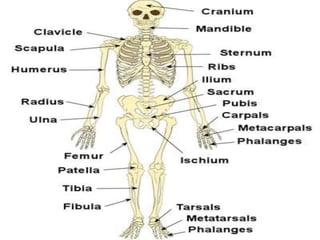
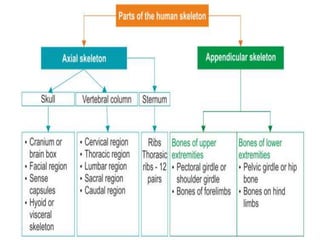
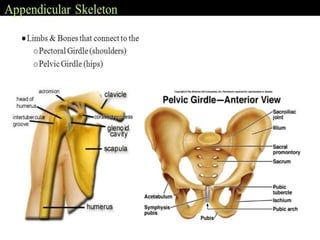
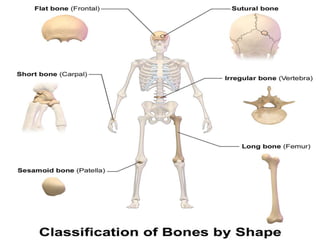
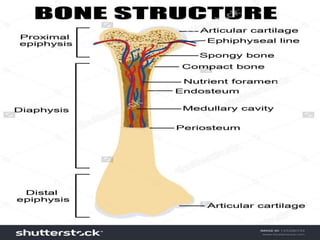
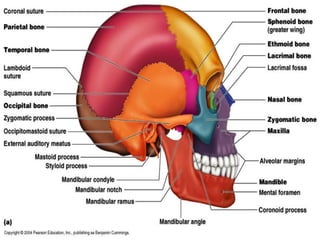
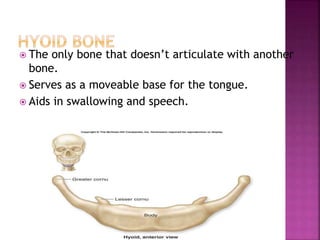
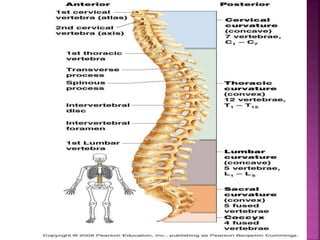
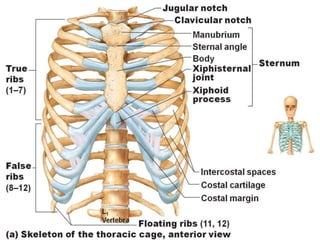
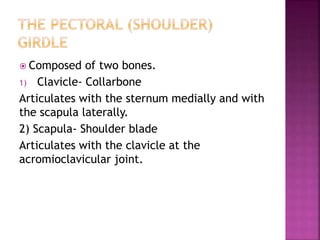
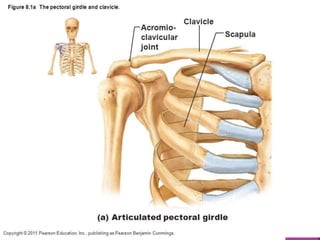
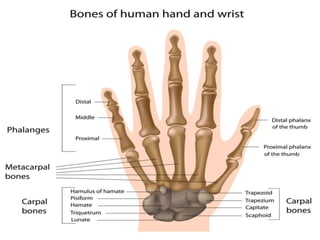
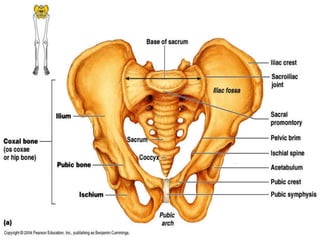
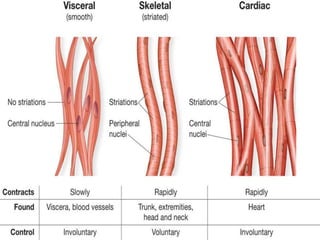
The skeletal system provides structure and support to the body, protects vital organs, allows for movement, stores minerals and fat, and produces blood cells. The skeleton is composed of bones of different shapes - long bones in the limbs, short bones in the wrists and ankles, flat bones like ribs, and irregular bones like the sacrum. Bones are joined by sutures or movable joints. The skull consists of the cranium and facial bones. Vertebrae make up the spine and are separated by discs. The rib cage forms a protective cage around the thoracic organs. The shoulder girdle includes the collarbone and shoulder blades. Hands and feet contain carpals/tarsals, metacarpals/