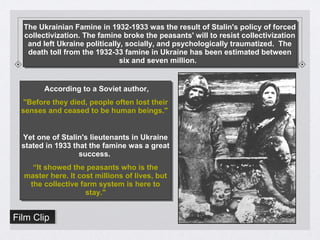
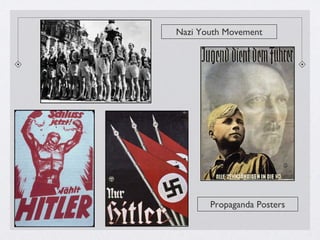
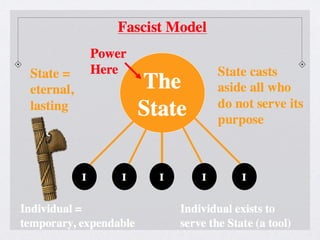
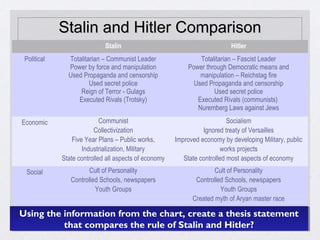
Stalin took power in the Soviet Union after Lenin's death and immediately began purging his opponents through death and terror. He implemented collectivization of farms and five-year plans to industrialize the USSR and build up its military through a command economy with total government control. This led to totalitarian rule through fear, censorship, propaganda, and secret police. Similarly, Mussolini and his fascists took power in Italy in 1922 and established a totalitarian fascist state through extreme nationalism, military expansionism, and by demanding total obedience to the state apparatus. Hitler also came to power in 1933 and quickly dismantled Germany's democracy to construct a Nazi totalitarian regime based on racial ideology that systematically oppressed Jews and other groups through the Gestapo secret police and fascist propaganda