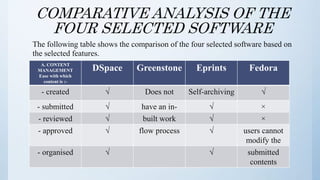
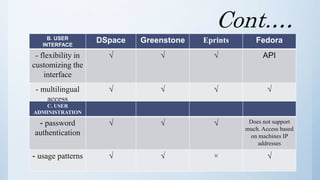
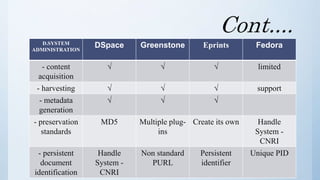
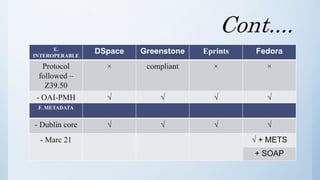
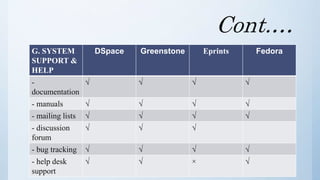
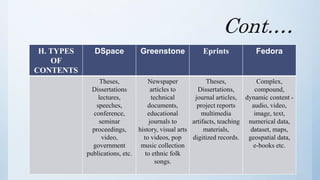
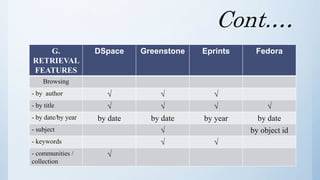
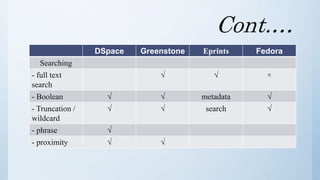
The document discusses the importance of software in modern libraries, particularly for creating digital libraries. It details four types of digital library software: DSpace, Greenstone, Eprints, and Fedora, including their features, capabilities, and target usage. A comparative analysis of these software packages highlights their strengths and weaknesses, suggesting that DSpace and Greenstone are well-suited for digital library creation.