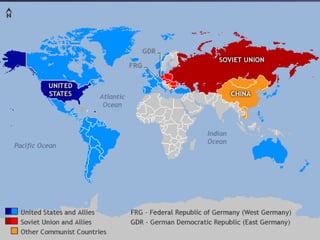
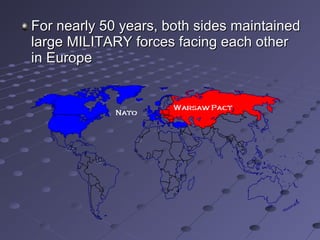
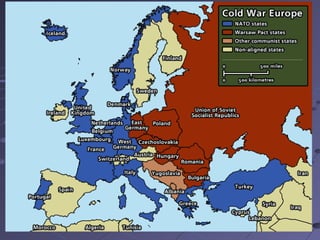
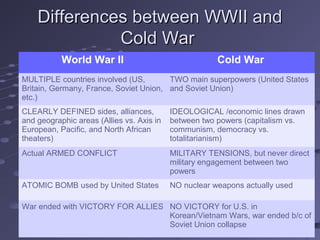
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and Soviet Union from 1945 to 1991. It arose due to conflicting ideologies around democracy/capitalism and communism/socialism. The two sides formed opposing military alliances like NATO and the Warsaw Pact and engaged in an arms race. While direct war was avoided, conflicts emerged in places like Korea and Vietnam as the superpowers supported opposing sides by proxy. The Cold War ended with the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991.