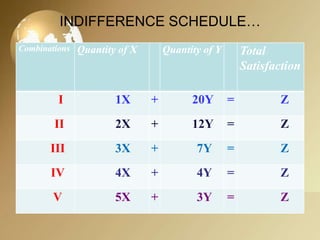
The document discusses the theories of consumer behavior, specifically focusing on cardinal and ordinal utility analysis. It explains the concepts of total utility, marginal utility, and the law of diminishing marginal utility while introducing indifference curve theory. Key aspects include how consumers maximize satisfaction within constraints, the properties of indifference curves, and their applications in economic analysis.