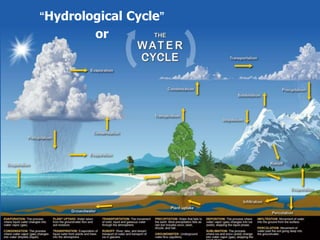
The document discusses the essential role of water in daily life, including its uses for domestic, agricultural, and bodily functions, emphasizing the need for water conservation. It explains the water cycle, highlighting processes like evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, while also addressing the impacts of pollution and deforestation on water availability. Additionally, it suggests methods for water management and conservation to ensure sustainable use for future generations.