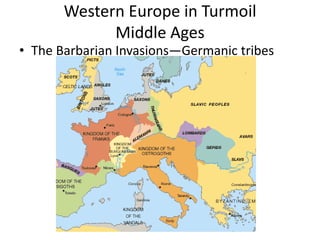
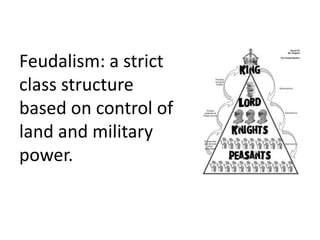
The document summarizes several key aspects of life in medieval Europe during the Middle Ages, including the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the rise of the Byzantine Empire; the development of feudalism and manorialism; the power and influence of the Catholic Church; major events like the Crusades, Black Death, and Hundred Years War; and the introduction of new ideas, technologies, and crops from other parts of the world.