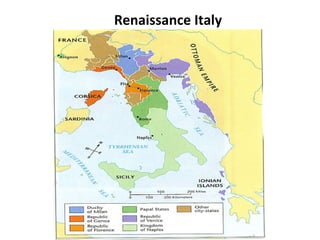
During the 1400s in Italy, a revival of interest in ancient Greek and Roman culture known as the Renaissance developed. Wealthy patrons supported artists and scholars in the Italian city-states of Milan, Venice, and Florence. Renaissance thinkers explored humanism and secular ideas and used observation rather than religious teachings to explain the world. Artists like Michelangelo, Leonardo da Vinci, and others developed new techniques and created extremely lifelike paintings.