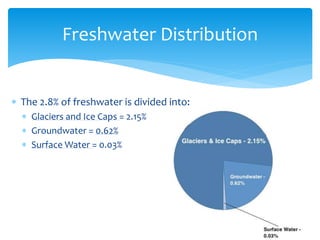
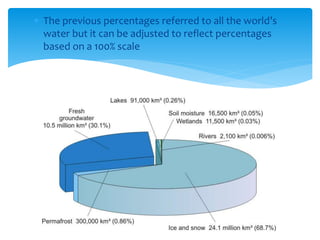
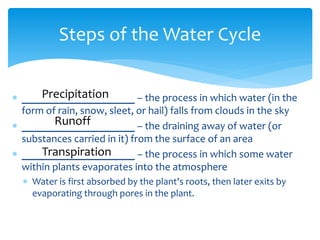
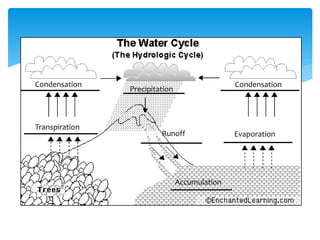
The hydrosphere encompasses all water on or near the Earth's surface, with 97.2% of this water located in the oceans, leaving only 2.8% as freshwater, of which a mere 0.8% is drinkable. Freshwater is mainly found in glaciers, groundwater, and surface water, with the surface water being primarily in lakes and very small quantities in soil and the atmosphere. The document also describes the water cycle, which involves processes such as accumulation, evaporation, condensation, precipitation, runoff, and transpiration that continuously moves water through various forms.