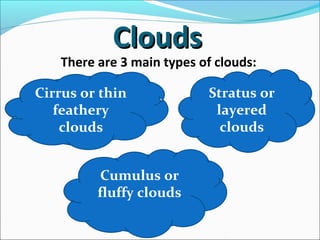
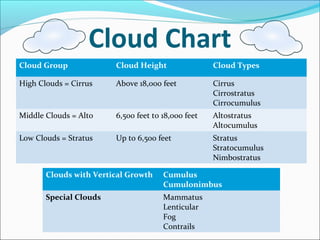
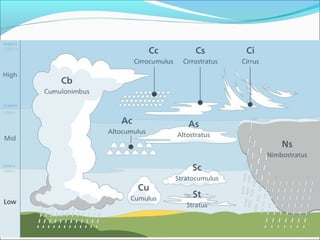
Clouds are large collections of tiny water droplets or ice crystals that float in the air, forming when warm air cools and moisture condenses. There are three main types of clouds: cumulus (fluffy), stratus (layered), and cirrus (feathery), each predicting different weather conditions. Clouds play a critical role in regulating Earth's energy balance, facilitating precipitation, and indicating atmospheric processes.