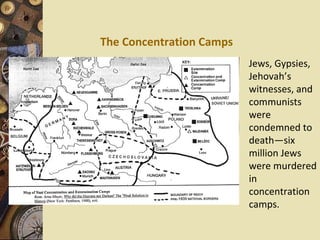
The document provides an overview of the key players and major events of World War II. It identifies the leaders of the Axis Powers (Hitler, Mussolini, Tojo) and Allied Powers (Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin). It describes Hitler's early military successes through 1941 and the Nazi ideology of Aryan racial supremacy. It also outlines the major political and military developments that occurred between 1939-1945, including the US entry into the war after Pearl Harbor and the final Allied victories over Germany and Japan in 1945.