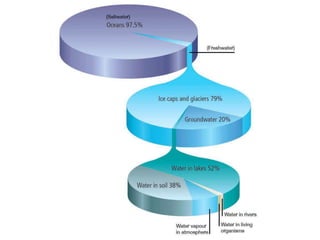
The document discusses the hydrologic cycle, which involves the continuous circulation of water on Earth through different states and processes. It explains that evaporation occurs when water molecules gain energy and change from liquid to gas, condensation is when water vapor condenses to form clouds, and precipitation delivers water to the Earth's surface. The hydrologic cycle begins with evaporation from the ocean, water being transported through the atmosphere, precipitation, and water running off or seeping into the ground to eventually return to the oceans.