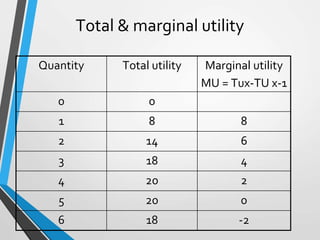
Utility refers to the satisfaction or want-fulfilling capacity of a product. There are two types of utility analysis: cardinal and ordinal. Utility is subjective, relative, and independent of morality. The total utility of consuming more of a product increases at a decreasing rate, following the law of diminishing marginal utility. Indifference curves show combinations of goods that provide equal satisfaction to a consumer. A consumer reaches equilibrium where their highest indifference curve is tangent to their price line or budget constraint. Indifference curve analysis is superior to traditional utility analysis as it is more realistic and free of some restrictive assumptions.