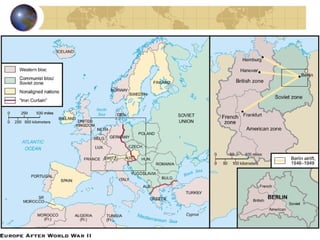
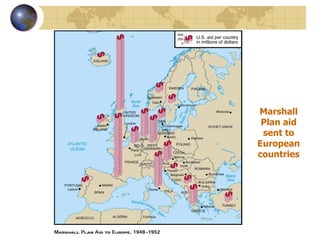
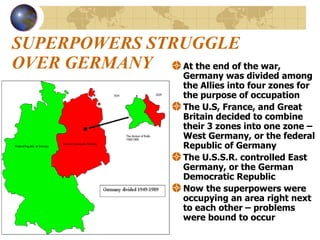
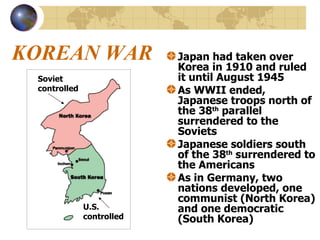
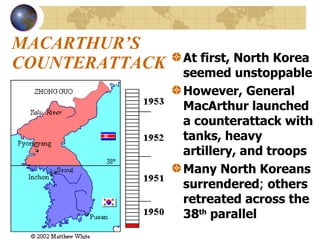
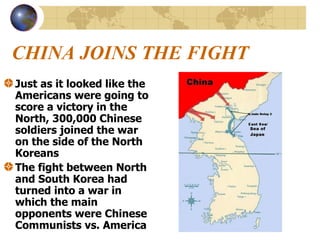
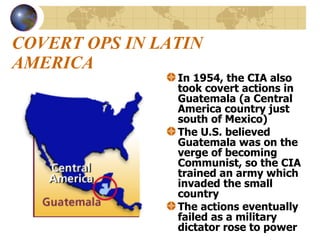
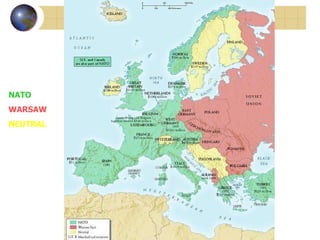
The document summarizes the origins and key events of the Cold War between the United States and Soviet Union from 1945-1953. After being allies in WWII, political and ideological differences grew between the capitalist US and communist USSR, plunging them into a state of tension and rivalry known as the Cold War. The Soviets set up communist governments in Eastern Europe, while the US sought to contain the spread of communism through policies like the Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan. This division of Europe and clashes over issues like the Berlin Blockade and Korean War marked increased hostility between the two superpowers.