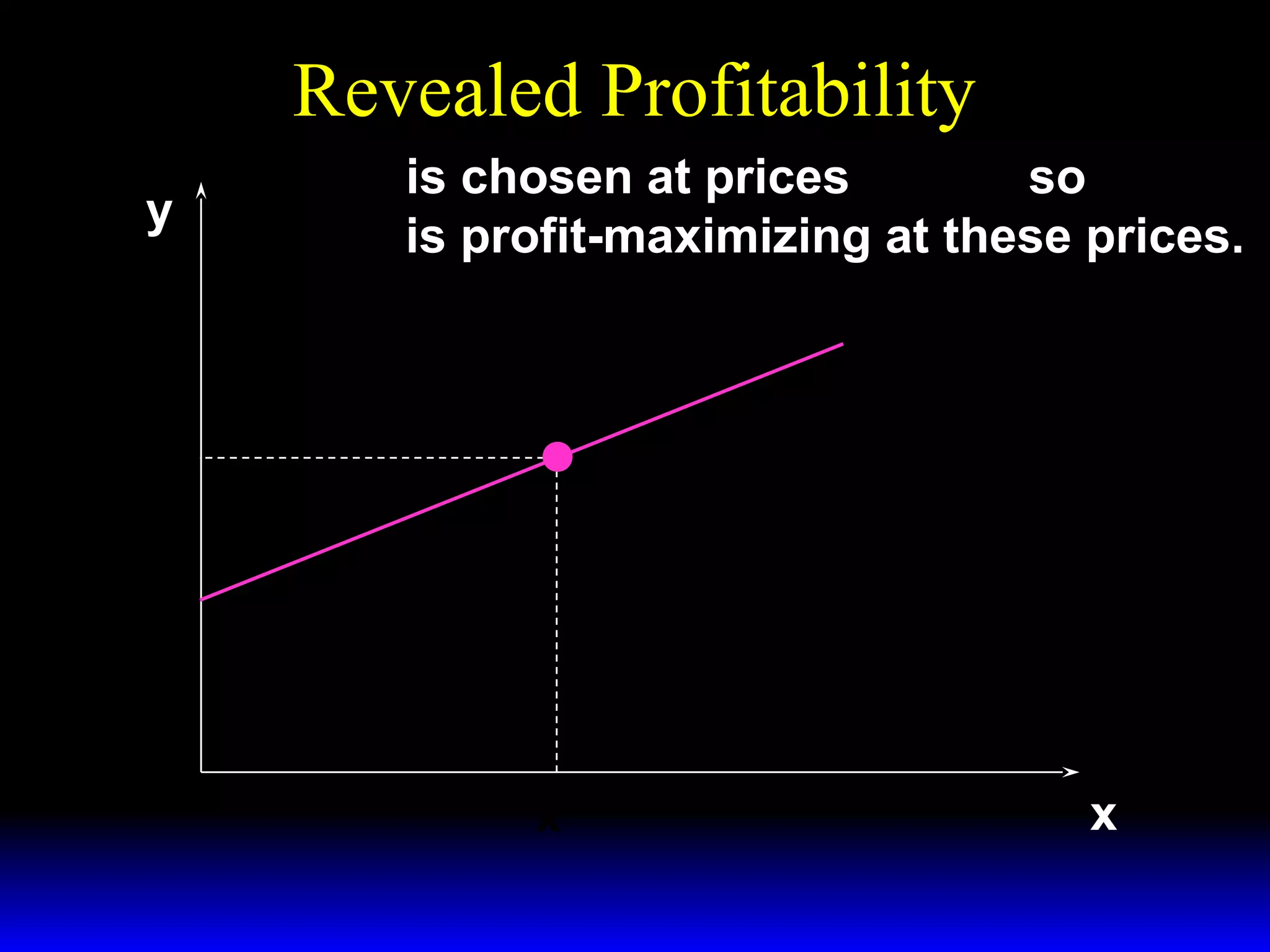
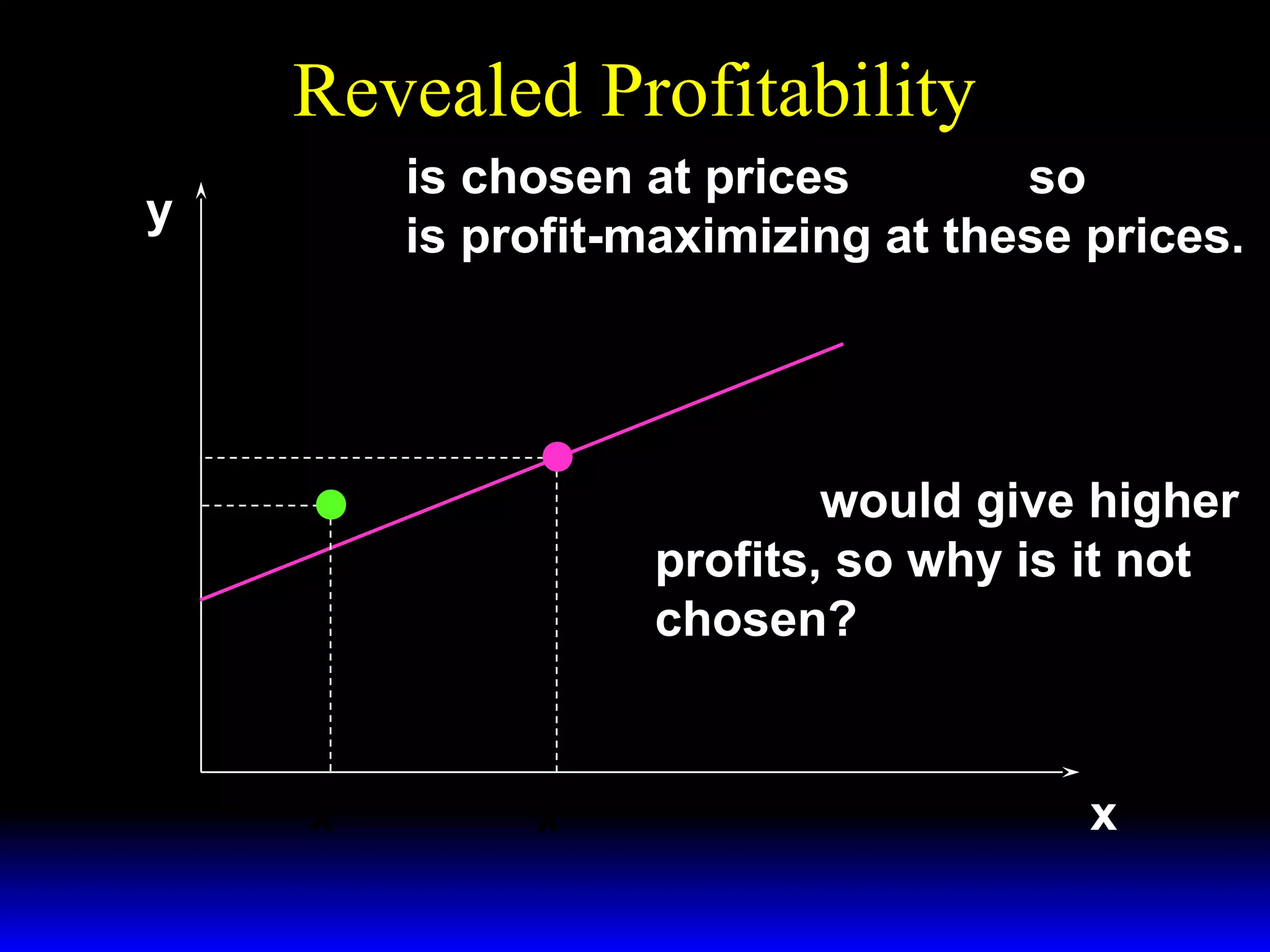
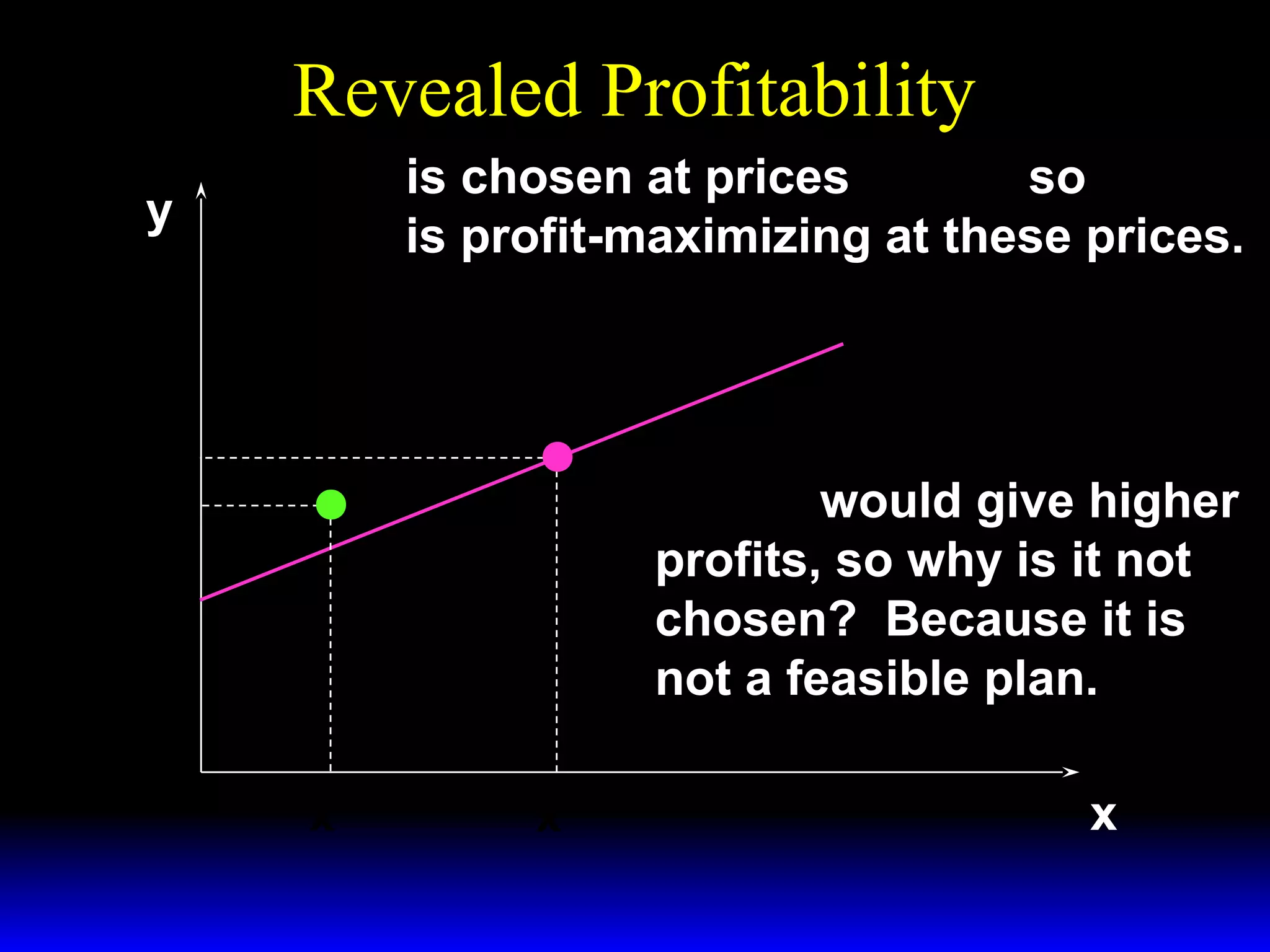
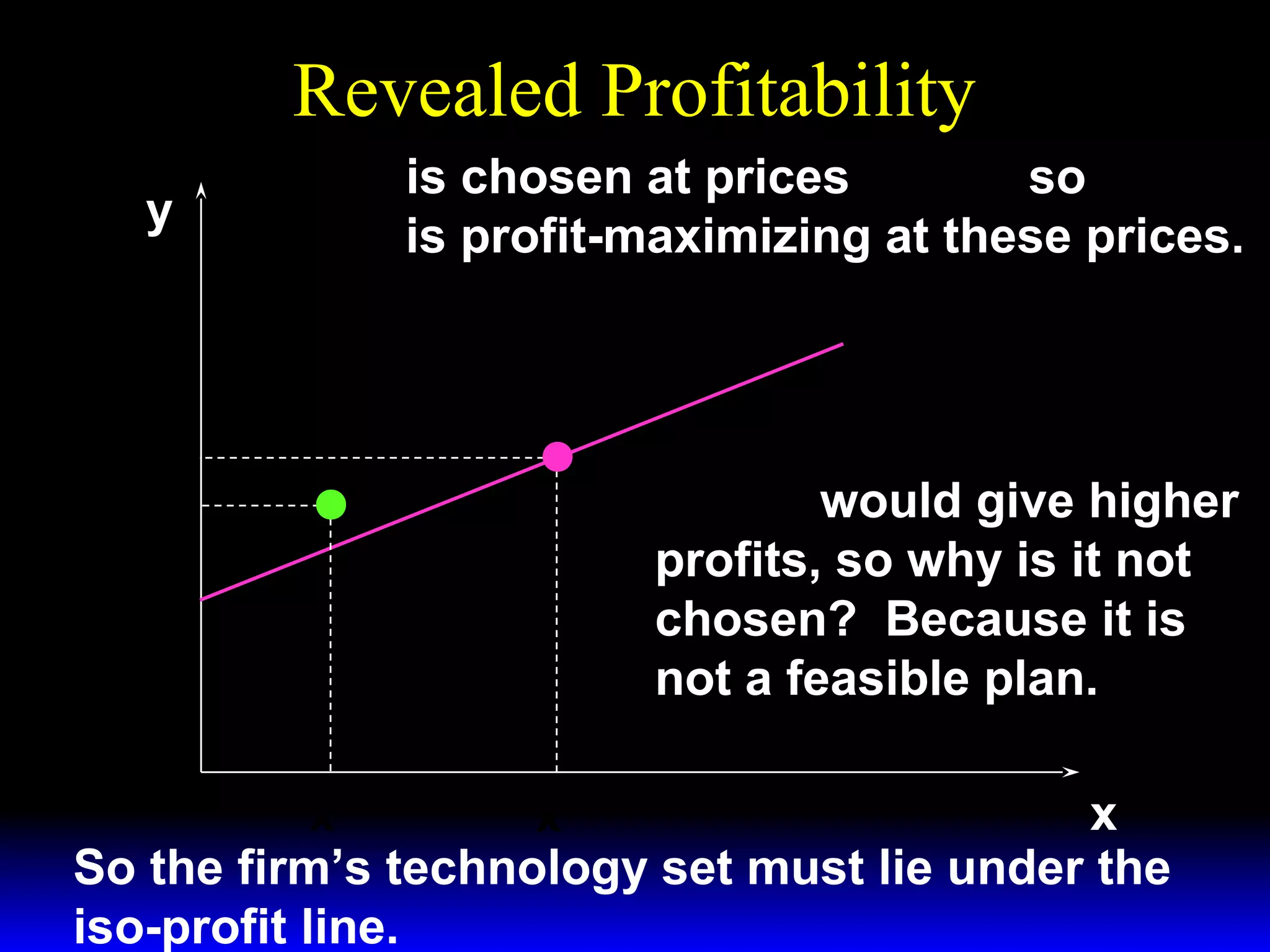
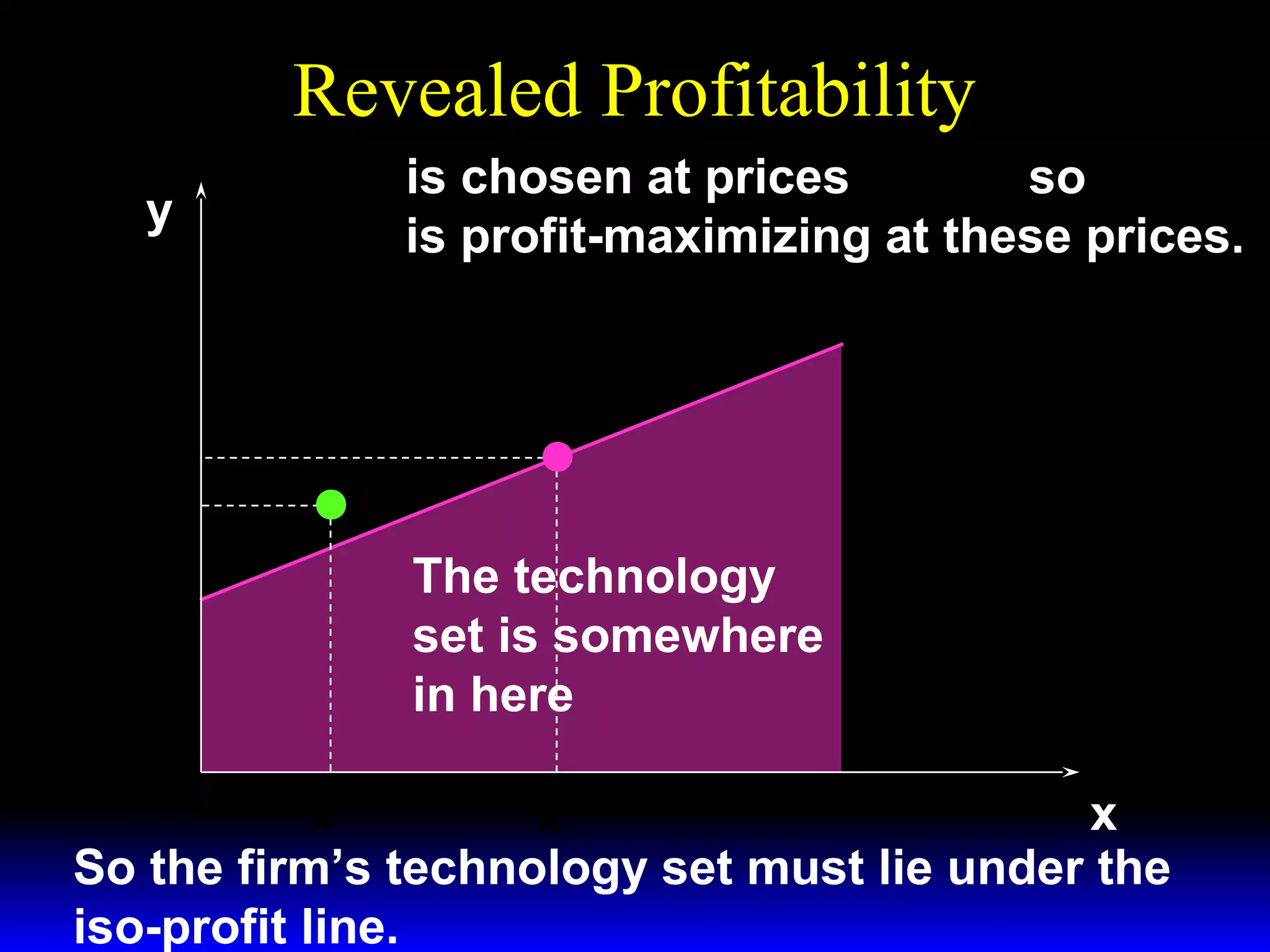
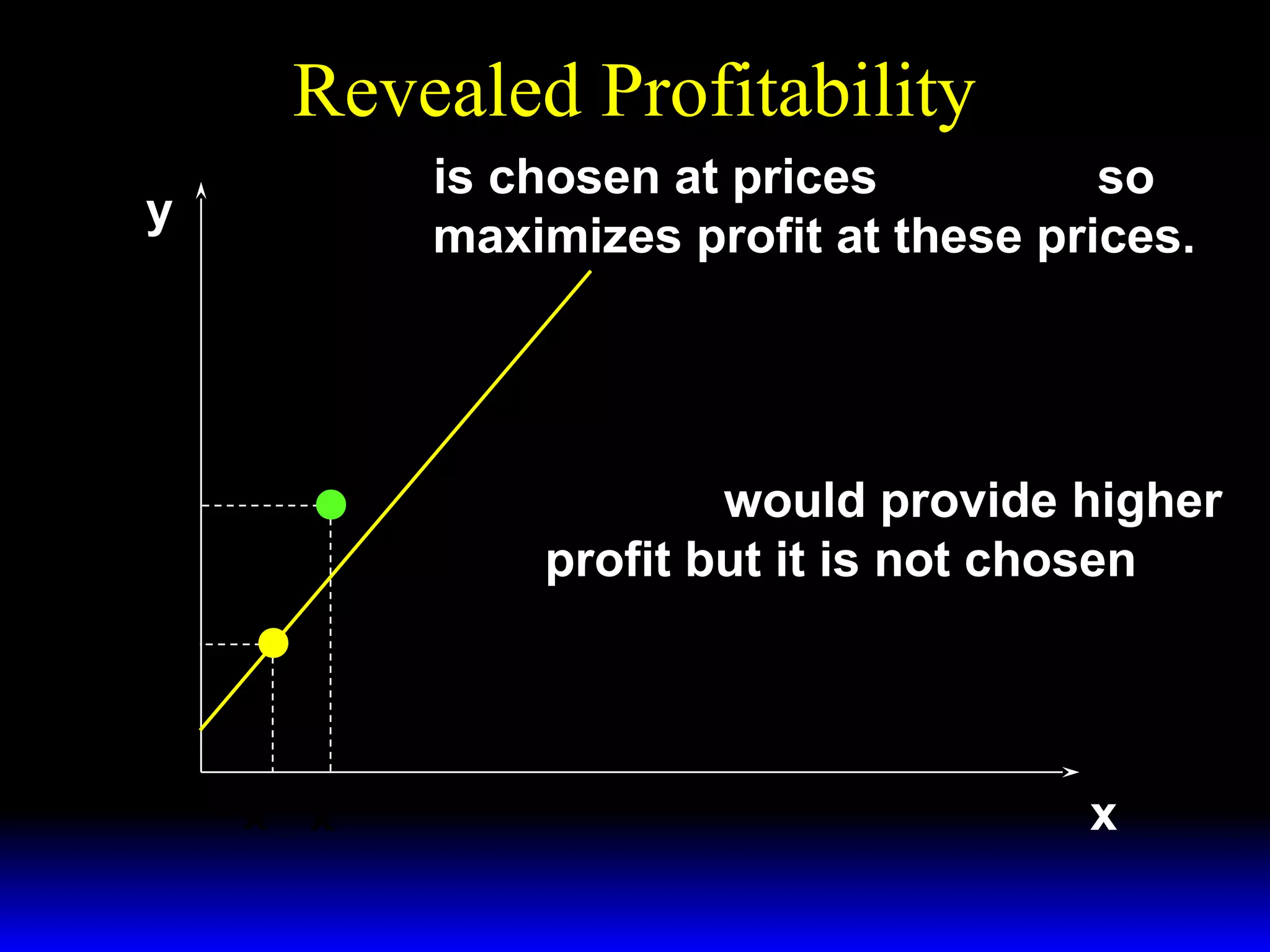
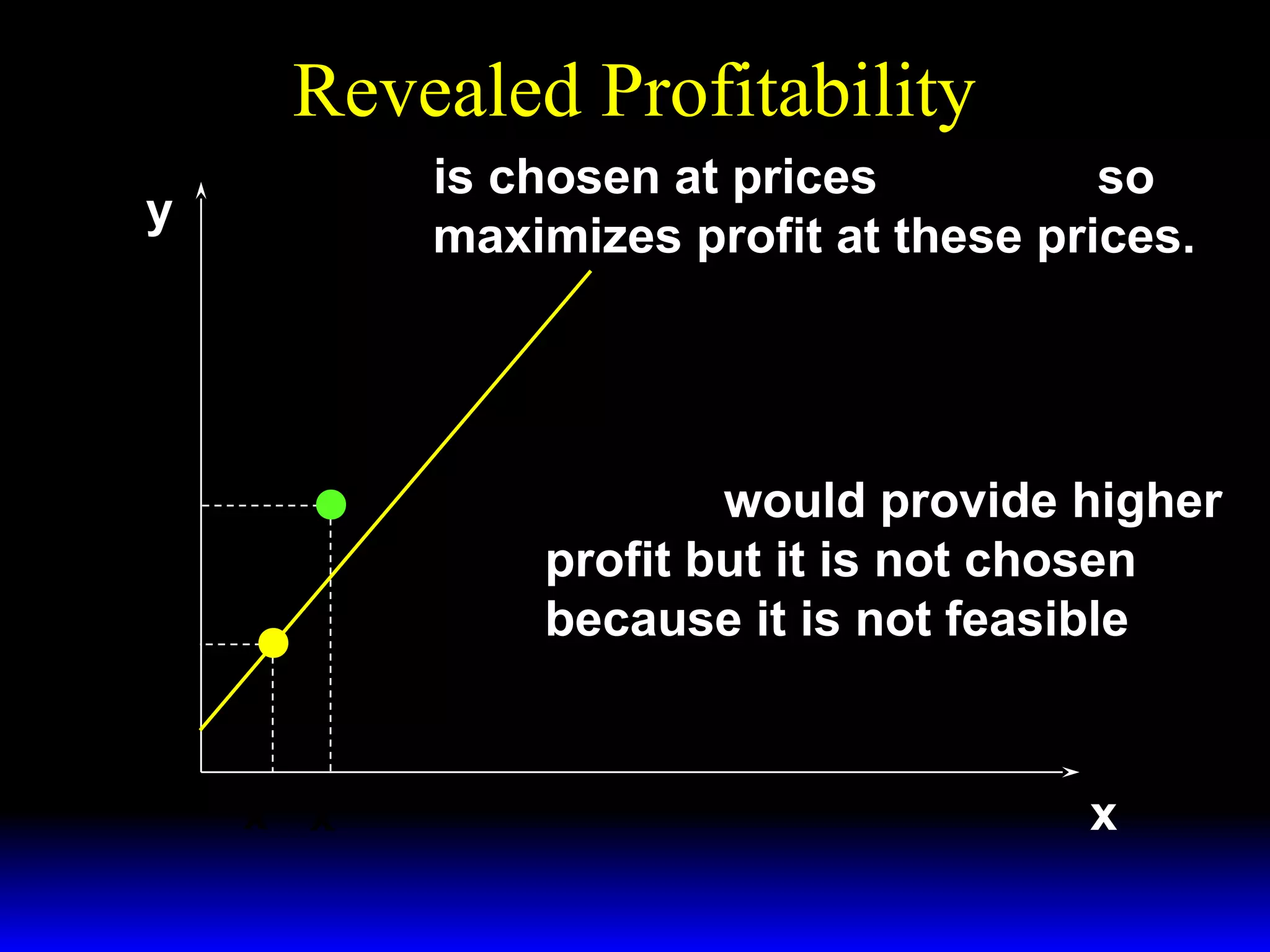
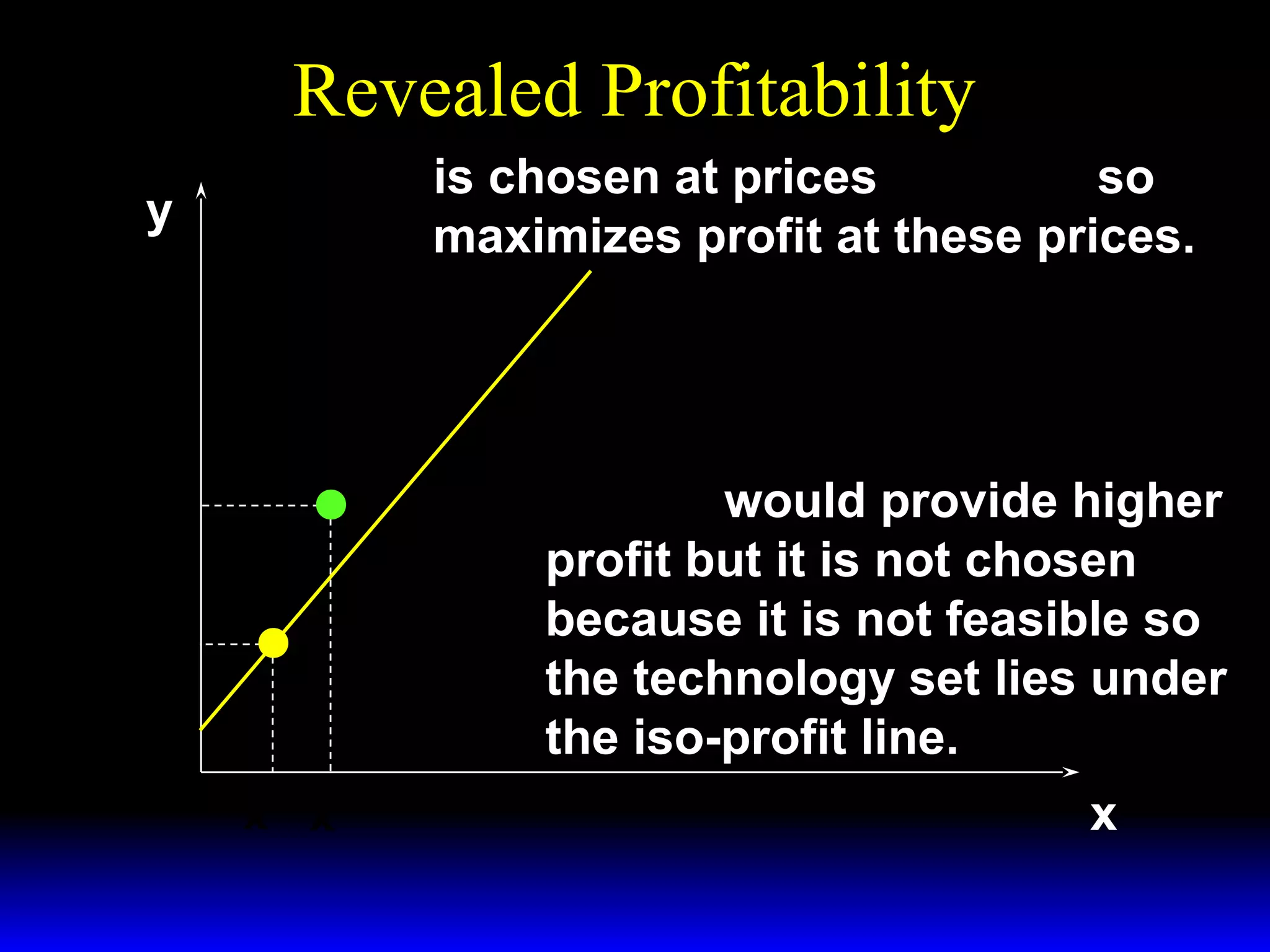
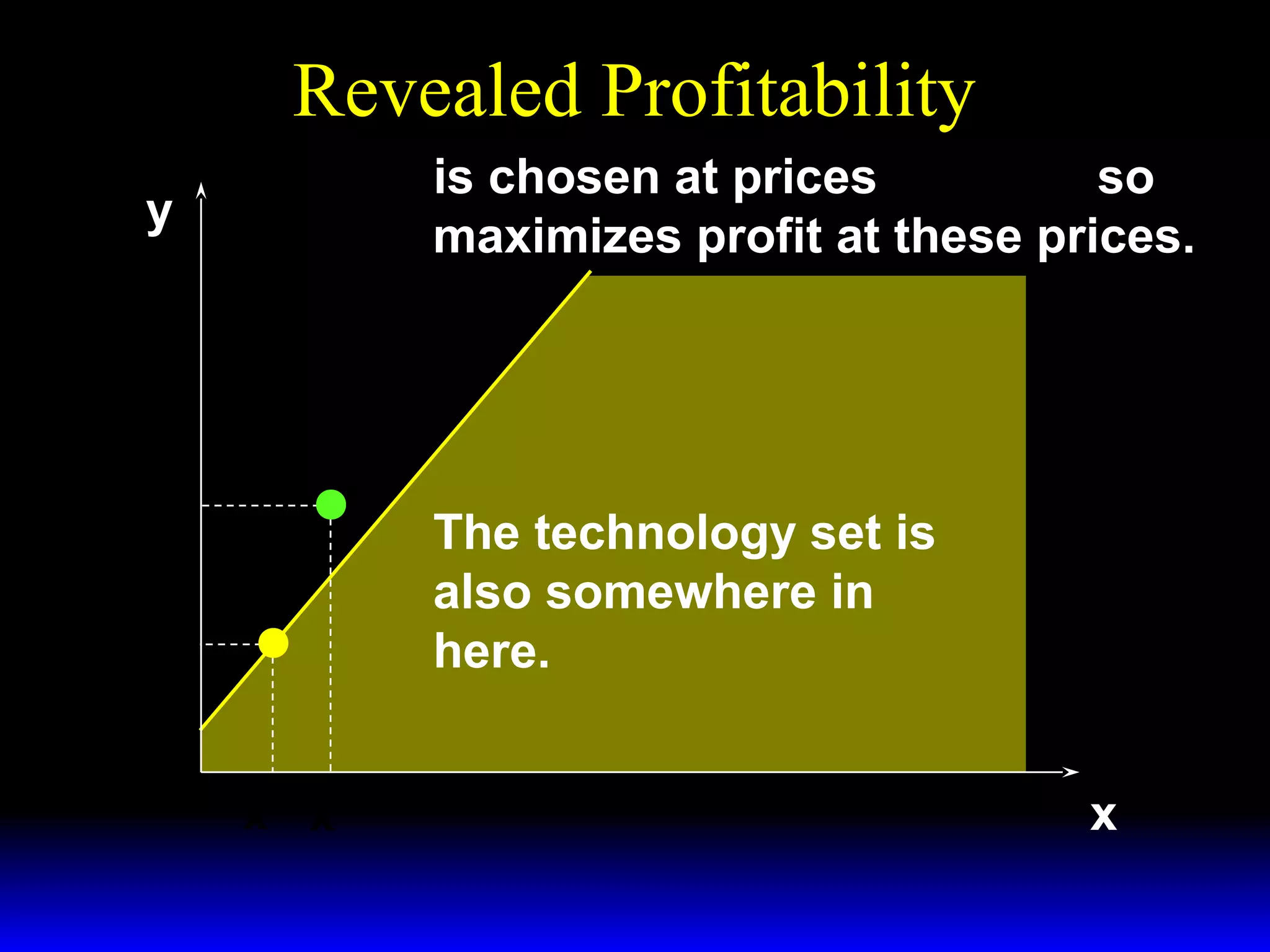
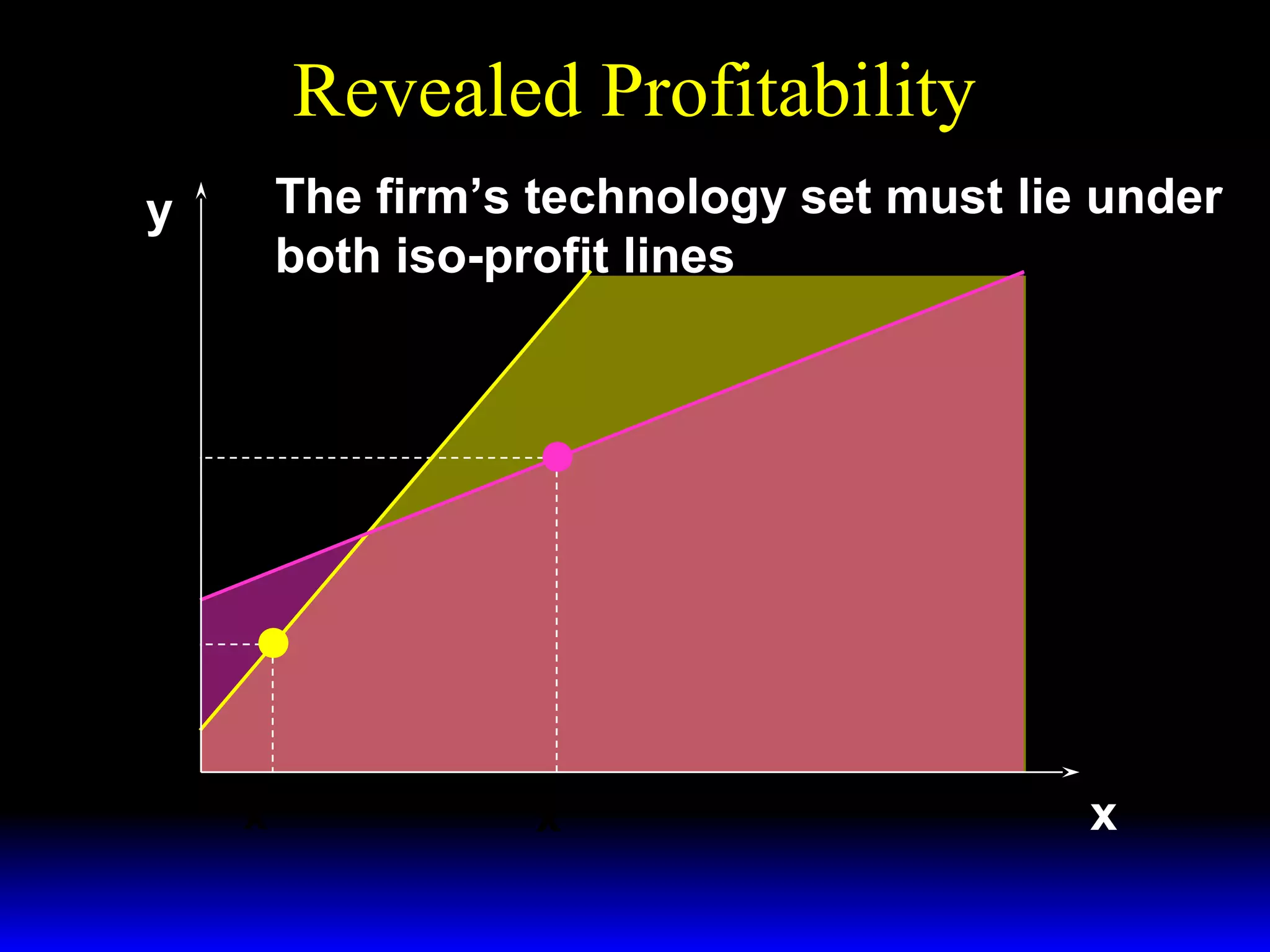
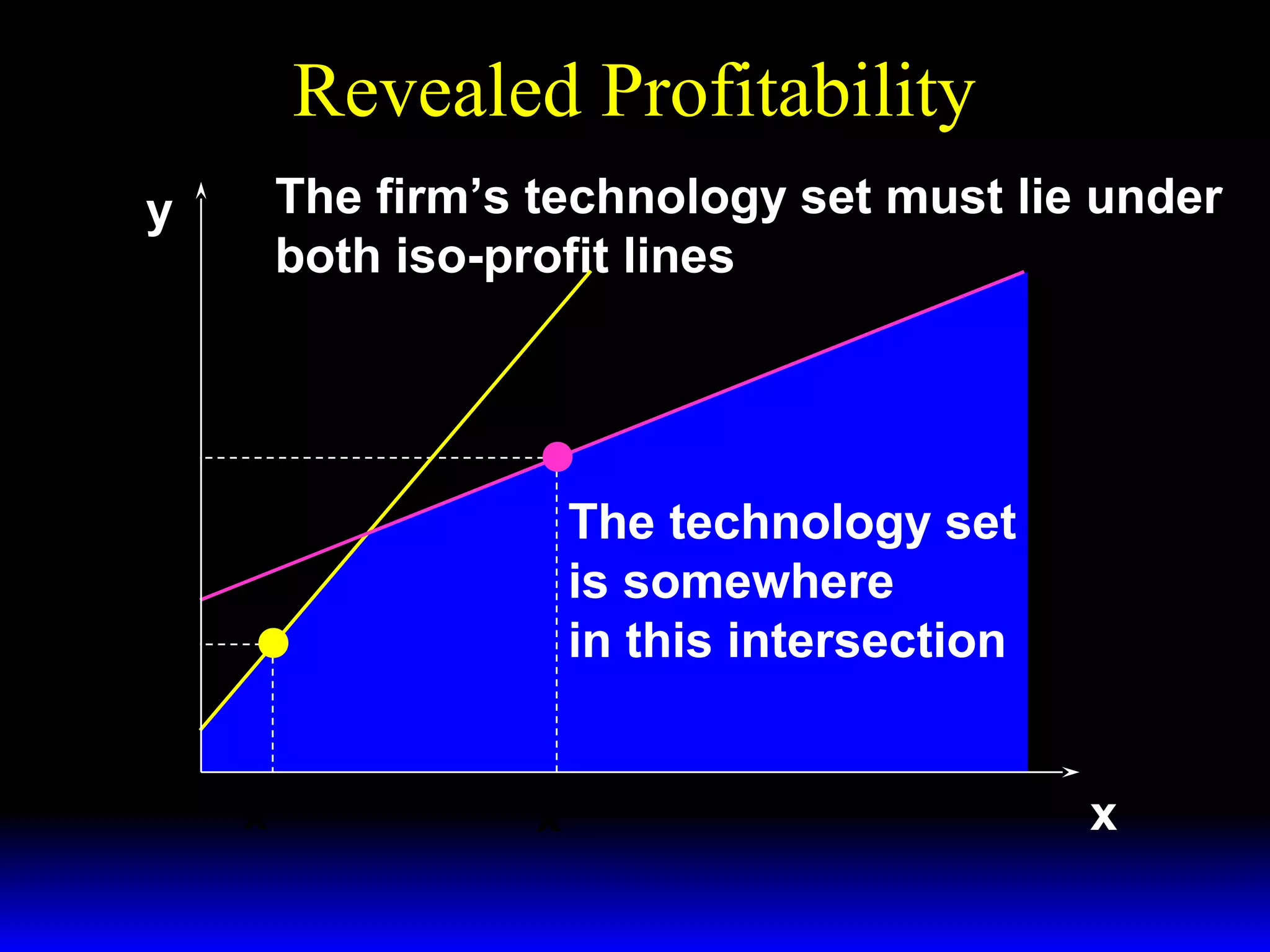
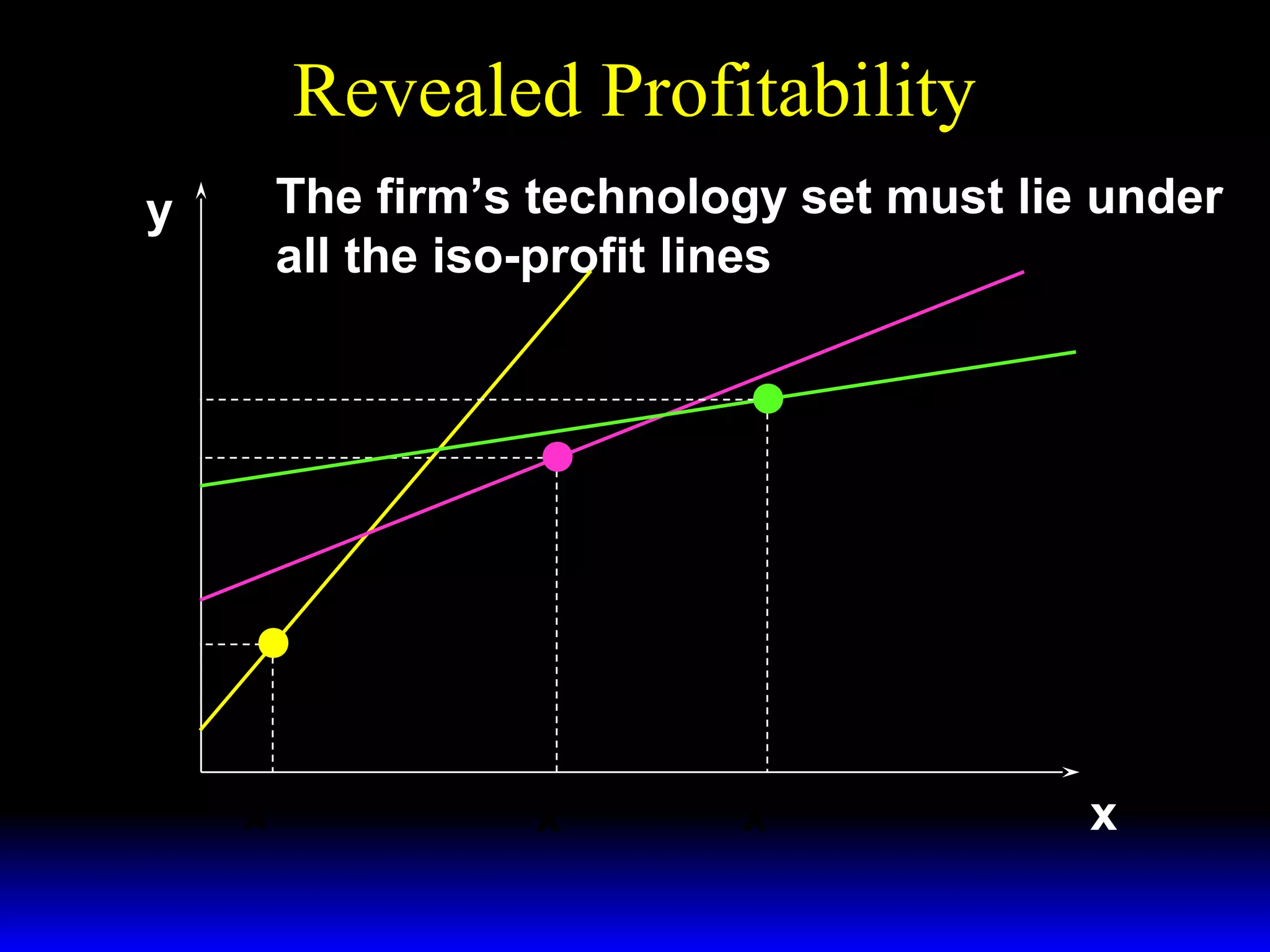
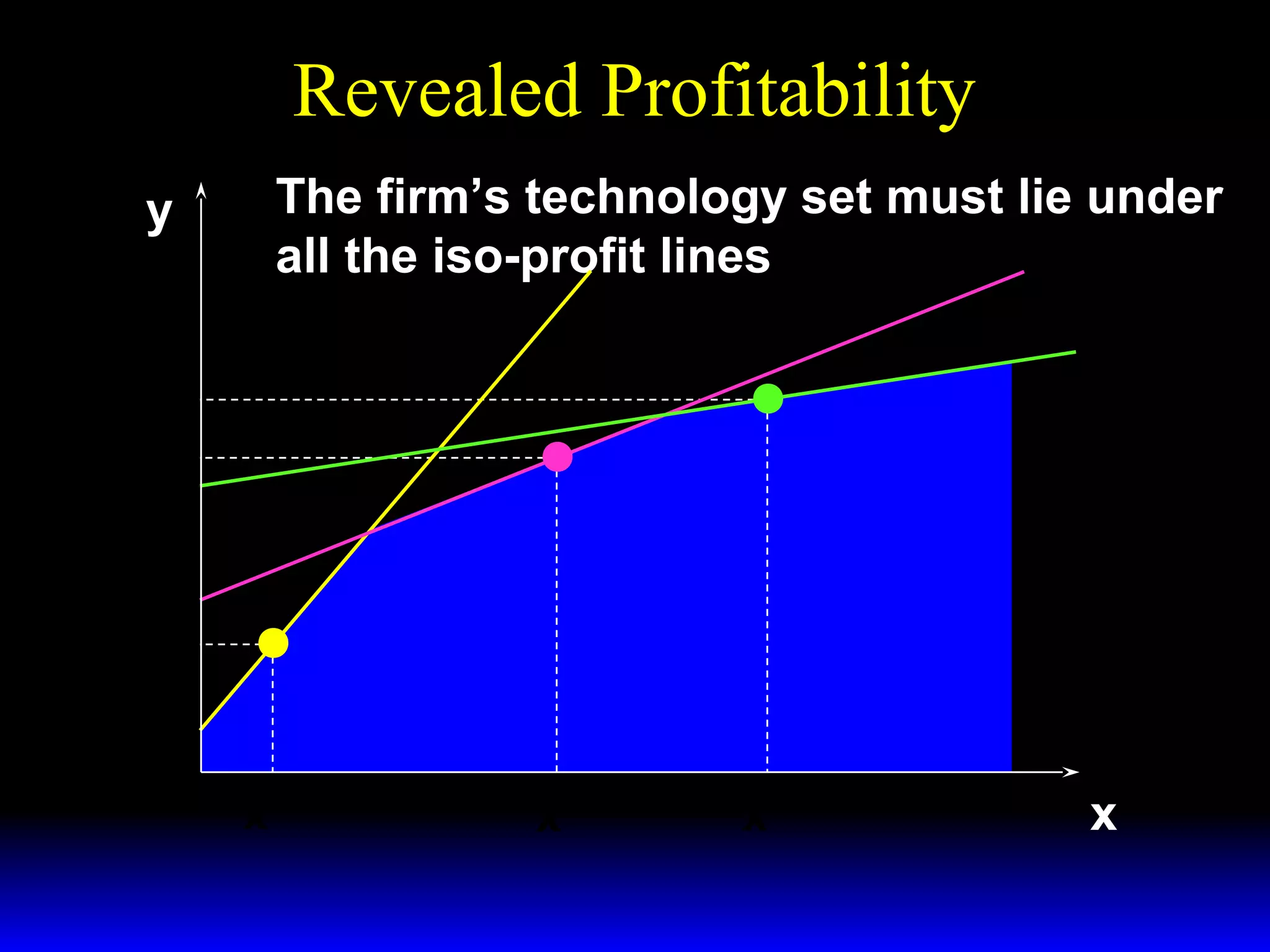
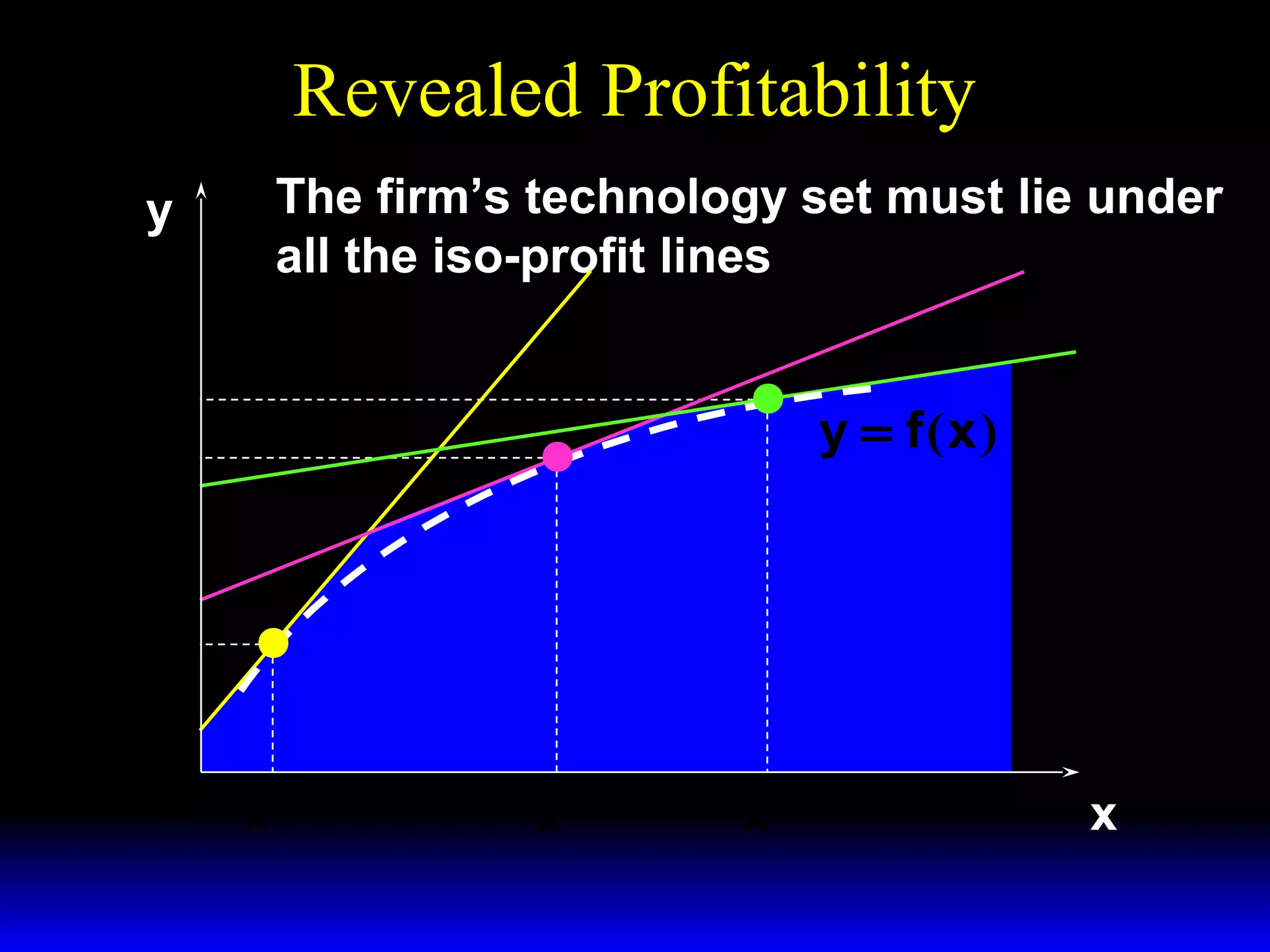
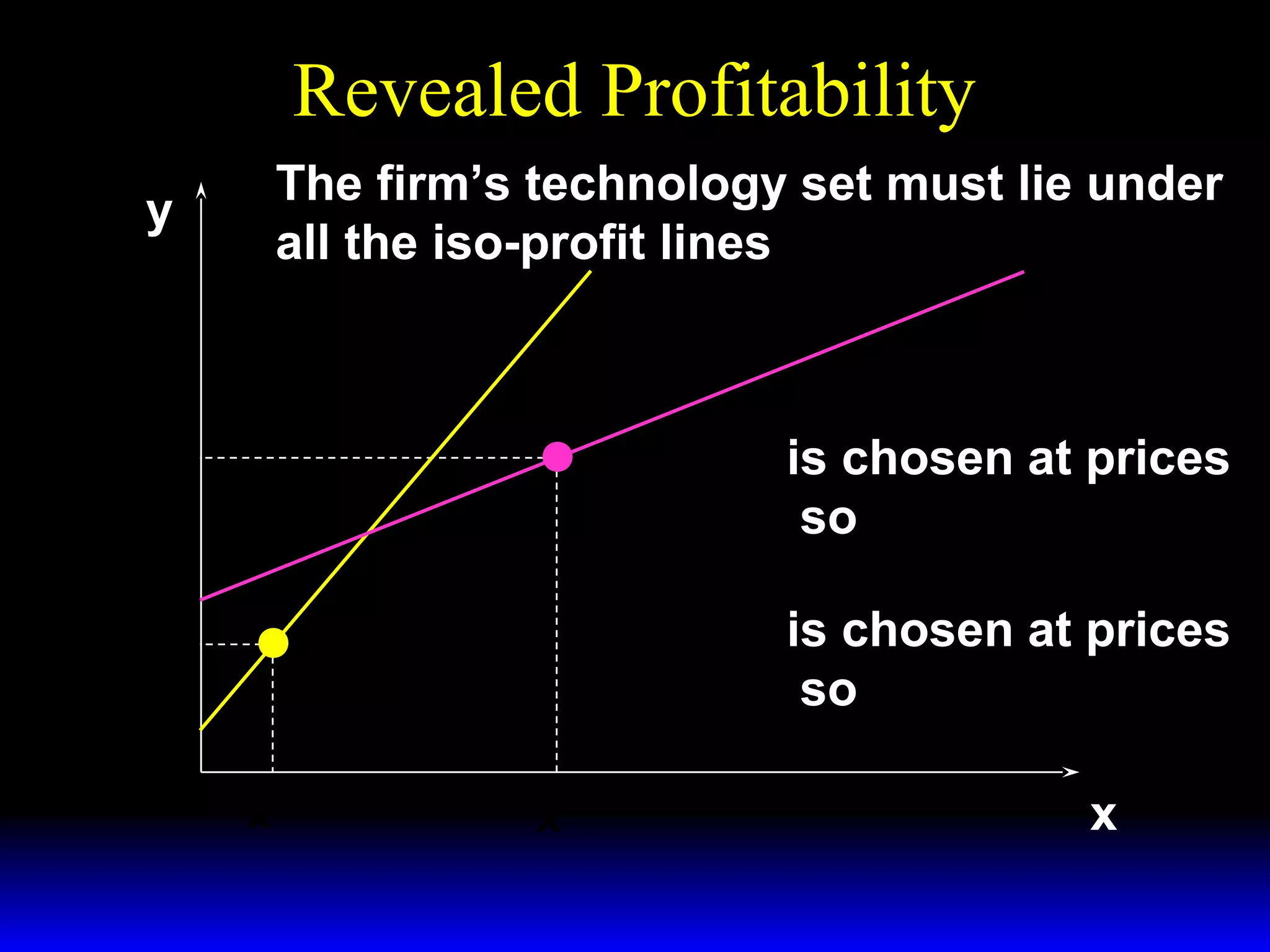
An increase in output price (p) or a decrease in variable input price (w1) causes the firm's short-run supply curve to shift outward and the demand curve for the variable input to shift outward. Conversely, an increase in w1 causes the supply curve to shift inward and the demand curve for the variable input to shift inward. This is shown using iso-profit lines and a Cobb-Douglas production function example, where the profit-maximizing levels of output (y*) and the variable input (x1*) both increase with higher p or lower w1, and decrease with higher w1.