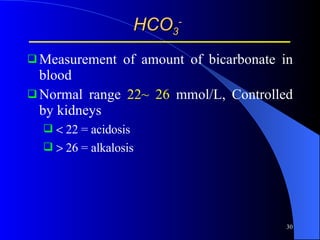
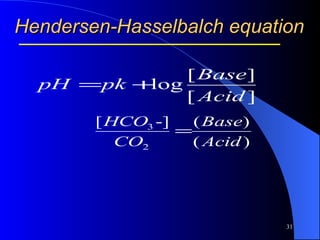
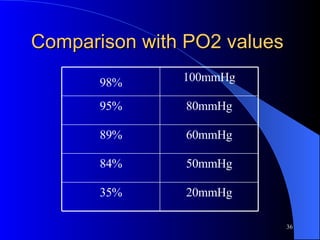
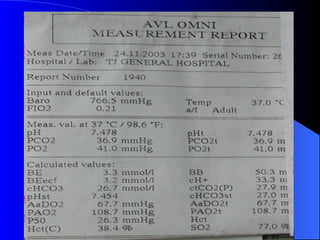
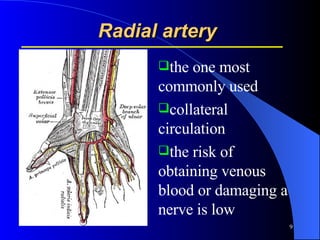
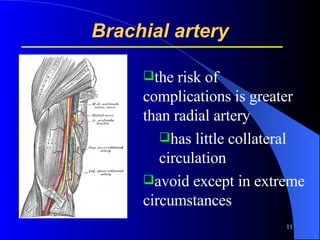
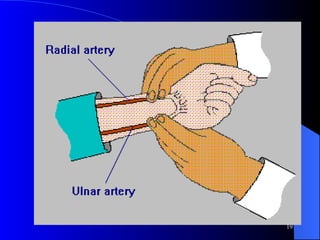
This document summarizes arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, including indications, sample collection techniques, measurement interpretations, and compensation mechanisms. It describes how ABG tests are used to assess respiratory and acid-base status by measuring pH, pCO2, pO2, HCO3, and other values. The radial artery is most commonly used for puncture due to low risk of complications. Interpretation of ABG values indicates acid-base and oxygenation status, and whether the lungs or kidneys are compensating. Normal ABG ranges are also provided for reference.



















![Body is open If add 12 mM H + to closed system if all acid is buffered [CO 2 ] = 13.2, [HCO 3 ] = 12, pH = 6.06 : lethal If add 12 mM H + to body Body is open through lungs, all extra CO2 expelled [CO 2 ] = 1.2, [HCO 3 ] =12, pH = 7.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abg-090509015237-phpapp02/85/Abg-26-320.jpg)


![PCO 2 Carried as carbonic acid , so it has an inverse ration with pH Controlled by the lungs Normal range 35~ 45 mmHg 35 = hyperventilation or base (alkalosis) 45 = hypoventilation or acidic (acidosis) [H 2 CO 3 ]: 40×0.03=1.2mmol/L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abg-090509015237-phpapp02/85/Abg-29-320.jpg)