- Bone tissues makes up about 18% of the total human body weight.
- The skeletal system supports and protects the body while giving it shape and form.
-Osteology: It is the branch of science that deals with the study of the skeletal system, their structure and functions.
-- Skeletal System Composed Of
Bones
Cartilage
Joints
Ligaments
Dense connective tissues
Adipose tissue
-Functions Of Skeletal System
1. Support: Hard framework that supports and the soft organs of the body and provide attachment for the tendons of skeletal muscles.
2. Protection: Skeleton protects vital internal organs from injury, e.g. cranial ones protects the brain.
3. Movement: Allows for muscle attachment to bones and brings about movement.
4. Storage: Yellow bone marrow consist of adipose cells, which stores triglycerides.
5. Blood Cell Formation: The bone marrow is responsible for blood cell production (RBC, WBC and platelets) a process is called hemopoiesis.
6. Mineral Homeostasis: Bone store several minerals like calcium and phosphourus which strengthen the bone.
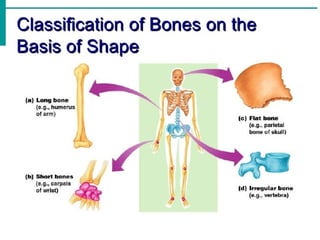
--Classification Of Bone Based On Shape
Bones can be classified into five types based on shape:
1. Long Bones
- Greater length than width and are slightly curved for strength.
e.g., Femur, tibia, fibula, humerus, ulna, radius, phalanges.
2. Short bones
- Cube-shaped and are nearly equal in length and width.
e.g., Carpal, tarsal
3. Flat bones
- Thin and composed of two nearly parallel plates of compact bone tissue enclosing a layer of spongy bone tissue.
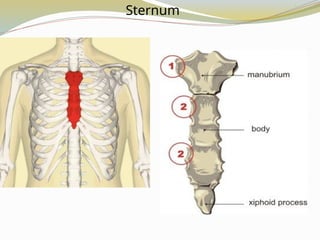
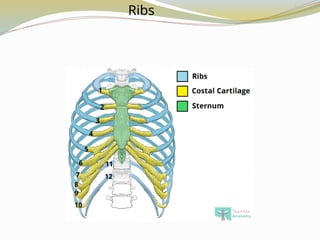
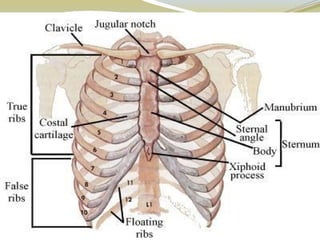
e.g., Cranial, sternum, ribs, scapulae.
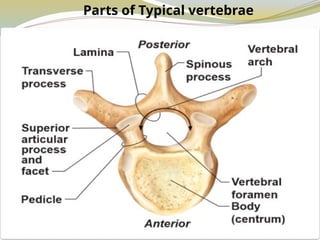
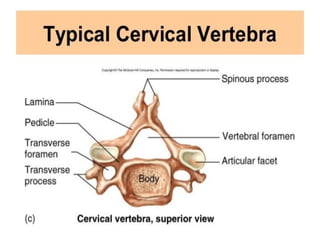
4. Irregular bones
- Complex shapes and cannot be grouped into any of the previous categories.
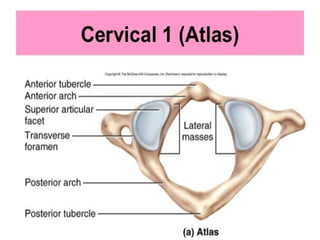
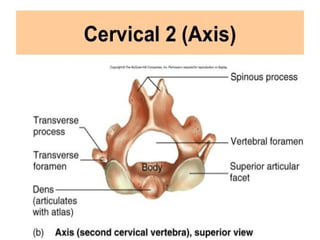
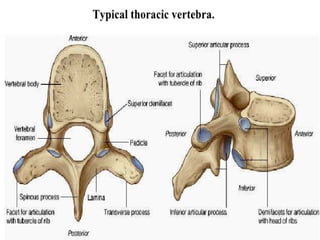
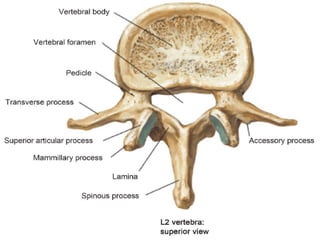
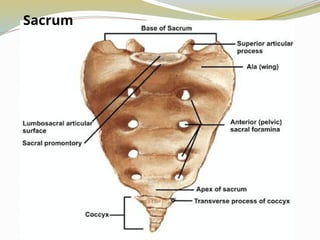
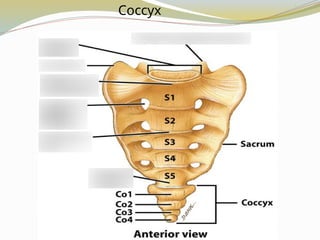
E.g., Vertebrae, hip bones, some facial bones, calcaneus.
5. Sesamoid bones
- Protect tendons from excessive wear and tear.
e.g., Patellae, foot, hand.
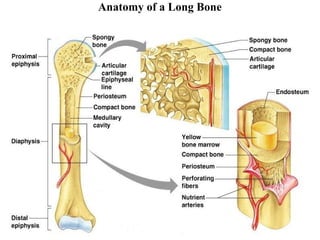
-- Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone
1. Diaphysis
Shaft
Composed of compact bone
2. Epiphysis
- These are distal and proximal ends of the bone
-Composed mostly of spongy bone
3. Metaphysis
- The region where epiphysis meets the diaphysis.
4. Articular cartilage
- A thin layer of hyaline cartilage that reduces friction and acts as a shock absorber.
5. Periosteum
- Outside covering of the diaphysis
- It is dense irregular connective tissue membrane
- Protects the bone, assist in fracture repair
- Helps to nourish bone tissue
6. Medullary cavity
- Inside the diaphysis is the medullary cavity, which is filled with yellow bone marrow.
7. Endosteum
- Thin membrane that lines the medullary cavity
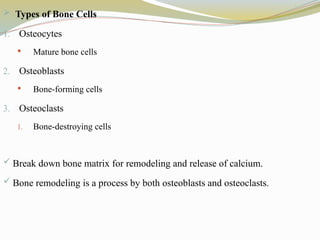
--Types of Bone Cells
Osteocytes
Osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
--Divisions Of The Skeletal System
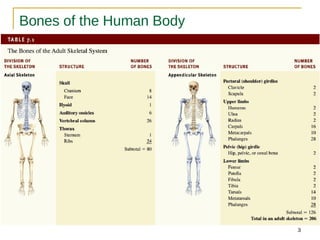
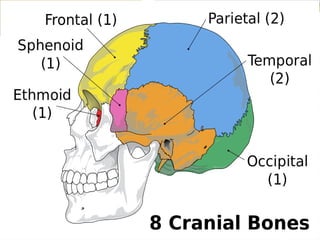
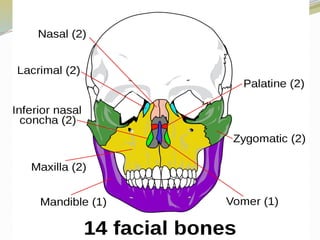
The human skeleton consists of 206 named bones.
Bones of the skeleton are grouped into two principal divisions:
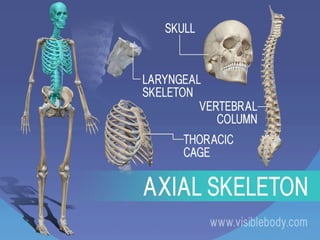
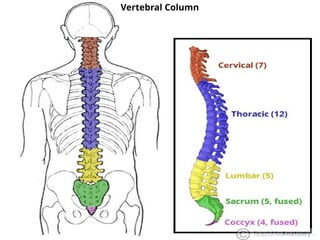
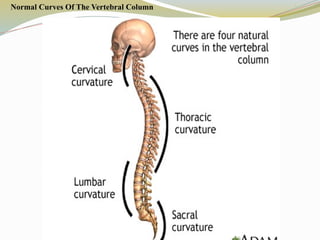
1.Axial skeleton
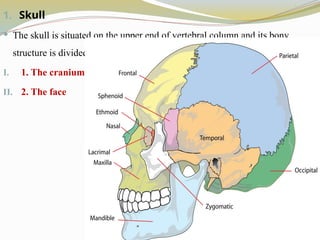
Skull bones, auditory ossicles (ear bones), hyoid bone, ribs, sternum (breastbone) and bones of the vertebral column
Appendicular skeleton
Consists of the bones of the upper and lower limbs (extremities), plus the bones forming the girdles that connect the limb