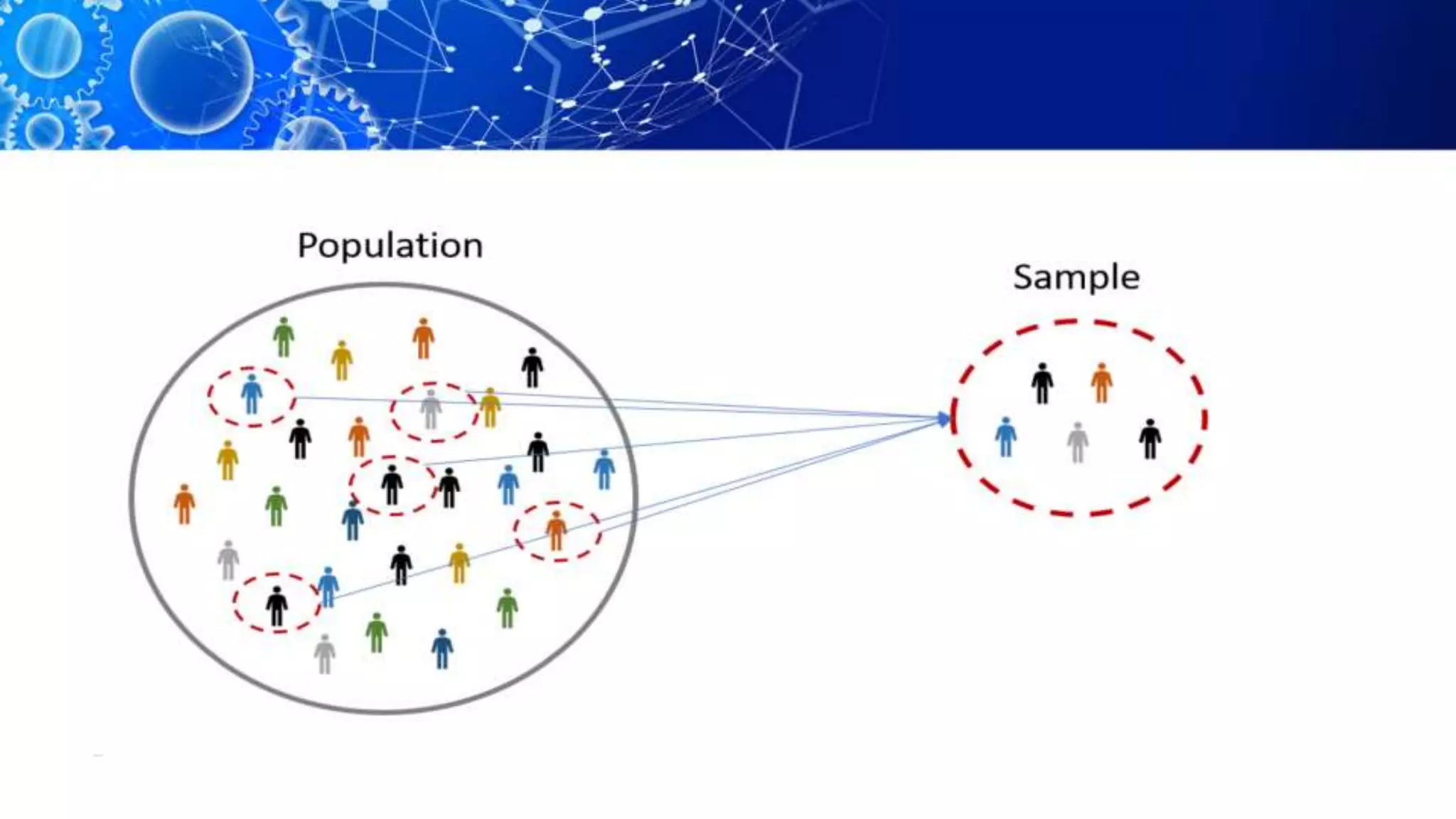
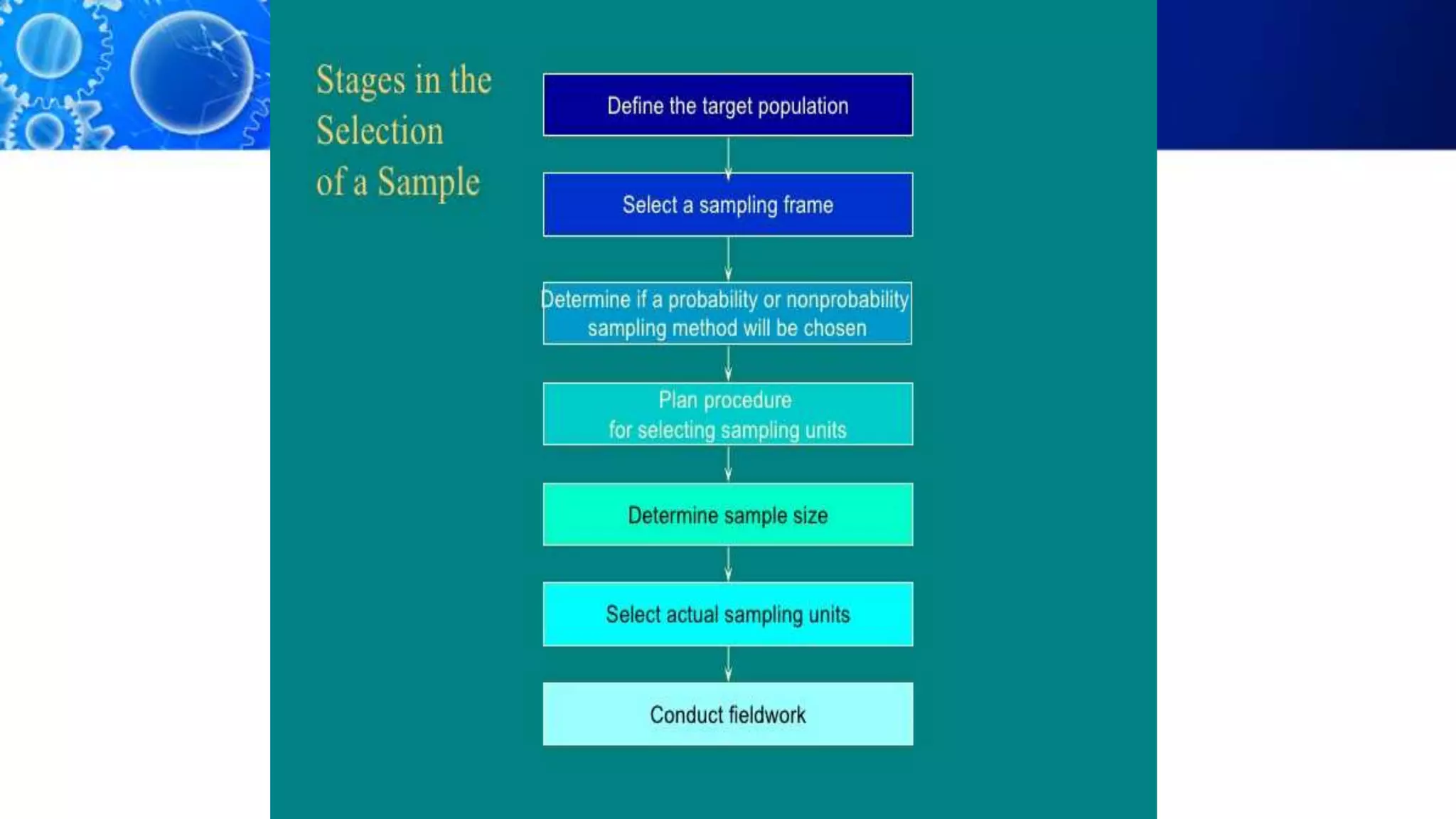
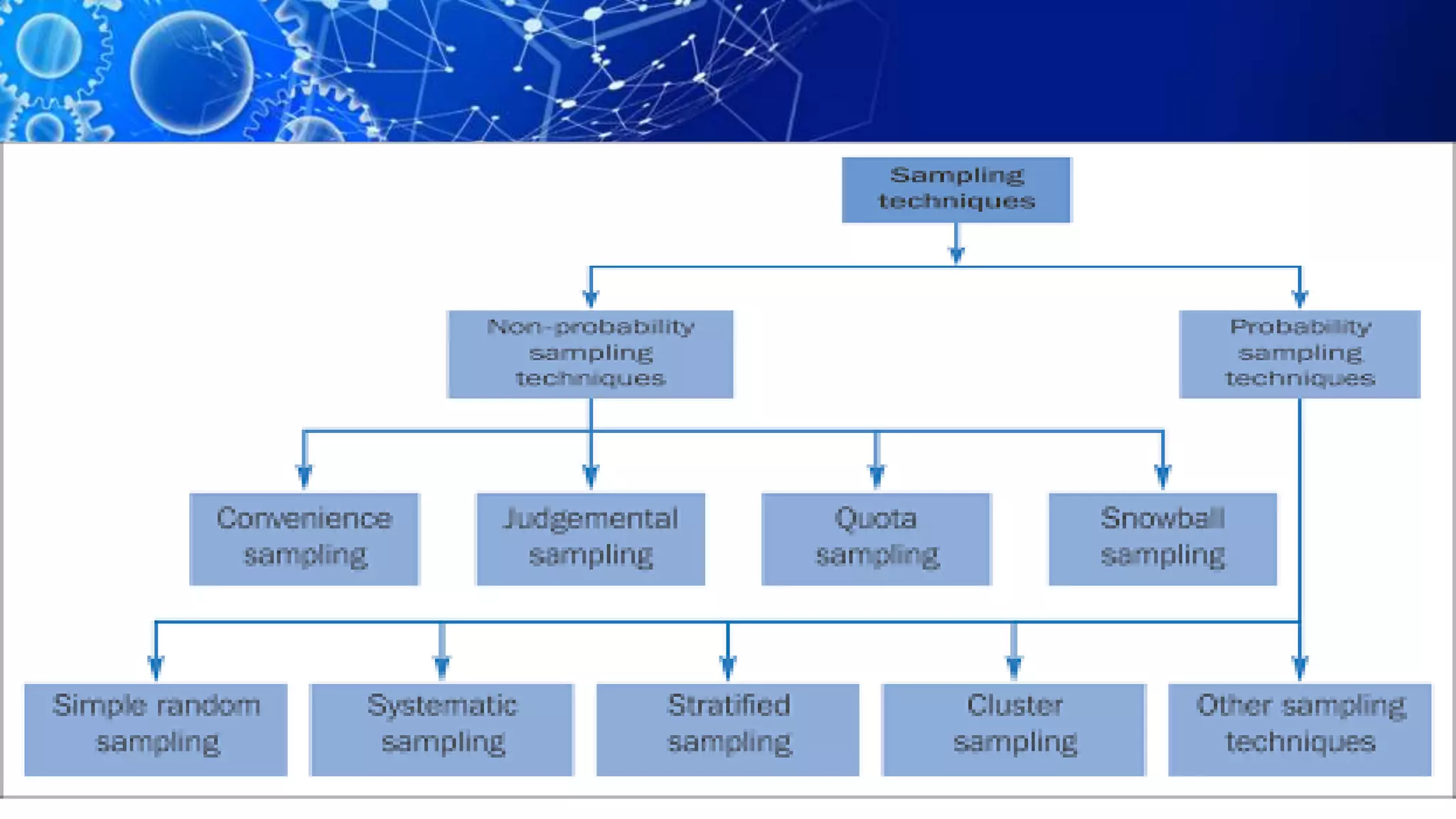
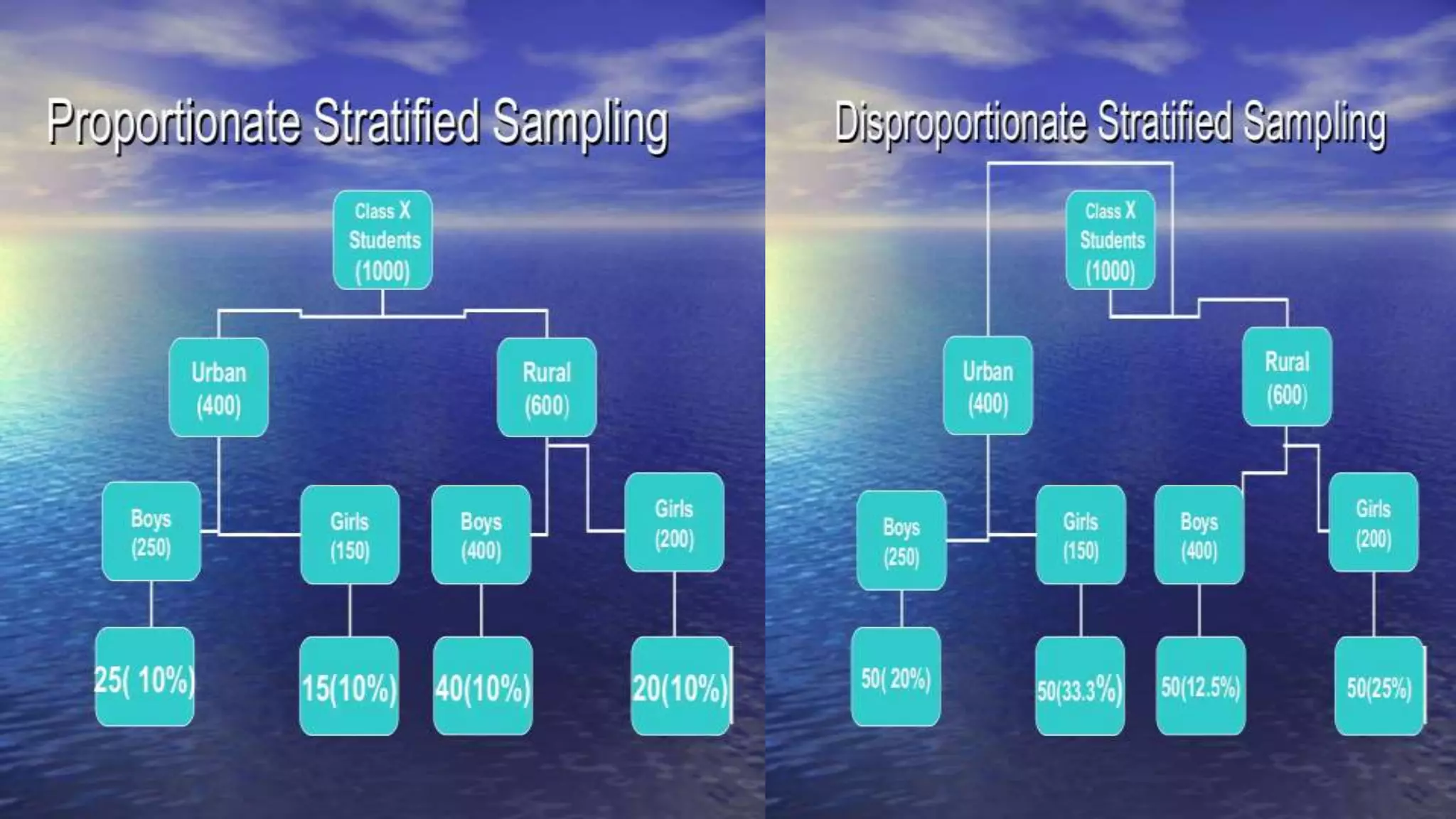
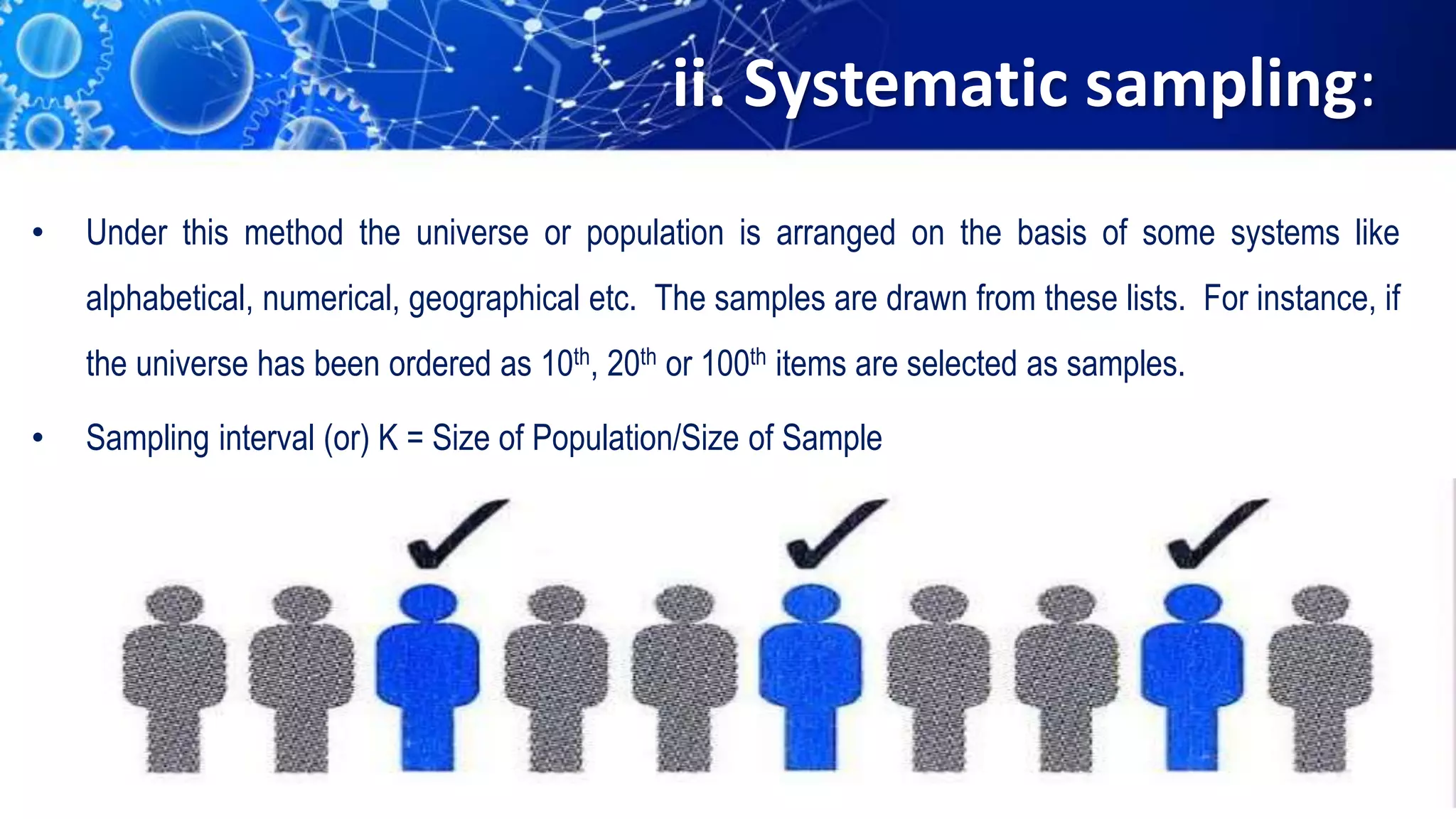
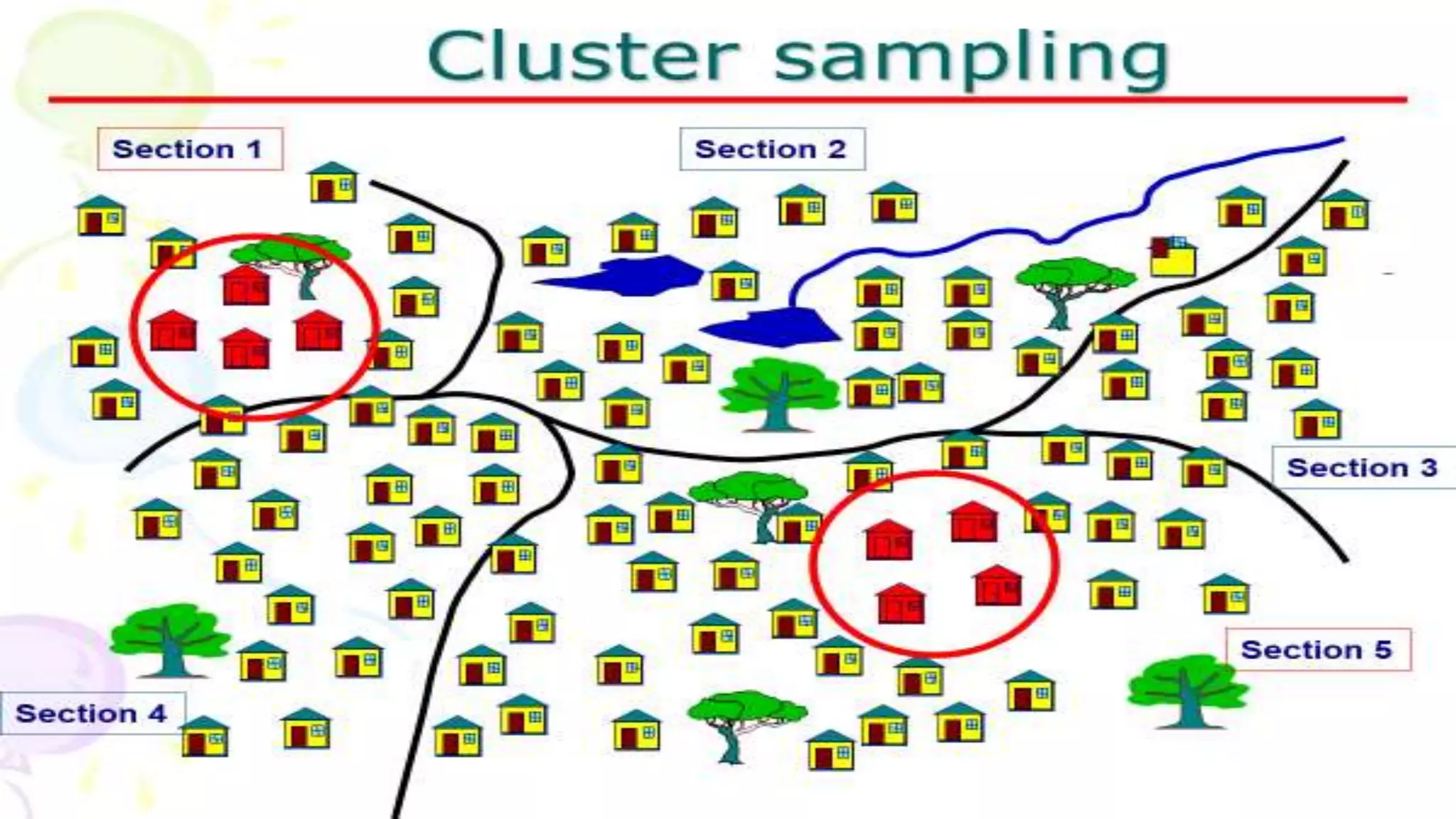
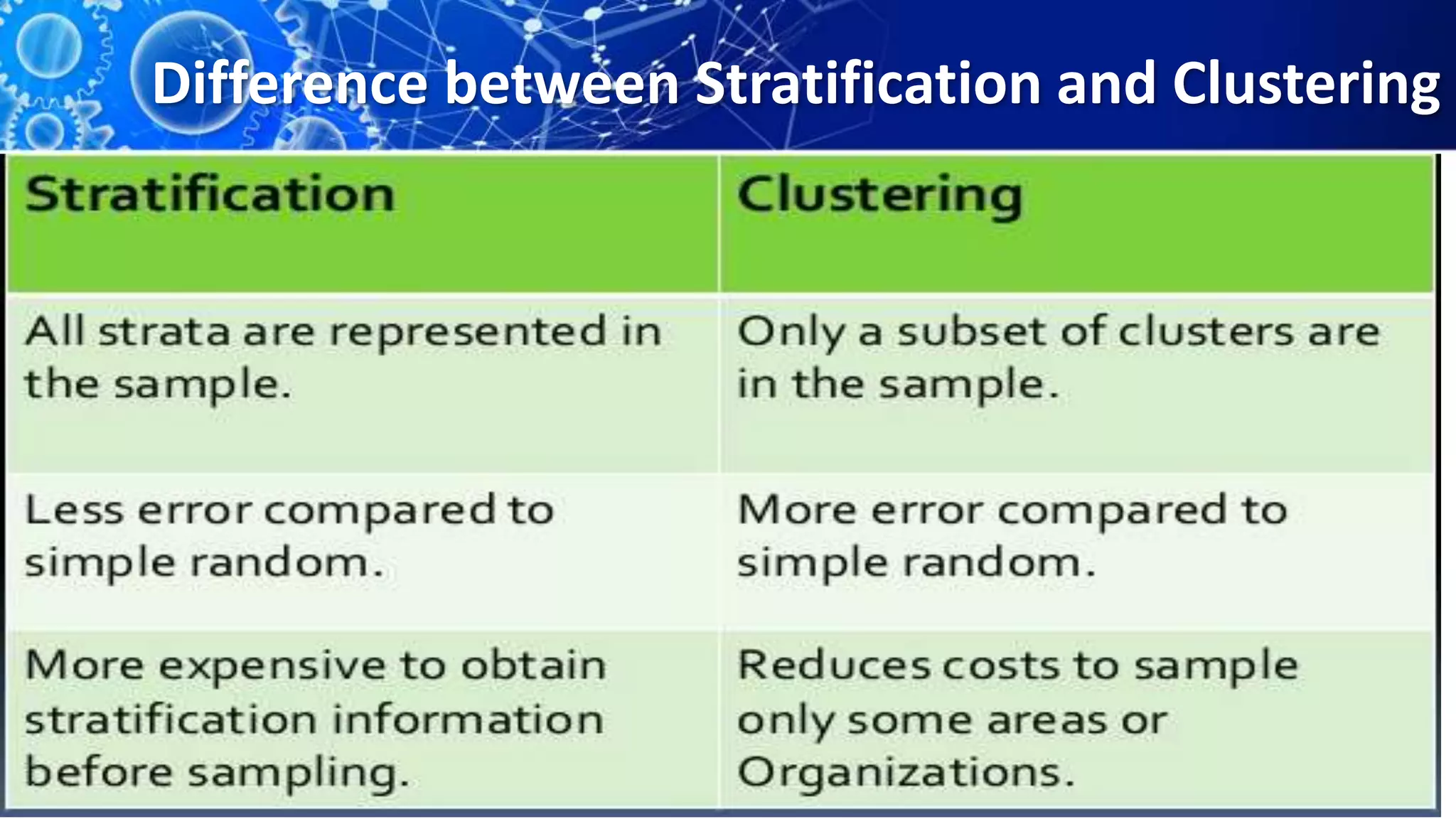
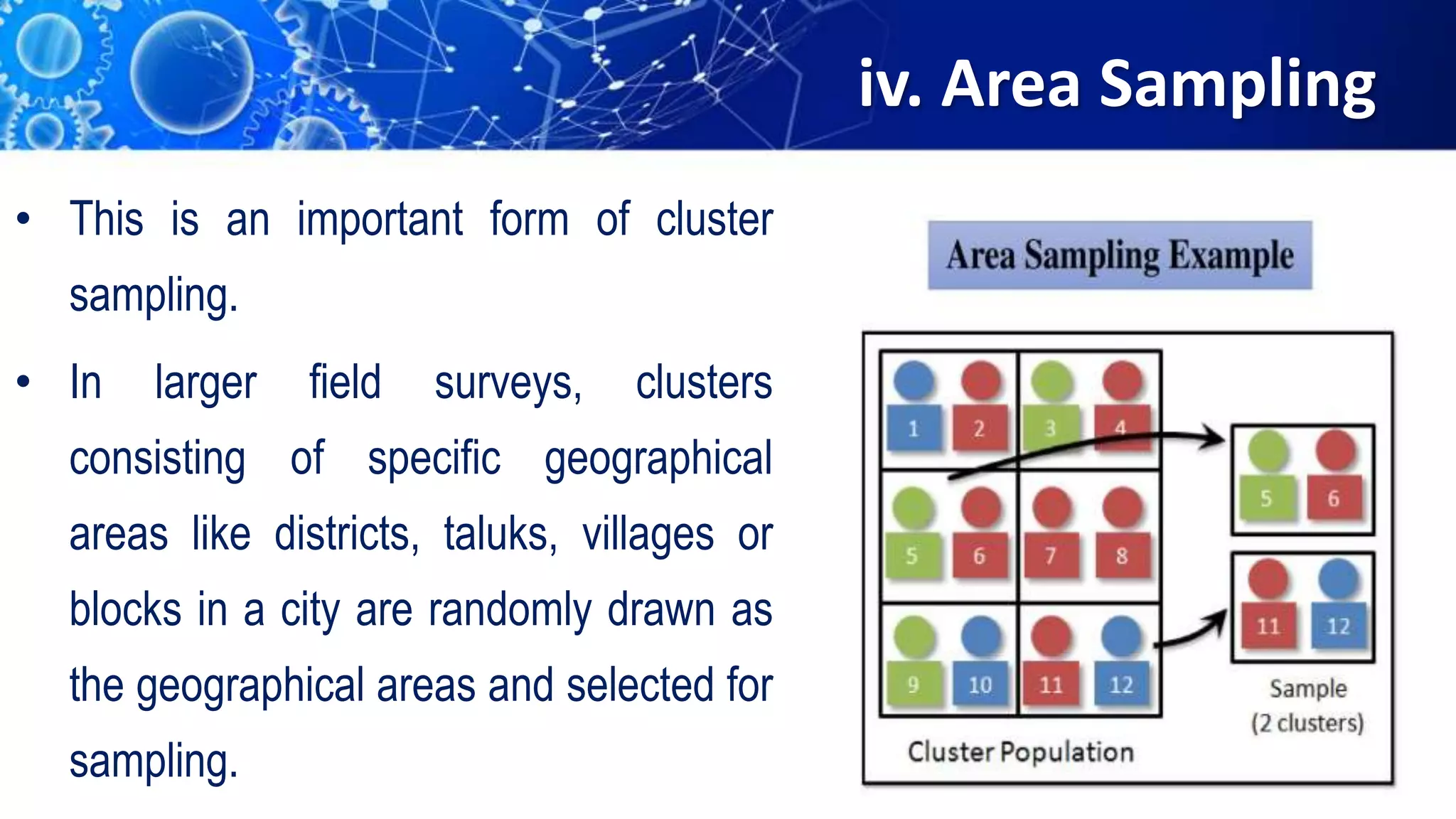
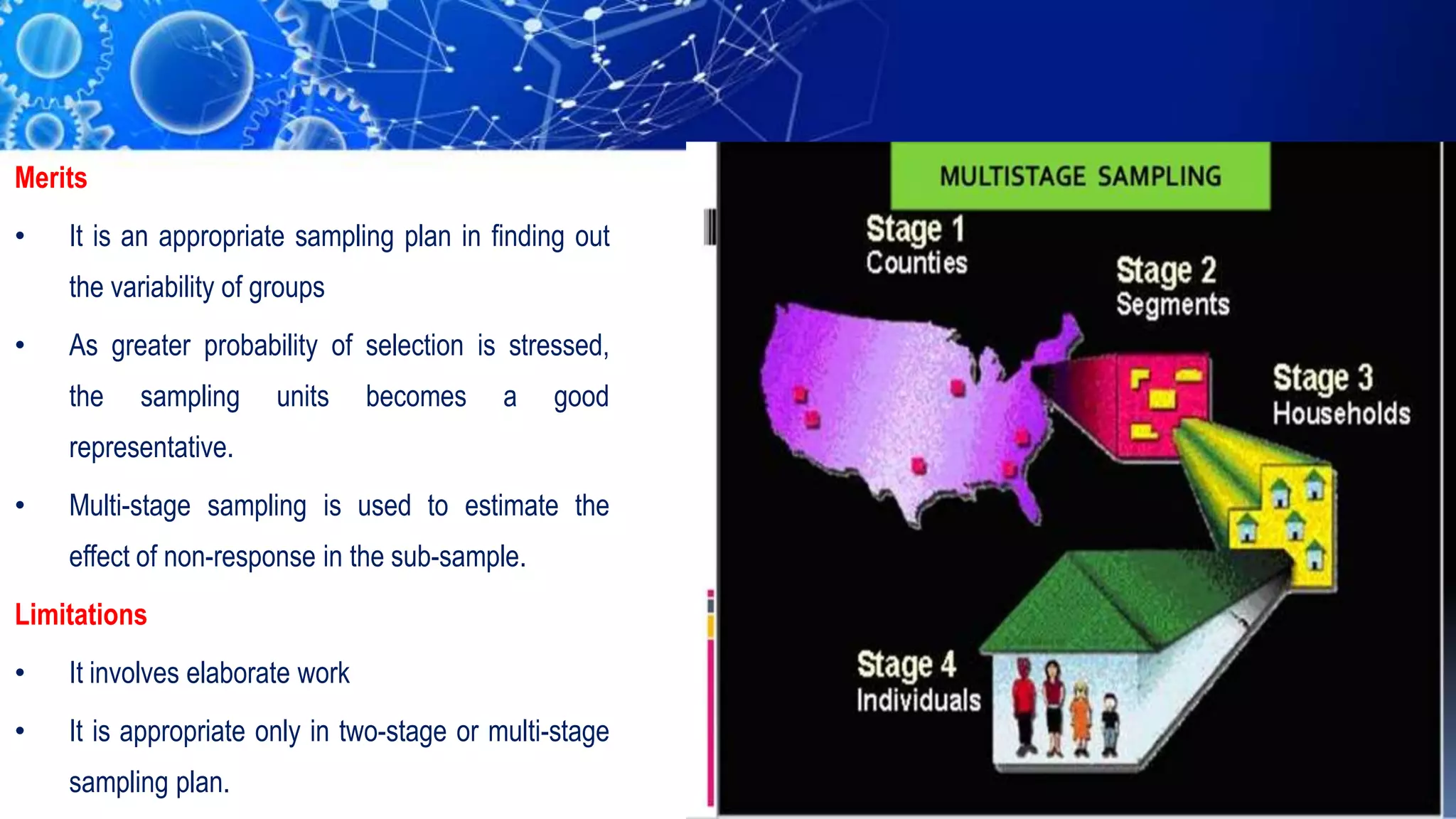
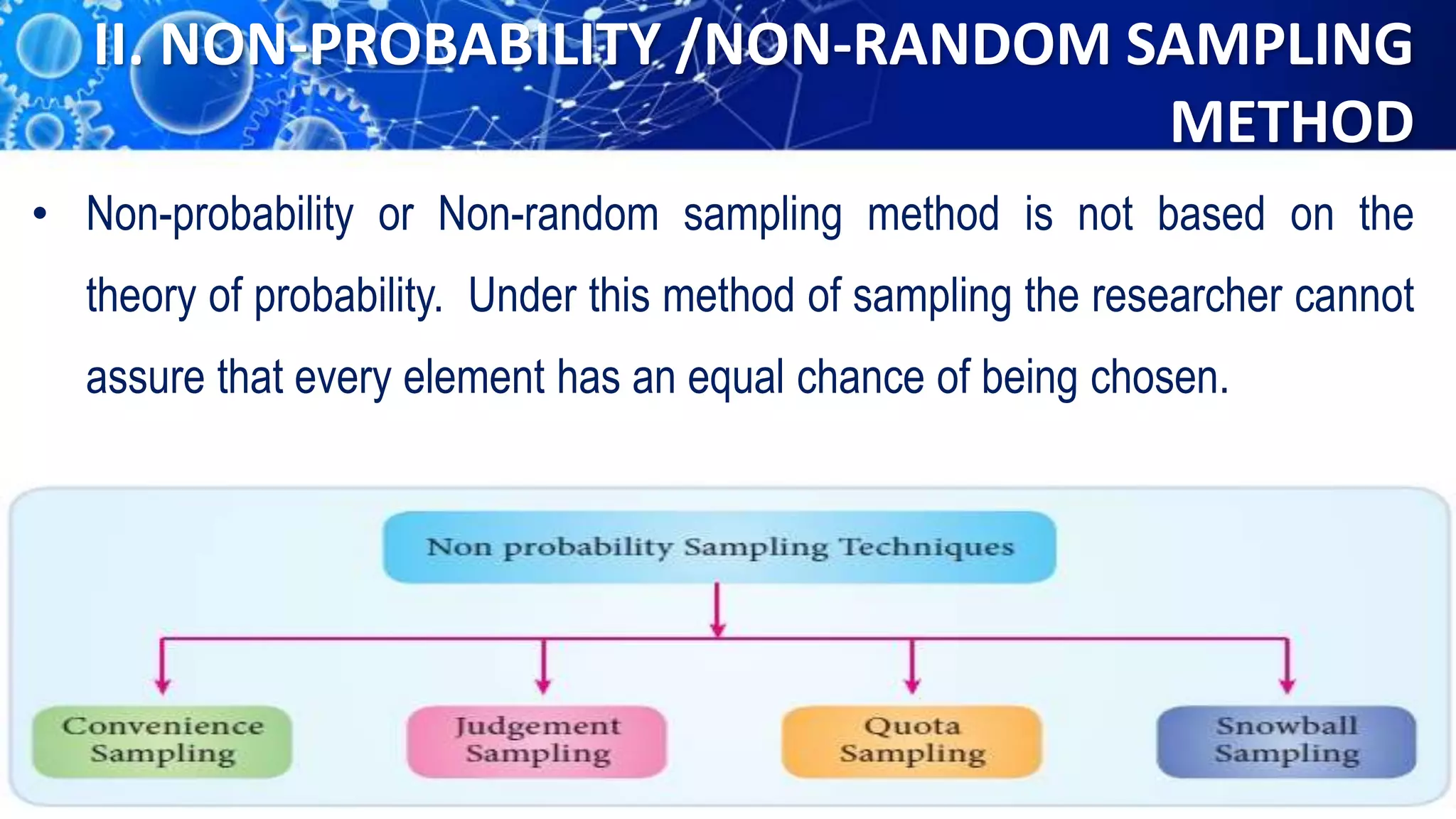
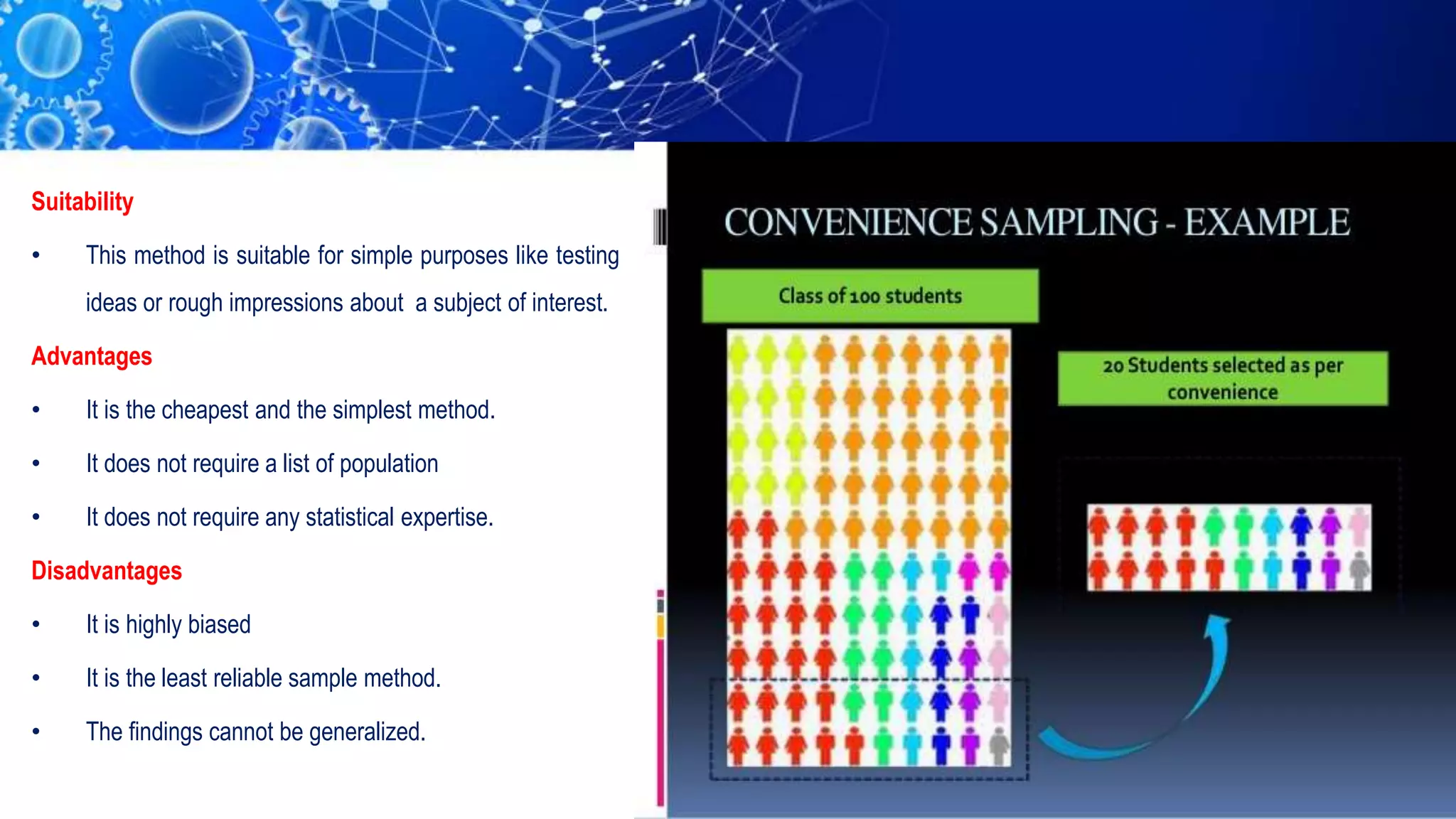
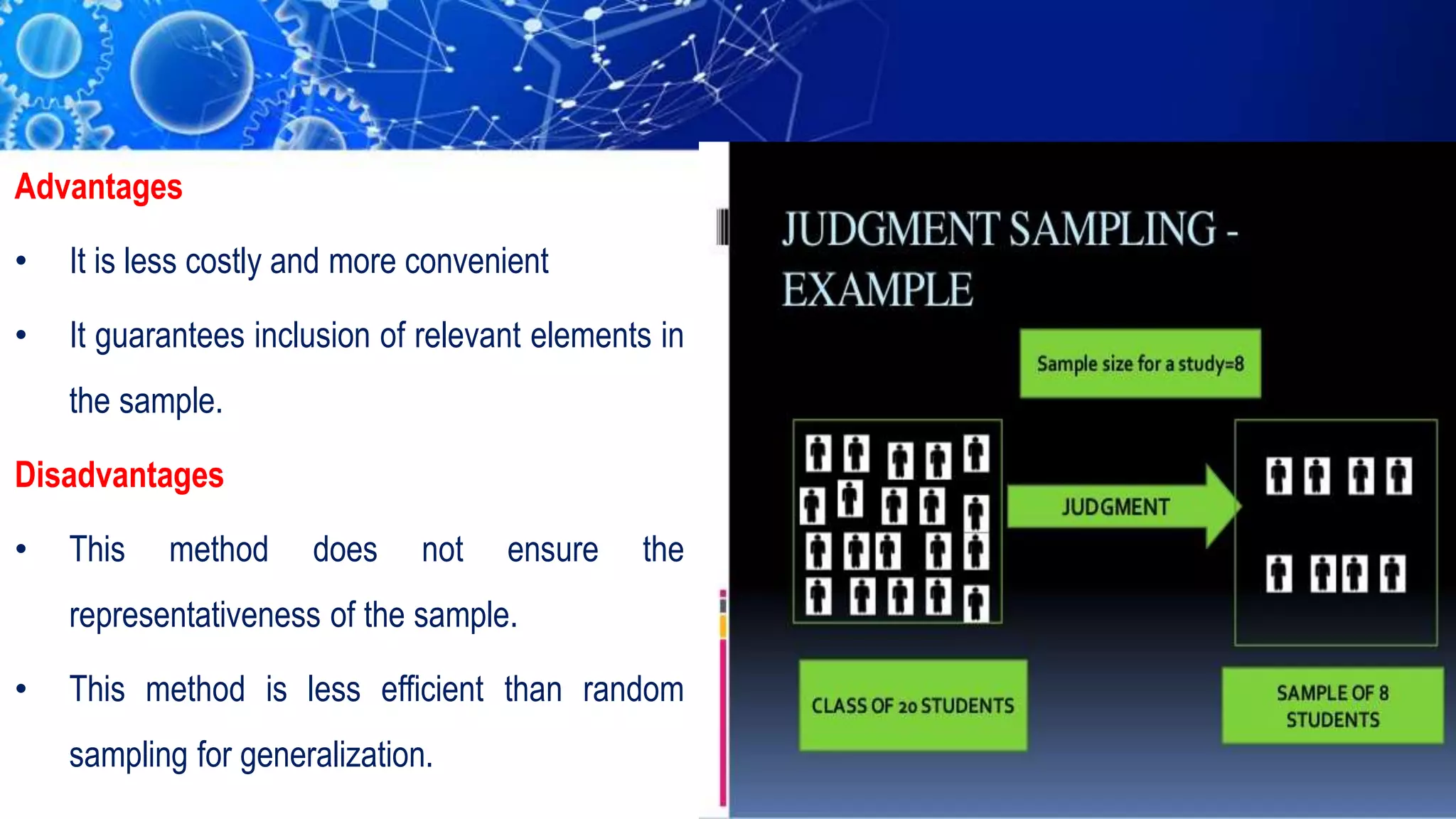
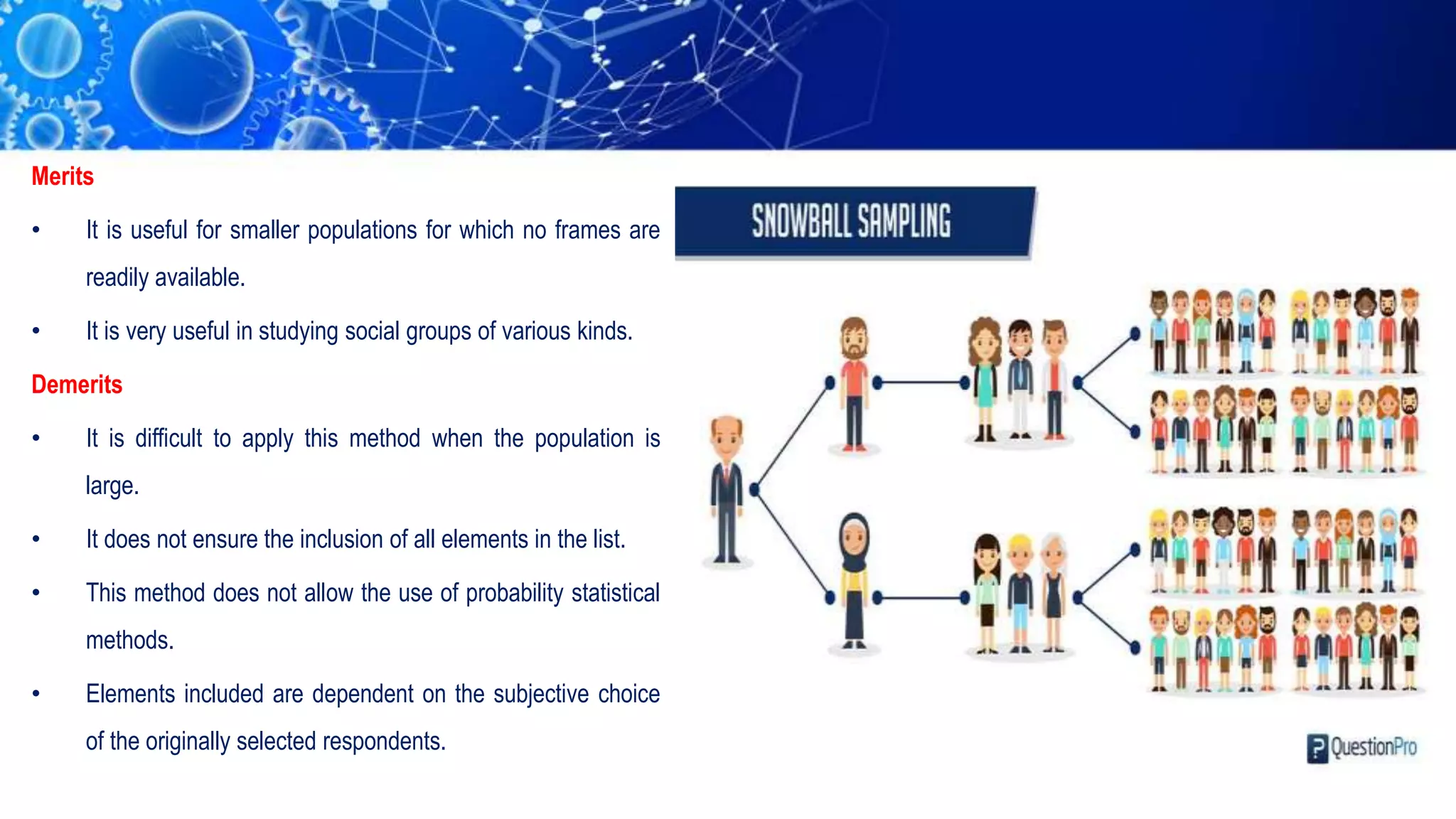
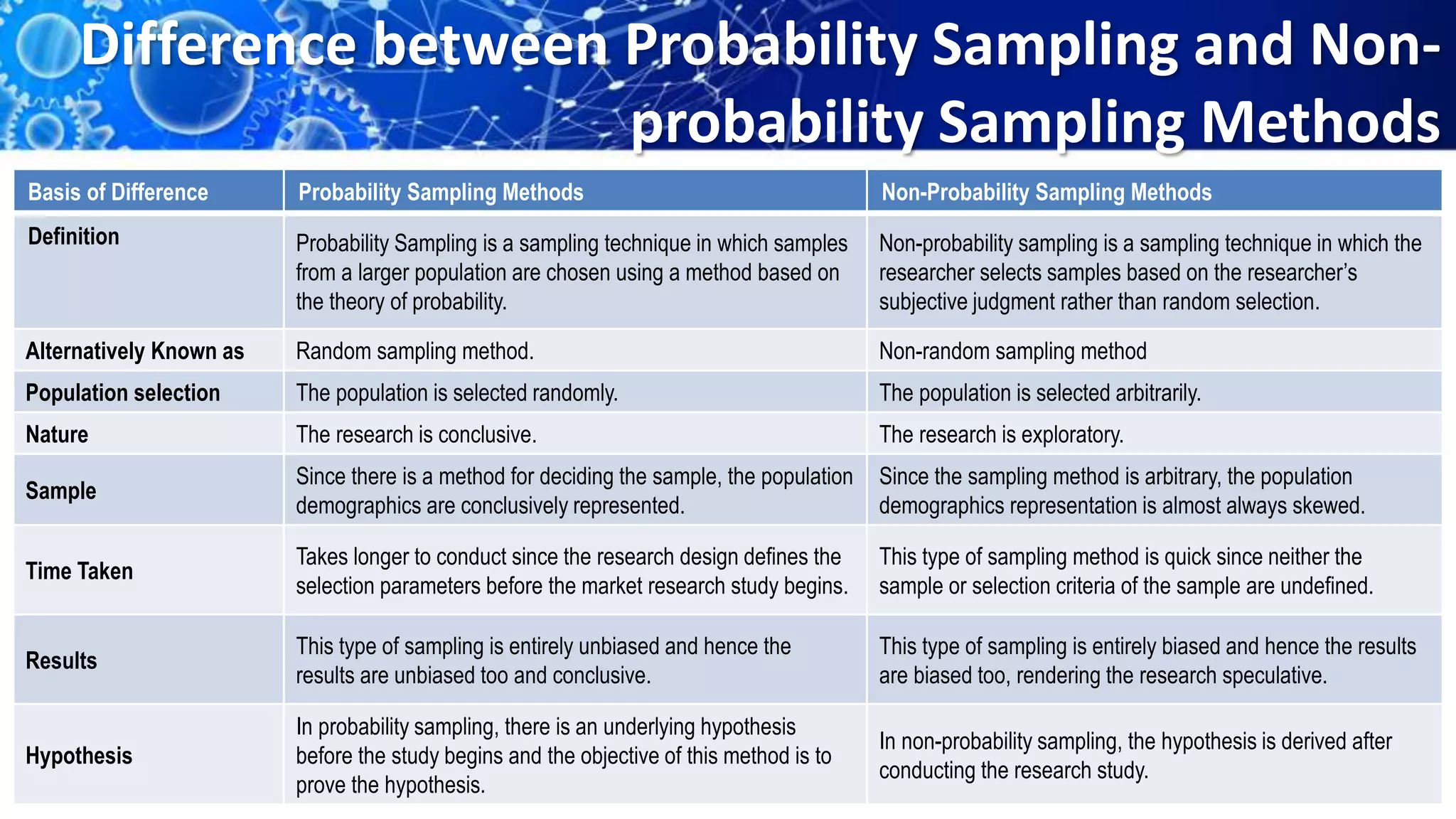
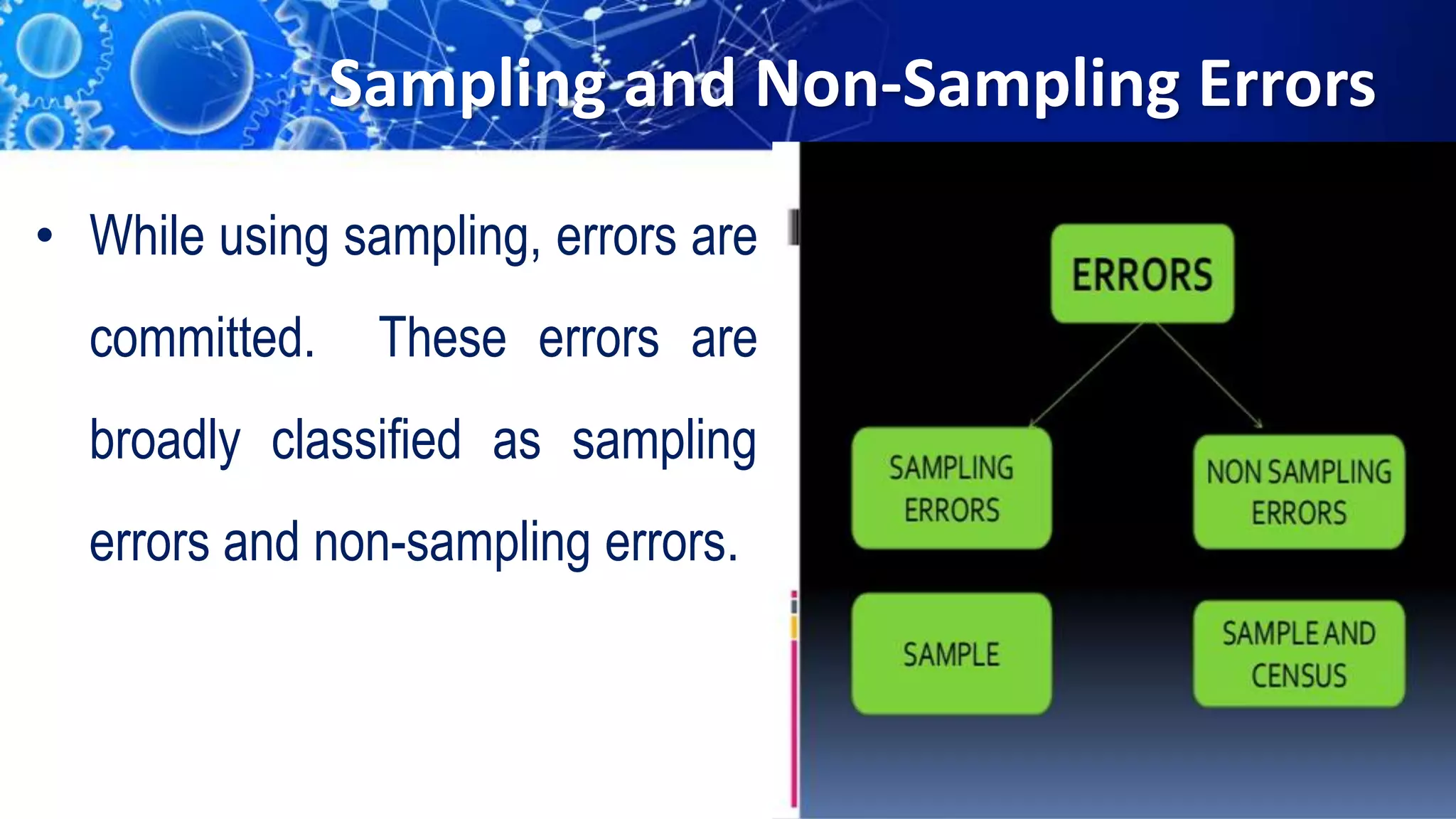
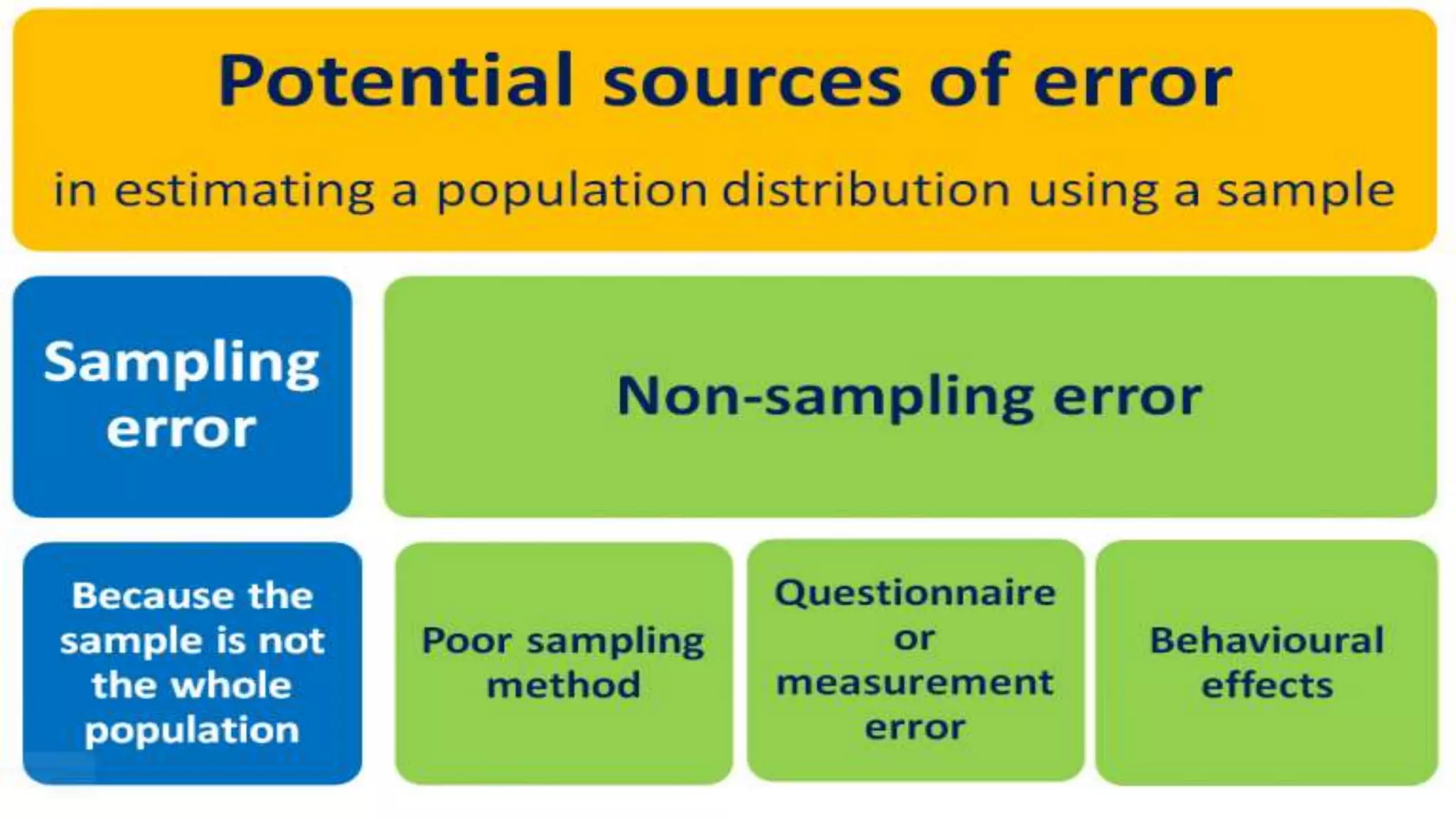
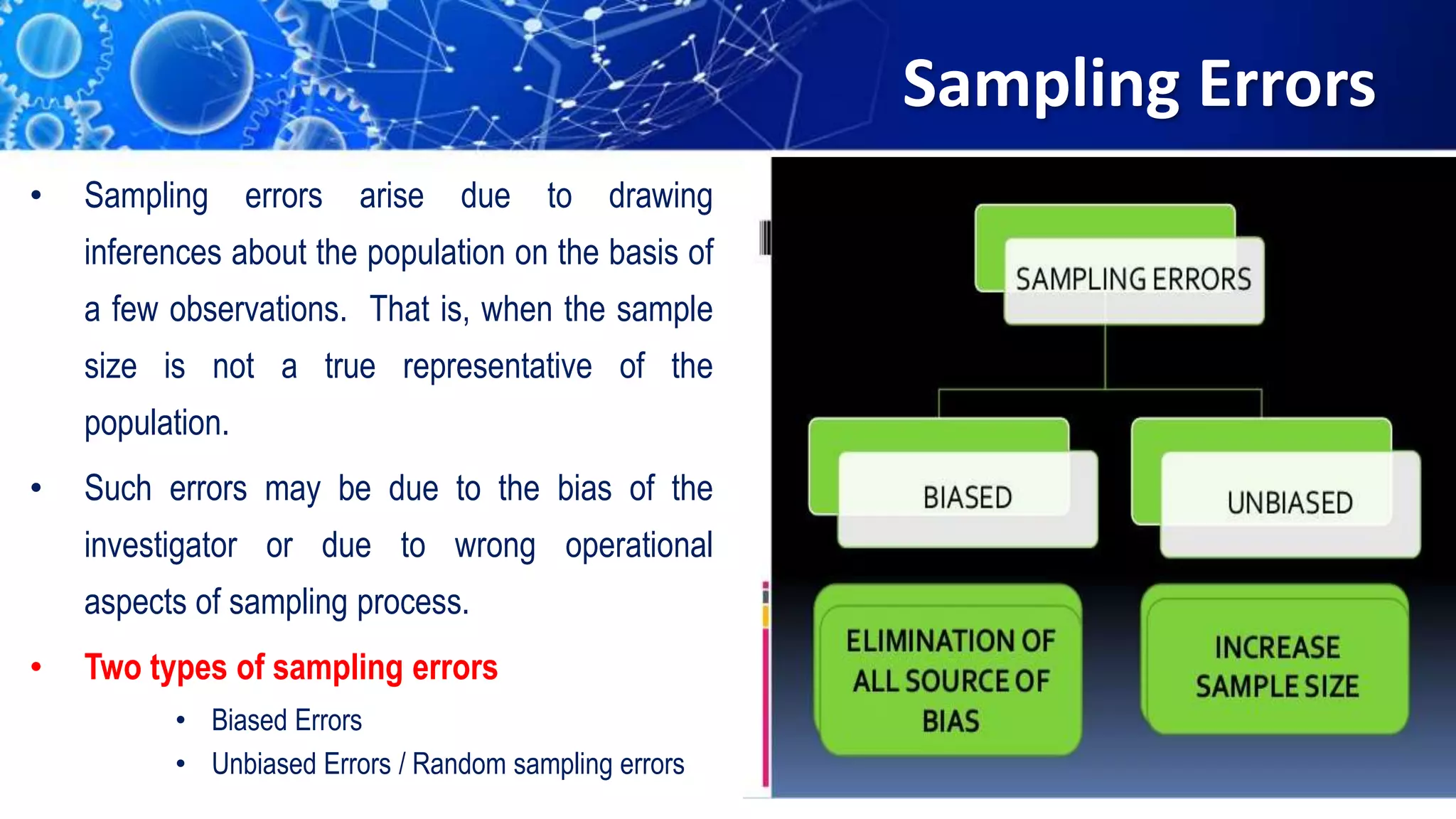
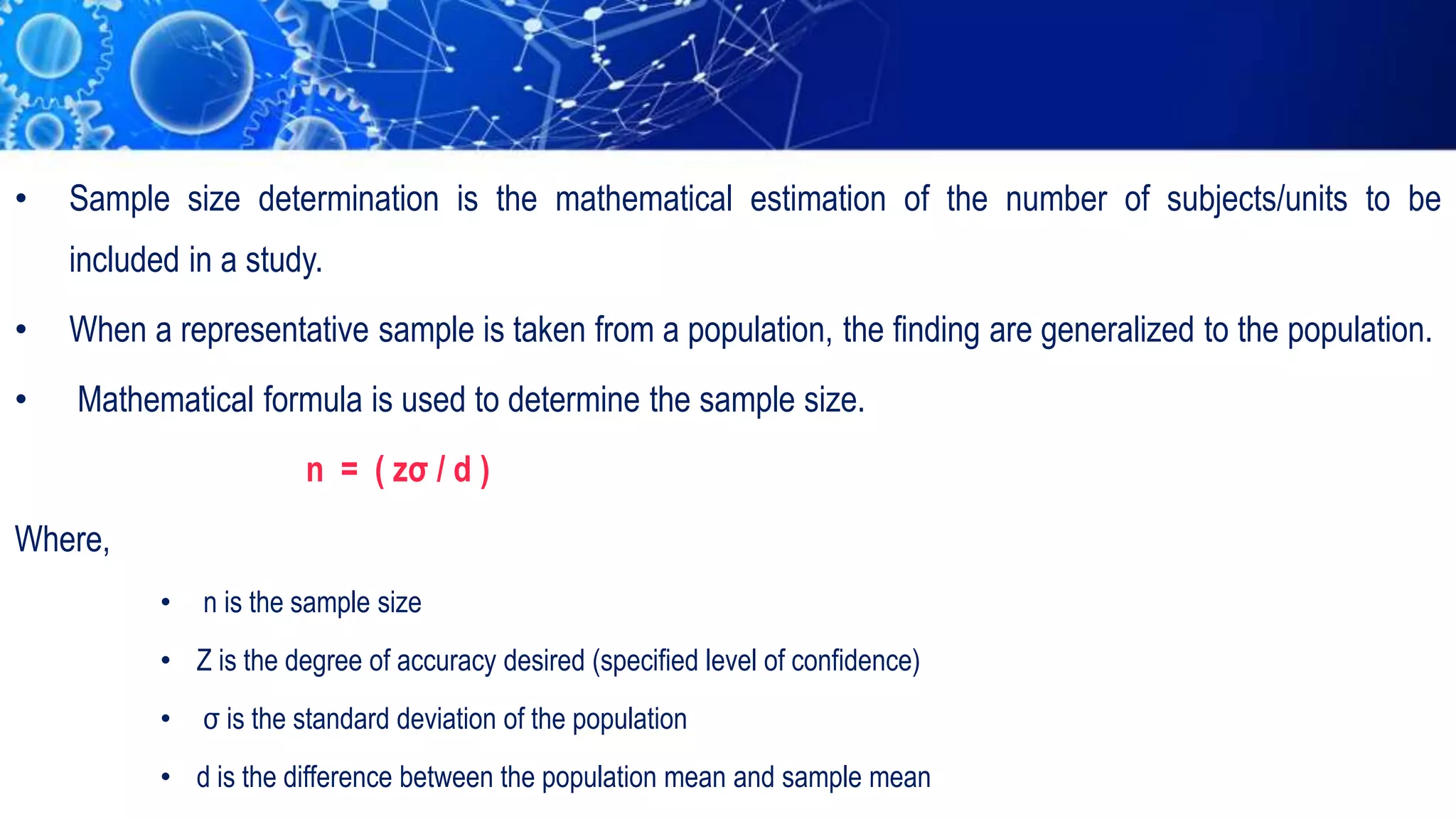
Sampling is the process of selecting a representative subset of a population for research purposes. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling uses random selection to give every member of the population an equal chance of being selected, reducing bias. Common probability sampling techniques include simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster sampling. Non-probability sampling does not use random selection and cannot accurately represent the entire population. Common non-probability techniques include convenience sampling, judgement sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling. The choice of sampling technique depends on factors like the size and nature of the population.