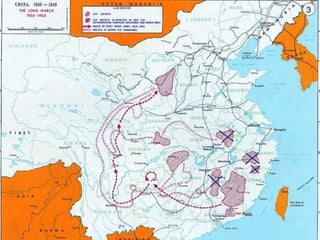
This document discusses the origins and development of Marxism-Leninism and its spread to power in early communist states. It describes how Karl Marx developed communist ideas around class struggle and ownership of production. Vladimir Lenin then led the Bolsheviks Revolution in Russia, establishing the Soviet Union and implementing Marxist-Leninist policies like secret police and executions. Stalin later industrialized the Soviet Union through five-year plans and collectivization. Marxism-Leninism also spread to China where Mao Zedong led the Communist Party of China after a long struggle against the Kuomintang nationalists culminating in the Chinese Civil War.