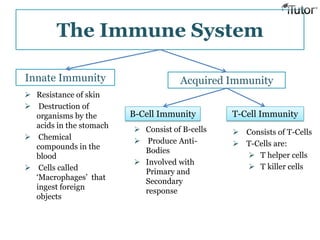
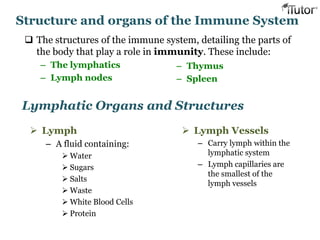
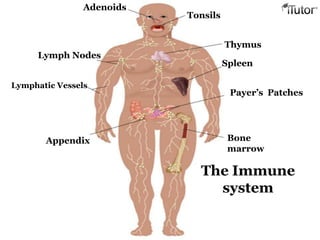
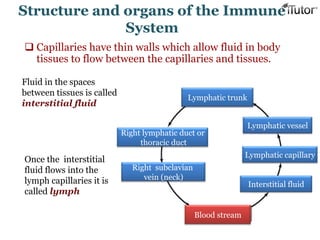
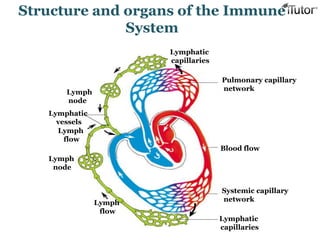
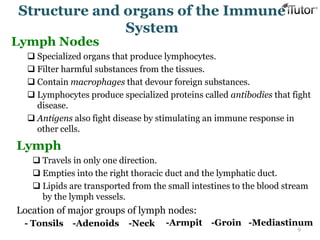
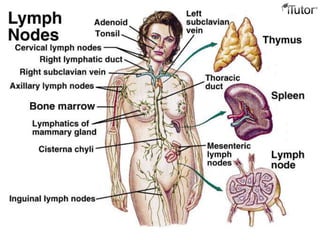
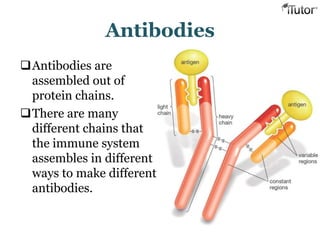
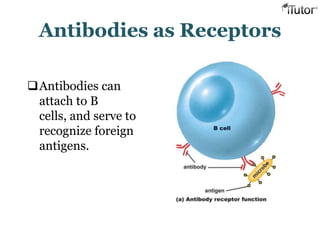
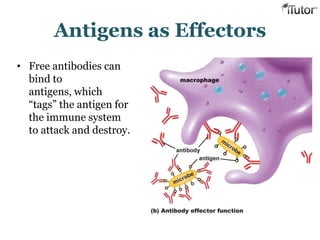
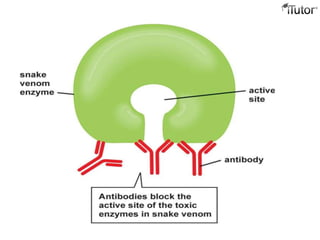
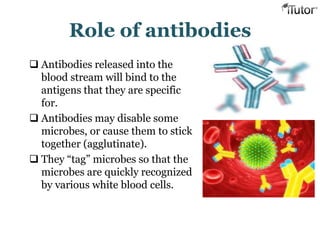
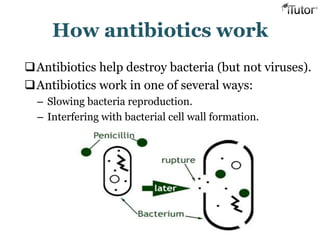
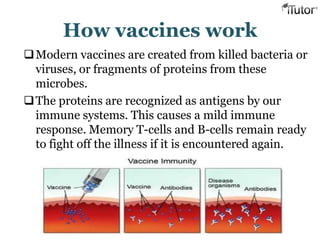
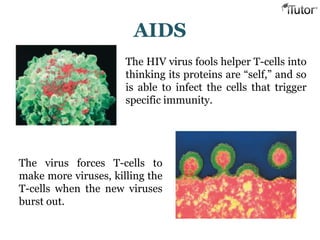
The document summarizes the key components and functions of the human immune system. It describes the innate and acquired immune systems, including skin barriers, stomach acids, phagocytes, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, antibodies, and memory cells. It also outlines the roles of lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, and bone marrow in housing and producing immune cells. Common infections like colds are caused by viruses while antibiotics can treat bacterial infections. Vaccines help prime the immune system to recognize pathogens.