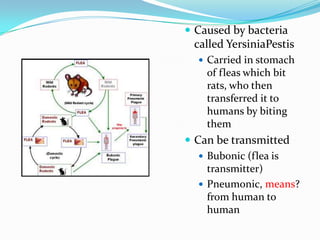
The document summarizes key events and developments during the Late Middle Ages in Europe, including the Black Death plague pandemic from 1347-1350 that killed around half of Europe's population, weakening the feudal system. It also discusses the Avignon Papacy from 1309-1378 when the seat of the Catholic Church was moved to Avignon, France, leading to the Great Schism and calls for church reform through the Conciliar movement. Peasant revolts erupted across Europe in response to worsening economic and social conditions exacerbated by the plague and ongoing wars.