The Universal Declaration of Human Rights was adopted by the UN General Assembly in 1948. It recognizes the inherent dignity and equal and inalienable rights of all members of the human family. It establishes that all people are free and equal, regardless of attributes like race, color, sex, language, religion, political opinion, or other status. Everyone is entitled to the rights and freedoms in the Declaration without discrimination.



























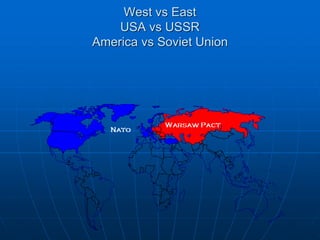

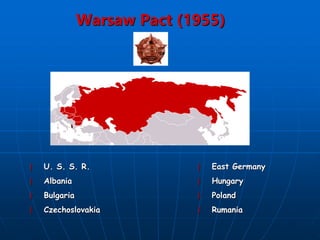
![Warsaw pact
Response to NATO (1949) and the re-
militarization of West Germany in 1954
[both were viewed as a threat to the
Eastern countries]
Supposedly the pact was based on total
equality of member nations & mutual non-
interference in one another’s internal
affairs
In reality—the Pact quickly became a
powerful political tool for the Soviet Union
to hold sway over its allies and harness
the powers of their combined military.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apcoldwar2014-230429215808-58441b2e/85/AP-Cold-War-2014-ppt-31-320.jpg)



























![Neil Armstrong
“That's one small step for [a] man, one giant leap for
mankind”
July 21, 1969](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apcoldwar2014-230429215808-58441b2e/85/AP-Cold-War-2014-ppt-64-320.jpg)