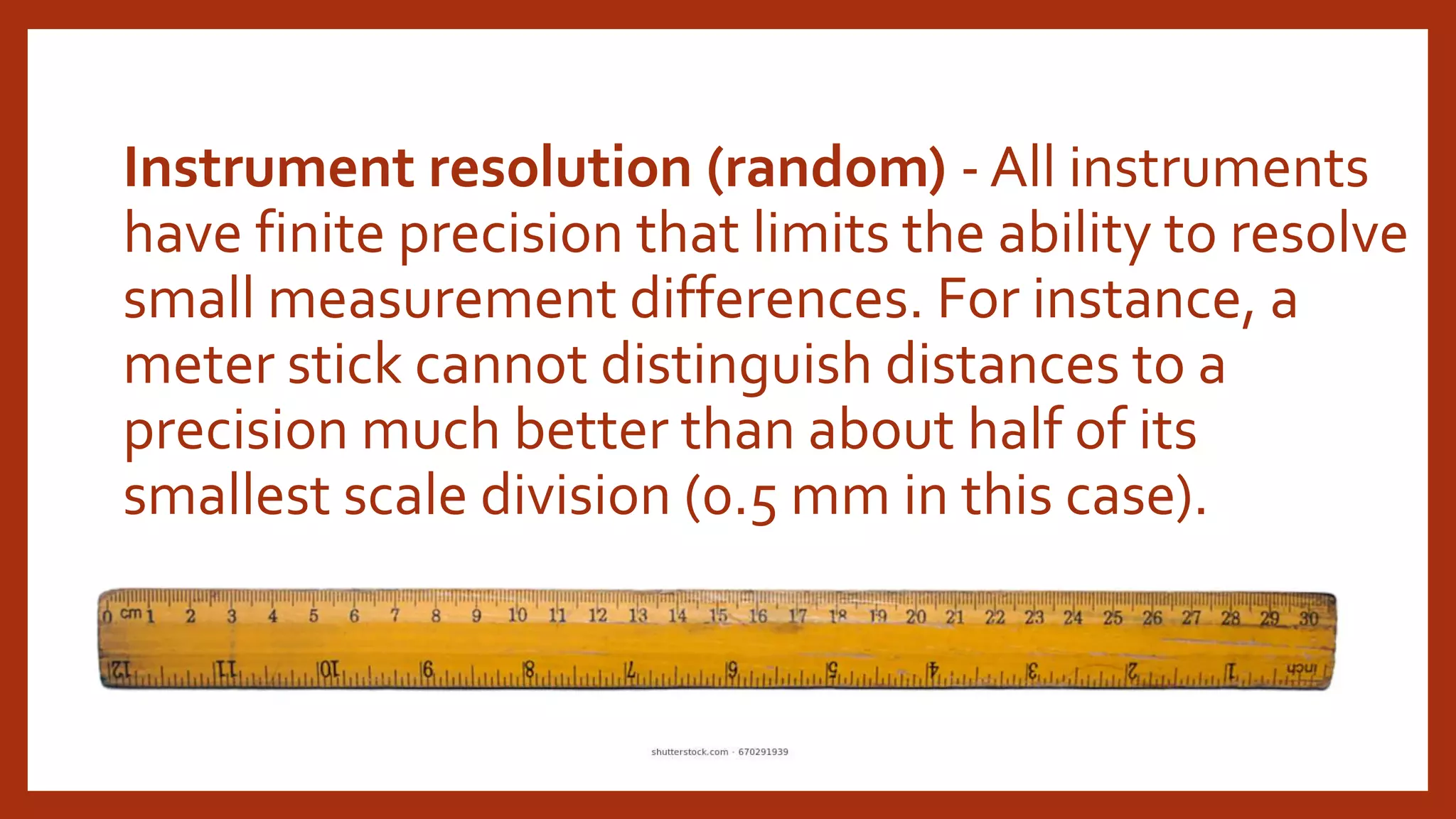
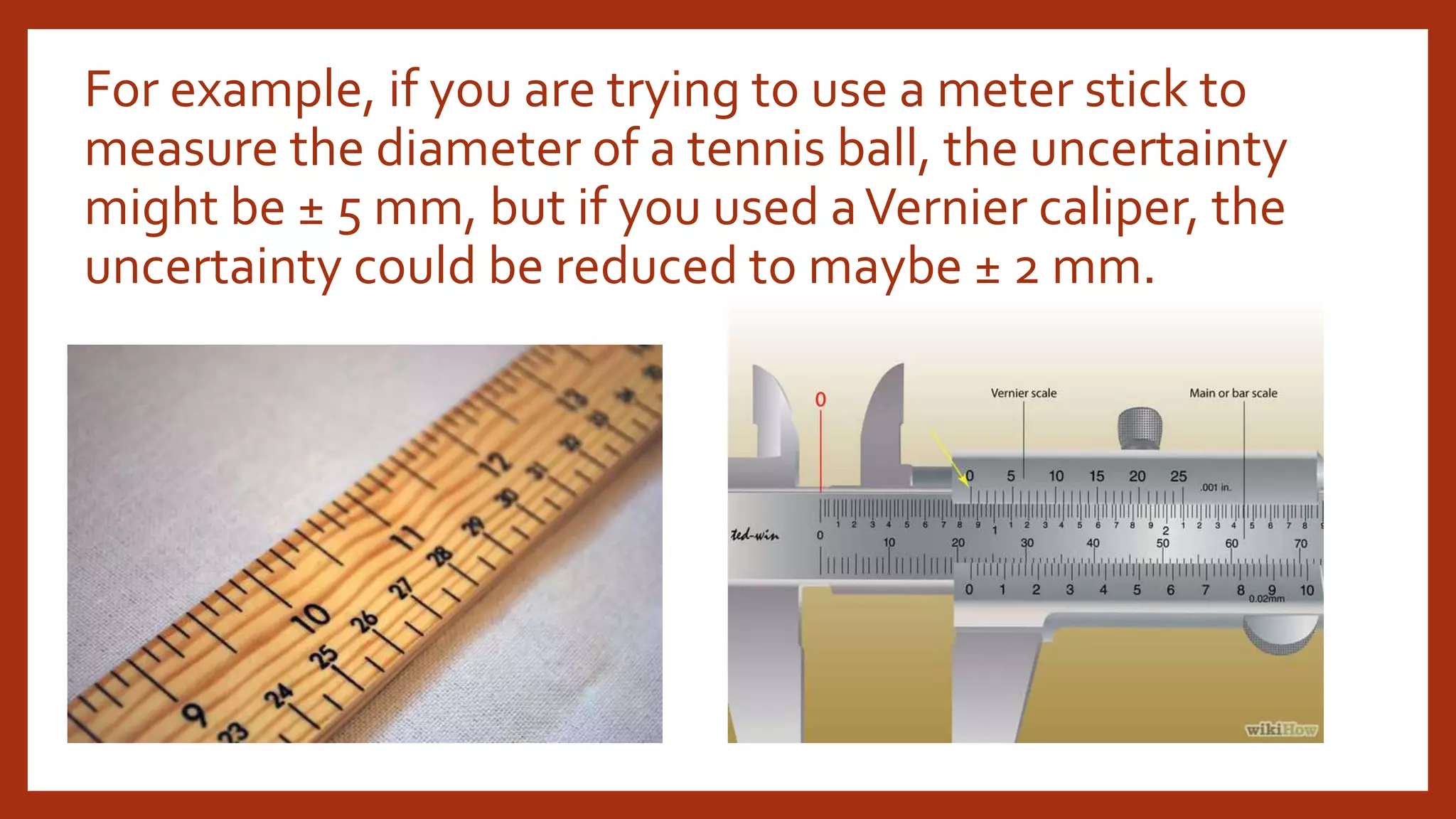
This document discusses various sources of uncertainty in physics measurements, including incomplete definitions, unaccounted factors, environmental influences, instrument limitations, calibration errors, physical variations, drifts, response times, and parallax. It emphasizes that all measurements have some degree of uncertainty from multiple sources. Properly reporting uncertainty allows evaluation of experimental quality and comparison to other results. While the true value may not be known exactly, uncertainty analysis helps ascertain a measurement's accuracy and precision.