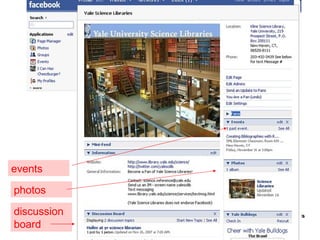
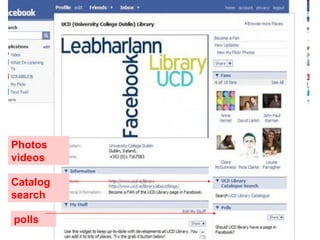
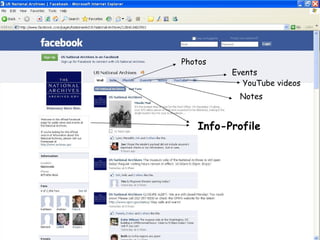
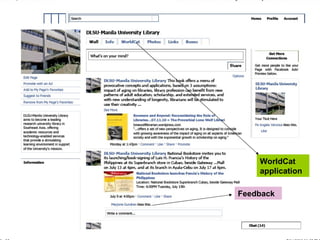
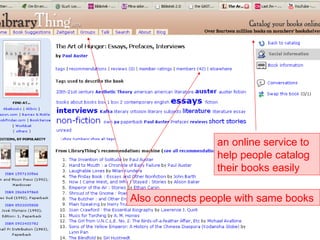
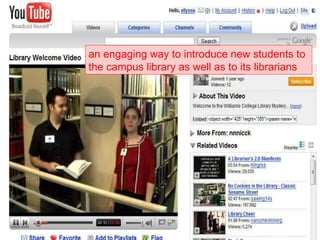
The document discusses the changing environment of technical services in libraries. It notes the increasing digitization of collections and resources, as well as the impact of library automation and Library 2.0 initiatives that support social learning. This has resulted in challenges and opportunities for technical services, including developing digital preservation expertise, providing digital archives, and training staff. Collaborating across libraries can help optimize resources and save money through activities like consortial acquisitions and shared cataloging, databases, and repositories.